
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, is a type of sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis during sexual activity. ED can have psychological consequences as it can be tied to relationship difficulties and self-image.

Priapism is a condition in which a penis remains erect for hours in the absence of stimulation or after stimulation has ended. There are three types: ischemic (low-flow), nonischemic (high-flow), and recurrent ischemic (intermittent). Most cases are ischemic. Ischemic priapism is generally painful while nonischemic priapism is not. In ischemic priapism, most of the penis is hard; however, the glans penis is not. In nonischemic priapism, the entire penis is only somewhat hard. Very rarely, clitoral priapism occurs in women.

Peyronie's disease is a connective tissue disorder involving the growth of fibrous plaques in the soft tissue of the penis. Specifically, scar tissue forms in the tunica albuginea, the thick sheath of tissue surrounding the corpora cavernosa, causing pain, abnormal curvature, erectile dysfunction, indentation, loss of girth and shortening.
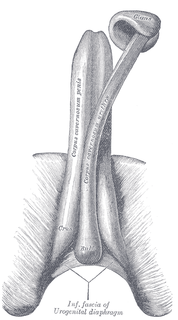
Penis enlargement, or male enhancement, is any technique aimed to increase the size of a human penis. Some methods aim to increase total length, others the shaft's girth, and yet others the glans size. Techniques include surgery, supplements, ointments, patches, and physical methods like pumping, jelqing, and traction.
A penis pump, or penis vacuum, is an external medical device developed to treat male erectile dysfunction. The device is designed for the patient to get and maintain erection by blood flow suction to the penis, via a vacuum. It is also used to recover from the effects of Peyronie's disease and penis enlargement therapy.
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or a couple during any stage of a normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal or orgasm. According to the DSM-5, sexual dysfunction requires a person to feel extreme distress and interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunctions can have a profound impact on an individual's perceived quality of sexual life. The term sexual disorder may not only refer to physical sexual dysfunction, but to paraphilias as well; this is sometimes termed disorder of sexual preference.

Penile fracture is rupture of one or both of the tunica albuginea, the fibrous coverings that envelop the penis's corpora cavernosa. It is caused by rapid blunt force to an erect penis, usually during vaginal intercourse, or aggressive masturbation. It sometimes also involves partial or complete rupture of the urethra or injury to the dorsal nerves, veins and arteries.

Phalloplasty is the construction or reconstruction of a penis, or the artificial modification of the penis by surgery. The term phalloplasty is also occasionally used to refer to penis enlargement.
Metoidioplasty or metaoidioplasty is a female-to-male sex reassignment surgery.
Tumescence is the quality or state of being tumescent or swollen. Tumescence usually refers to the normal engorgement with blood of the erectile tissues, marking sexual excitation, and possible readiness for sexual activity. The tumescent sexual organ in men is the penis and in women is the clitoris and other parts of the genitalia like the vestibular bulbs.
Nocturnal penile tumescence is a spontaneous erection of the penis during sleep or when waking up. Along with nocturnal clitoral tumescence, it is also known as sleep-related erection. All men without physiological erectile dysfunction experience nocturnal penile tumescence, usually three to five times during a period of sleep, typically during rapid eye movement sleep. Nocturnal penile tumescence is believed to contribute to penile health.
Venous leak, also called venogenic erectile dysfunction and penile venous insufficiency, is one category of vasculogenic impotence -a cause of erectile dysfunction in males. It affects all ages, being particularly awkward in young men. Much about venous leaks has not reached a consensus among the medical community, and many aspects of the condition, particularly its treatment strategies, are controversial. The prevalence of the condition is still unknown, although some sources claim it to be a common cause of erectile dysfunction.

Penile implants are urological surgical procedures, primarily for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and Peyronie's disease as opposed to enlargement as is commonly believed. Although there are many distinct types of implants, most fall into one of two categories: malleable and inflatable.

An erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection varies considerably in humans.

Human penises vary in size on a number of measures, including length and circumference when flaccid and erect. Besides the natural variability of human penises in general, there are factors that lead to minor variations in a particular male, such as the level of arousal, time of day, room temperature, and frequency of sexual activity. Compared to other primates, including large examples such as the gorilla, the human penis is thickest, both in absolute terms and relative to the rest of the body.
Gary J. Alter is an American plastic surgeon. His specialties include sex reassignment surgery, genital reconstruction surgery and facial feminization surgery. He appeared in two episodes of the reality television series, Dr. 90210. PRNewswire reported on June 5, 2015 that Dr. Gary J. Alter performed the body work plastic surgery on Caitlyn Jenner. He has a practice in Beverly Hills, CA.
Ronald Virag, is a French cardiovascular surgeon, specialized in andrology. Inventor of the first medical treatment for impotence, andrology he designed many of the modern techniques of diagnosis and treatments for erectile dysfunction; and also a preventive program for the harmful effects of ageing in the cardiovascular, hormonal, sexual, urologic and nutritional areas. He is the author of several publications, scientific and popularization books.

Penile Artery Shunt Syndrome (PASS) is an iatrogenic clinical phenomenon first described by Tariq Hakky, Christopher Yang, Jonathan Pavlinec, Kamal Massis, and Rafael Carrion within the Sexual Medicine Program in the Department of Urology, at the University of South Florida, and Ricardo Munarriz, of Boston University School of Medicine Department of Urology in 2013. It may be a cause of refractory Erectile Dysfunction in patients who have undergone Penile Revascularization Surgery.
Culley Clyde Carson III is an American retired urologist who specializes in Peyronie's disease, penile prostheses and erectile dysfunction. After serving two years as a flight surgeon with the United States Air Force, he took on a urology residency at the Mayo Clinic and then taught at the Duke University Medical Center as an assistant professor, subsequently gaining full professorship.
Zephyr Surgical Imlants (ZSI) is a Swiss-based medical device manufacturer that produces and distributes artificial urinary sphincters and penile implants worldwide. ZSI products are used in the management of moderate-to-severe urinary incontinence in men, erectile dysfunction, Peyronie's disease, penis enlargement, female-to-male gender reassignment surgery.










