Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member is benzene. Heteroarenes are closely related, since at least one carbon atom of CH group is replaced by one of the heteroatoms oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples of non-benzene compounds with aromatic properties are furan, a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring that includes a single oxygen atom, and pyridine, a heterocyclic compound with a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom. Hydrocarbons without an aromatic ring are called aliphatic.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R−COOH or R−CO2H, with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R2C=O, where R can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula CH3C(O)CH3. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.

In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.
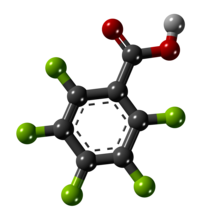
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid. The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom.
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base.

Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H5. It is a colorless liquid with a smell reminiscent of anise seed, and in fact many of its derivatives are found in natural and artificial fragrances. The compound is mainly made synthetically and is a precursor to other synthetic compounds. It is an ether. Anisole is a standard reagent of both practical and pedagogical value.
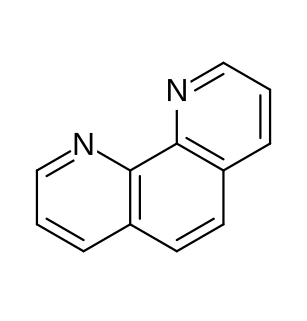
1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refer to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene.
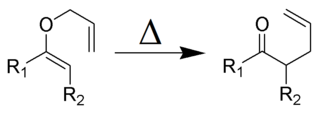
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation.

The Duff reaction or hexamine aromatic formylation is a formylation reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of benzaldehydes with hexamine as the formyl carbon source. It is named after James Cooper Duff, who was a chemist at the College of Technology, Birmingham, around 1920–1950.
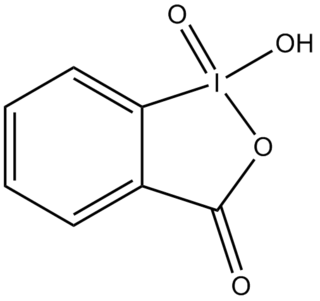
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) is an organic compound used in organic synthesis as an oxidizing agent. This periodinane is especially suited to oxidize alcohols to aldehydes. IBX is prepared from 2-iodobenzoic acid, potassium bromate, and sulfuric acid. Frigerio and co-workers have also demonstrated, in 1999 that potassium bromate may be replaced by commercially available Oxone. One of the main drawbacks of IBX is its limited solubility; IBX is insoluble in many common organic solvents. In the past, it was believed that IBX was shock sensitive, but it was later proposed that samples of IBX were shock sensitive due to the residual potassium bromate left from its preparation. Commercial IBX is stabilized by carboxylic acids such as benzoic acid and isophthalic acid.

Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process.
Phenol oxidation with hypervalent iodine reagents leads to the formation of quinone-type products or iodonium ylides, depending on the structure of the phenol. Trapping of either product is possible with a suitable reagent, and this method is often employed in tandem with a second process.
Heteroatom-promoted lateral lithiation is the site-selective replacement of a benzylic hydrogen atom for lithium for the purpose of further functionalization. Heteroatom-containing substituents may direct metalation to the benzylic site closest to the heteroatom or increase the acidity of the ring carbons via an inductive effect.

The Quelet reaction is an organic coupling reaction in which a phenolic ether reacts with an aliphatic aldehyde to generate an α-chloroalkyl derivative. The Quelet reaction is an example of a larger class of reaction, electrophilic aromatic substitution. The reaction is named after its creator R. Quelet, who first reported the reaction in 1932, and is similar to the Blanc chloromethylation process.

The Jones oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. It is named after its discoverer, Sir Ewart Jones. The reaction was an early method for the oxidation of alcohols. Its use has subsided because milder, more selective reagents have been developed, e.g. Collins reagent.
Metal-catalyzed C–H borylation reactions are transition metal catalyzed organic reactions that produce an organoboron compound through functionalization of aliphatic and aromatic C–H bonds and are therefore useful reactions for carbon–hydrogen bond activation. Metal-catalyzed C–H borylation reactions utilize transition metals to directly convert a C–H bond into a C–B bond. This route can be advantageous compared to traditional borylation reactions by making use of cheap and abundant hydrocarbon starting material, limiting prefunctionalized organic compounds, reducing toxic byproducts, and streamlining the synthesis of biologically important molecules. Boronic acids, and boronic esters are common boryl groups incorporated into organic molecules through borylation reactions. Boronic acids are trivalent boron-containing organic compounds that possess one alkyl substituent and two hydroxyl groups. Similarly, boronic esters possess one alkyl substituent and two ester groups. Boronic acids and esters are classified depending on the type of carbon group (R) directly bonded to boron, for example alkyl-, alkenyl-, alkynyl-, and aryl-boronic esters. The most common type of starting materials that incorporate boronic esters into organic compounds for transition metal catalyzed borylation reactions have the general formula (RO)2B-B(OR)2. For example, bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2Pin2), and bis(catecholato)diborane (B2Cat2) are common boron sources of this general formula.