
Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics.

Honolulu is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. An unincorporated city, it is the county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oʻahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions.
Hawaiian is a Polynesian language and critically endangered language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the US state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840.

Oahu is the most populated and third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. The island of Oahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. In 2021, Oahu had a population of 995,638, up from 953,207 in 2010.

Hawaiian Airlines is a commercial U.S. airline, headquartered at Honolulu, Hawaii. It is the largest operator of commercial flights to and from the island state of Hawaii, and the tenth largest commercial airline in the United States by passengers carried.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands by Europeans, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900, until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding Palmyra Island, was admitted to the United States as the 50th U.S. state, the State of Hawaii. The Hawaii Admission Act specified that the State of Hawaii would not include Palmyra Island, the Midway Islands, Kingman Reef, and Johnston Atoll, which includes Johnston Island and Sand Island.

Native Hawaiians are the Indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.

Sacred Hearts Academy, also known as Sacred Hearts or SHA, is located on 3253 Waiʻalae Avenue, in the town of Kaimuki in Honolulu, Hawaiʻi, is a historic Roman Catholic college preparatory school for girls founded in 1909 to serve the needs of early Hawaiʻi Catholics in the former Territory of Hawaiʻi. The school maintains a special relationship with Chaminade University of Honolulu and the all-boys Saint Louis School, both administered by the Society of Mary.

The Hawaiian sovereignty movement is a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom of Hawaii out of a desire for sovereignty, self-determination, and self-governance.

Ypsolophidae is a family of moths with some 160 species. They are included in the Plutellidae by many authors.

The cuisine of Hawaii incorporates five distinct styles of food, reflecting the diverse food history of settlement and immigration in the Hawaiian Islands.[a]
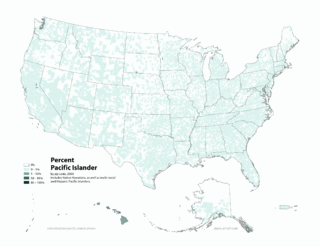
Pacific Islander Americans are Americans who are of Pacific Islander ancestry. For its purposes, the United States census also counts Aboriginal Australians as part of this group.

The Hawaiian Kingdom, also known as Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands which existed from 1795 to 1893. It was established during the late 18th century when Hawaiian chief Kamehameha I, from the island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi, and Lānaʻi, and unified them under one government. In 1810, the Hawaiian Islands were fully unified when the islands of Kauaʻi and Niʻihau voluntarily joined the Hawaiian Kingdom. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom, the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.

Zygaena lonicerae, the narrow-bordered five-spot burnet, is a moth of the family Zygaenidae. The species was first described by Theodor Gottlieb von Scheven in 1777.

Tulsi Gabbard is an American politician, United States Army Reserve officer, and political commentator who was the U.S. representative for Hawaii's 2nd congressional district from 2013 to 2021. Gabbard was the first Samoan-American to become a voting member of Congress. She was a candidate for the Democratic nomination in the 2020 United States presidential election, before announcing in October 2022 that she had left the Democratic Party to become an independent.

Hawaii Five-0 is an American action police procedural television series that centers around a special police major crimes task force operating at the behest of the governor of Hawaii. It is a reboot of the 1968–1980 series Hawaii Five-O, which also aired on CBS. The series was produced by K/O Paper Products and 101st Street Television, initially in association with CBS Television Studios. The show received praise for its modern take on the original series.

The Makauwahi Cave is the largest limestone cave found in Hawaii. It lies on the south coast of the island of Kauaʻi, in the Māhāʻulepū Valley close to Māhāʻulepū Beach, and is important for its paleoecological and archaeological values. It is reached via a sinkhole and has been described as “…maybe the richest fossil site in the Hawaiian Islands, perhaps in the entire Pacific Island region”.















