
Tremella mesenterica is a common jelly fungus in the family Tremellaceae of the Agaricomycotina. It is most frequently found on dead but attached and on recently fallen branches, especially of angiosperms, as a parasite of wood decay fungi in the genus Peniophora. The gelatinous, orange-yellow fruit body of the fungus, which can grow up to 7.5 cm (3.0 in) diameter, has a convoluted or lobed surface that is greasy or slimy when damp. It grows in crevices in bark, appearing during rainy weather. Within a few days after rain it dries into a thin film or shriveled mass capable of reviving after subsequent rain. This fungus occurs widely in deciduous and mixed forests and is widely distributed in temperate and tropical regions that include Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North and South America. Although considered bland and flavorless, the fungus is edible. Tremella mesenterica produces carbohydrates that are attracting research interest because of their various biological activities.

Exidia is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. The species are saprotrophic, occurring in attached or recently fallen dead wood, and produce gelatinous basidiocarps. The fruit bodies are diverse, pustular, lobed, button-shaped or cup-shaped. Several species, including the type species Exidia glandulosa, have sterile pegs or pimples on their spore-bearing surface. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution and around 20 species are currently recognized worldwide. Initial molecular research indicates the genus is artificial.

Tremella is a genus of fungi in the family Tremellaceae. All Tremella species are parasites of other fungi and most produce anamorphic yeast states. Basidiocarps, when produced, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi". Over 100 species of Tremella are currently recognized worldwide. One species, Tremella fuciformis, is commercially cultivated for food.

Myxarium nucleatum is a species of fungus in the family Hyaloriaceae. In the UK, it has been given the recommended English name of crystal brain. Basidiocarps are watery white, pustular or lobed, and gelatinous with small, white, mineral inclusions visible to the naked eye. It is a common, wood-rotting species in Europe, typically growing on dead attached or fallen branches of broadleaf trees. It is currently not clear whether collections from North America and elsewhere represent the same species.

Phaeotremella is a genus of fungi in the family Phaeotremellaceae. All Phaeotremella species are parasites of other fungi and produce anamorphic yeast states. Basidiocarps, when produced, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi". Fifteen or so species of Phaeotremella are currently recognized worldwide. Tremella sanguinea, shown to be a Phaeotremella species by DNA sequencing, is cultivated in China as an ingredient in traditional Chinese medicine.

Naematelia is a genus of fungi in the family Naemateliaceae. All Naematelia species are parasites of other fungi and produce anamorphic yeast states. When produced, Basidiocarps ,, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi."Four species of Naematelia are currently recognized worldwide. One species, Naematelia aurantialba, is commercially cultivated for food.

Naematelia aurantia is a species of fungus producing yellow, frondose, gelatinous basidiocarps. It is widespread in north temperate regions and is parasitic on another species of fungus that grows on dead attached and recently fallen branches of broadleaf trees. It is commonly called golden ear in North America.
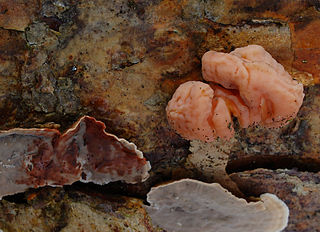
Naematelia encephala is a species of fungus producing pink, brain-like, gelatinous basidiocarps. It is widespread in north temperate regions and is parasitic on another species of fungus that grows on dead attached and recently fallen branches of conifers. In the UK, its recommended English name is conifer brain.
Cystobasidium fimetarium is a species of fungus in the order Cystobasidiales. It is a fungal parasite forming small gelatinous basidiocarps on various ascomycetous fungi on dung. Microscopically, it has auricularioid basidia producing basidiospores that germinate by budding off yeast cells. The species is known from Europe and North America.

Sirobasidium is a genus of fungi in the order Tremellales. Basidiocarps are gelatinous and appear to be parasitic on ascomycetous fungi on wood. Microscopically they are distinguished by producing septate basidia in chains which give rise to deciduous sterigmata. Species are distributed worldwide.

Sirobasidium brefeldianum is a species of fungus in the order Tremellales. Basidiocarps are gelatinous and appear to be parasitic on ascomycetous fungi on wood. The species was originally described from Brazil, but has also been reported from Asia and Europe.
Phaeotremella fimbriata is a species of fungus in the family Phaeotremellaceae. It produces blackish, frondose, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on the mycelium of Stereum rugosum, a fungus that grows on dead attached and recently fallen branches of broad-leaved trees. It is widespread in northern Europe. Prior to 2017, the species was generally considered a synonym of Tremella foliacea, but this latter species is restricted to conifers. Phaeotremella frondosa is a similar-looking but paler, brown species on broad-leaved trees and occurs in North America as well as Europe.

Phaeotremella mycophaga is a species of fungus in the family Phaeotremellaceae. It produces small, pustular, gelatinous basidiocarps on the hymenium of the corticioid fungi Aleurodiscus amorphus and A. grantii on conifers.

Tremella vesiculosa is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces light brown, lobed, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on other fungi on dead branches of broad-leaved trees. It was originally described from New Zealand.
Tremella samoensis is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces red to orange-yellow, lobed to firmly foliaceous, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on other fungi on dead branches of broad-leaved trees. It was originally described from Samoa and the Philippines, but is widely distributed in the region.

Tremella globispora is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces hyaline, pustular, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on pyrenomycetous fungi on dead herbaceous stems and wood. It was originally described from England.
Tremella roseolutescens is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces rose-pink to salmon, pustular, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on other fungi on dead attached branches of broad-leaved trees. It was originally described from Costa Rica.
Tremella versicolor is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces small, pustular, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on the basidiocarps of Peniophora species, a genus of corticioid fungi, on dead attached or recently fallen branches. It was originally described from England.
Tremella exigua is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces small, dark, pustular, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on pyrenomycetous fungi on dead branches of trees and shrubs. It was originally described from France.
Tremella mesenterella is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces yellowish to reddish brown, foliose, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on corticioid fungi on dead branches of broadleaf trees and shrubs. It was originally described from Canada.












