
Ciglitazone (INN) is a thiazolidinedione. Developed by Takeda Pharmaceuticals in the early 1980s, it is considered the prototypical compound for the thiazolidinedione class.
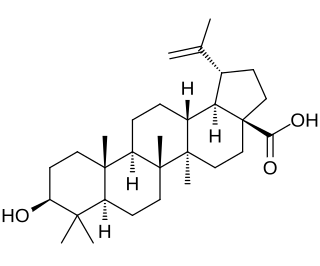
Betulinic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. It is found in the bark of several species of plants, principally the white birch from which it gets its name, same as the bracket fungus Fomitopsis betulina, but also the ber tree, selfheal, the tropical carnivorous plants Triphyophyllum peltatum and Ancistrocladus heyneanus, Diospyros leucomelas, a member of the persimmon family, Tetracera boiviniana, the jambul, flowering quince, rosemary, and Pulsatilla chinensis.

Boromycin is a bacteriocidal polyether-macrolide antibiotic. It was initially isolated from the Streptomyces antibioticus, and is notable for being the first natural product found to contain the element boron. It is effective against most Gram-positive bacteria, but is ineffective against Gram-negative bacteria. Boromycin kills bacteria by negatively affecting the cytoplasmic membrane, resulting in the loss of potassium ions from the cell. Boromycin has not been approved as a drug for medical use.

Gliotoxin is a sulfur-containing mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by several species of fungi, especially those of marine origin. It is the most prominent member of the epipolythiopiperazines, a large class of natural products featuring a diketopiperazine with di- or polysulfide linkage. These highly bioactive compounds have been the subject of numerous studies aimed at new therapeutics. Gliotoxin was originally isolated from Gliocladium fimbriatum, and was named accordingly. It is an epipolythiodioxopiperazine metabolite that is one of the most abundantly produced metabolites in human invasive Aspergillosis (IA).

Spirotryprostatin A is an indolic alkaloid from the 2,5-Diketopiperazine class of natural products found in the Aspergillus fumigatus fungus. Spirotryprostatin A and several other indolic alkaloids have been found to have anti-mitotic properties, and as such they have become of great interest as anti-cancer drugs. Because of this, the total syntheses of these compounds is a major pursuit of organic chemists, and a number of different syntheses have been published in the chemical literature.

Aplaviroc is a CCR5 entry inhibitor that belongs to a class of 2,5-diketopiperazines developed for the treatment of HIV infection. It was developed by GlaxoSmithKline.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies. It is produced commercially from vanillin.

Brevianamides are indole alkaloids that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced as secondary metabolites of fungi in the genus Penicillium and Aspergillus. Structurally similar to paraherquamides, they are a small class compounds that contain a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazoctane ring system. One of the major secondary metabolites in Penicillium spores, they are responsible for inflammatory response in lung cells.
Edelfosine is a synthetic alkyl-lysophospholipid (ALP). It has antineoplastic (anti-cancer) effects.

Cucurbitacin E is a biochemical compound from the family of cucurbitacins. These are found in plants which are member of the family Cucurbitaceae, most of them coming from traditional Chinese medicinal plants, but also in other plants such as pumpkins and gourds.
2,5-Diketopiperazine is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2C(O))2. The compound features a six-membered ring containing two amide groups at opposite positions in the ring. It was first compound containing a peptide bond to be characterized by X-ray crystallography in 1938. It is the parent of a large class of 2,5-Diketopiperazines (2,5-DKPs) with the formula (NHCH2(R)C(O))2 (R = H, CH3, etc.). They are ubiquitous peptide in nature. They are often found in fermentation broths and yeast cultures as well as embedded in larger more complex architectures in a variety of natural products as well as several drugs. In addition, they are often produced as degradation products of polypeptides, especially in processed foods and beverages. They have also been identified in the contents of comets.
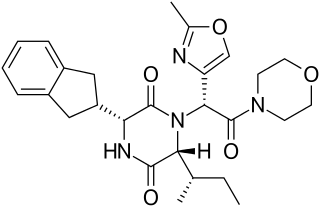
A diketopiperazine (DKP), also known as a dioxopiperazine or piperazinedione, is a class of organic compounds related to piperazine but containing two amide linkages. DKP's are the smallest known class of cyclic peptide. Despite their name, they are not ketones, but amides. Three regioisomers are possible, differing in the locations of the carbonyl groups.

(−)-Aurantiamine is a blue fluorescence metabolite produced by the fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum, the most common fungi found in cereals. (−)-Aurantiamine belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines featuring a dehydrohistidine residue that exhibit important biological activities, such as anti-cancer or neurotoxic effects. It is the isopropyl analog of the microtubule binding agent (−)-phenylahistin but is 40 times less active than the latter on P388 cell proliferation. The total asymmetric synthesis of (−)-aurantiamine has been described.

Verruculogen is a mycotoxin produced by certain strains of aspergillus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. It is an annulated analogue of cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) which belongs to the most abundant and structurally diverse class of tryptophan-proline 2,5-diketopiperazine natural products. It produces tremors in mice due to its neurotoxic properties. It also tested positive in a Salmonella/mammalian microsome assay and was shown to be genotoxic. It is a potent blocker of calcium-activated potassium channels.

Stephacidin A and B are antitumor alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus ochraceus that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. This unusual family of fungal metabolites are complex bridged 2,5-diketopiperazine alkaloids that possess a unique bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane core ring system and are constituted mainly from tryptophan, proline, and substituted proline derivatives where the olefinic unit of the isoprene moiety has been formally oxidatively cyclized across the α-carbon atoms of a 2,5-diketopiperazine ring. The molecular architecture of stephacidin B, formally a dimer of avrainvillamide, reveals a complex dimeric prenylated N-hydroxyindole alkaloid that contains 15 rings and 9 stereogenic centers and is one of the most complex indole alkaloids isolated from fungi. Stephacidin B rapidly converts into the electrophilic monomer avrainvillamide in cell culture, and there is evidence that the monomer avrainvillamide interacts with intracellular thiol-containing proteins, most likely by covalent modification.

(-)-Versicolamide B and (+)-Versicolamide B are spiroindole alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. The versicolamides are structurally complex spiro-cyclized versions of prenylated cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) derivatives which possess a unique spiro-fusion to a pyrrolidine at the 3-position of the oxindole core together with the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system. While (-)-versicolamide B was isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus sp. the enantiomer (+)-versicolamide B was isolated from the terrestrial fungi Aspergillus versicolor NRRL. The total asymmetric syntheses of both enantiomers have been achieved and the implications of their biosynthesis have been investigated.
Aspergillus ustus is a microfungus and member of the division Ascomycota. It is commonly found in indoor environments and soil. Isolated cases of human infection resulting from A. ustus have been described; however the majority of these are nail infections.

Dideoxyverticillin A, also known as (+)-11,11′-dideoxyverticillin A, is a complex epipolythiodioxopiperazine initially isolated from the marine fungus Penicillium sp. in 1999. It has also been found in the marine fungus Bionectriaceae, and belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines.

Brevianamide F , also known as cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Pro), belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. It is the simplest member and the biosynthetic precursor of a large family of biologically active prenylated tryptophan-proline 2,5-diketopiperazines that are produced by the fungi A. fumigatus and Aspergillus sp. It has been isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces sp. strain TN58 and shown to possess activity against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus and Micrococcus luteus. It has also been isolated from Bacillus cereus associated with the entomopathogenic nematode Rhabditis (Oscheius) sp. and shown to have antifungal activity against T. rubrum, C. neoformans, and C. albicans, better than amphotericin B. Although the proline 2,5-diketopiperazines are the most abundant and structurally diverse 2,5-diketopiperazines found in food, cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) has only been found as a minor 2,5-diketopiperazine (8.2 ppm) in autolyzed yeast extract. Initially, cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) and its DL, LD, and DD isomers showed potential for use in the treatment of cardiovascular dysfunction, but they were later shown to be hepatotoxic.
A podophyllotoxin hybrid is a molecule that obtained by combination of podophyllotoxin with other active pharmacophore that is ether designed to interact with multiple target, improve the biological properties or enhance the efficacy of target molecule. Since podophyllotoxin has an extensive pharmacological properties, this compound has been studied in term seeking for potential novel therapeutics. Molecule hybridization is a recent strategy in medicinal area to overcome the pharmacokinetic issues, toxicity, lowering side effects of drugs also reduce the potential resistance in cancer cells. Research development in podophyllotoxin hybrid is mainly focused on anti-cancer properties.

















