Sundaland heath forest, also known as Kerangas forest, is a type of tropical moist forest found on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia, as well as on the Indonesian islands of Belitung and Bangka, which lie to the west of Borneo.

Dolichoderinae is a subfamily of ants, which includes species such as the Argentine ant, the erratic ant, the odorous house ant, and the cone ant. The subfamily presents a great diversity of species throughout the world, distributed in different biogeographic regions, from the Palearctic, Nearctic, Afrotropical region and Malaysia, to the Middle East, Australian, and Neotropical regions.

Corallorhiza, the coralroot, is a genus of flowering plants in the orchid family. Except for the circumboreal C. trifida, the genus is restricted to North America.

Matthew Hilary Peter Jebb is an Irish botanist and taxonomist specialising in the ant plant genera Squamellaria, Myrmecodia, Hydnophytum, Myrmephytum and Anthorrhiza, as well as the carnivorous plant genus Nepenthes.

Myrmecodia is a genus of epiphytic myrmecophytes, native to Southeast Asia, but also present in Indochina, Malaysia, the Southwest Pacific, the Philippines, Fiji, and extending south to Queensland and Cape York in Australia. It is one of five ant-plant genera in the family Rubiaceae, the others being Anthorrhiza, Hydnophytum, Myrmephytum, and Squamellaria.

A domatium is a tiny chamber produced by plants that houses arthropods.

Myrmecotrophy is the ability of plants to obtain nutrients from ants, a form of mutualism. Due to this behaviour the invasion of vegetation into harsh environments is promoted. The dead remains of insects thrown out by the ants are absorbed by the lenticular warts in myrmecophytes like Hydnophytum and Myrmecodia. Myrmecodia uses its lenticular warts to suck nutrients from the insects thrown out by the ants. The ants in turn benefit with a secure location to form their colony. The pitcher plant Nepenthes bicalcarata obtains an estimated 42% of its total foliar nitrogen from ant waste.
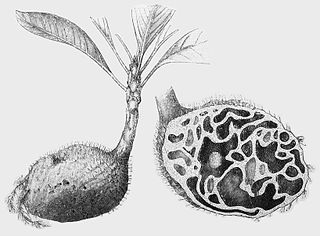
Hydnophytum is a genus of epiphytic myrmecophytes native to Southeast Asia, the Pacific region and also extending into Queensland in northern Australia. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek hydnon "tuber", and phyton "plant", after their appearance with their swollen succulent stems. The species grow in tree branches and on trunks. Like the related genus Myrmecodia, they are known as antplants or ant-house plants. The type species is Hydnophytum formicarum from the Philippines. The genus contains 55 species, of which 44 are found in and around the island of New Guinea. Many are poorly known, with 11 known only from the holotype.
Anthorrhiza is a genus of myrmecophytic flowering plants in the Rubiaceae family. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea, including the Louisiade Archipelago. It is one of five ant-plant genera in the family Rubiaceae, the others being Hydnophytum, Myrmecodia, Myrmephytum, and Squamellaria.
Myrmephytum is a genus of myrmecophytic flowering plants in the Rubiaceae family. It is distributed from central Malesia to New Guinea.

Squamellaria is a genus of myrmecophytic flowering plants in the Rubiaceae family. It is endemic to the islands of Fiji.

Psychotrieae is a tribe of flowering plants in the Rubiaceae family and contains about 2114 species in 17 genera. Its representatives are found in the tropics and subtropics.
Philidris cruda is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Smith in 1860, the species is endemic to Indonesia.
Philidris pubescens is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Donisthorpe in 1949, the species is endemic to New Guinea.
Philidris laevigata is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Emery in 1895, the species is endemic to Burma, India and China.
Philidris myrmecodiae is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Emery in 1887, the species is endemic to Asia.
Philidris nagasau is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Mann in 1921, the species is endemic to Fiji.
Philidris notiala is a species of ant in the genus Philidris. Described by Zhou and Zheng in 1998, the species is endemic to China.












