
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor coating on the inside of the lamp to glow. A fluorescent lamp converts electrical energy into useful light much more efficiently than an incandescent lamp. The typical luminous efficacy of fluorescent lighting systems is 50–100 lumens per watt, several times the efficacy of incandescent bulbs with comparable light output. For comparison, the luminous efficacy of an incandescent bulb may only be 16 lumens per watt.

A blacklight, also called a UV-A light, Wood's lamp, or ultraviolet light, is a lamp that emits long-wave (UV-A) ultraviolet light and very little visible light. One type of lamp has a violet filter material, either on the bulb or in a separate glass filter in the lamp housing, which blocks most visible light and allows through UV, so the lamp has a dim violet glow when operating. Blacklight lamps which have this filter have a lighting industry designation that includes the letters "BLB". This stands for "blacklight blue". A second type of lamp produces ultraviolet but does not have the filter material, so it produces more visible light and has a blue color when operating. These tubes are made for use in "bug zapper" insect traps, and are identified by the industry designation "BL". This stands for "blacklight".

Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a form of porphyria, which varies in severity and can be very painful. It arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the red blood cells (erythrocytes), plasma, skin, and liver. The severity varies significantly from individual to individual.
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light, such as heliophobia. The term photophobia comes from the Greek φῶς (phōs), meaning "light", and φόβος (phóbos), meaning "fear".
Photosensitive epilepsy (PSE) is a form of epilepsy in which seizures are triggered by visual stimuli that form patterns in time or space, such as flashing lights; bold, regular patterns; or regular moving patterns. PSE affects approximately one in 4,000 people.

Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders, cancers, and skin wound infections. Treating skin conditions such as neurodermatitis, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, and eczema with ultraviolet light is called ultraviolet light therapy.

Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is a form of visual hallucination that is characterized by the perception of small, flickering dots throughout the entire visual field. It is present in all conditions of illumination. The dots remain individual and do not clump together or change in size. Visual snow exists in one of two forms: the pulse type and the broadband type.
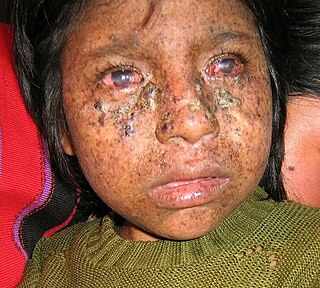
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a genetic disorder in which there is a decreased ability to repair DNA damage such as that caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. Symptoms may include a severe sunburn after only a few minutes in the sun, freckling in sun-exposed areas, dry skin and changes in skin pigmentation. Nervous system problems, such as hearing loss, poor coordination, loss of intellectual function and seizures, may also occur. Complications include a high risk of skin cancer, with about half having skin cancer by age 10 without preventative efforts, and cataracts. There may be a higher risk of other cancers such as brain cancers.
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision.
Computer vision syndrome (CVS) is a condition resulting from focusing the eyes on a computer or other display device for protracted, uninterrupted periods of time and the eye's muscles being unable to recover from the constant tension required to maintain focus on a close object.
PUVA is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: vitiligo, eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizing effects of the drug psoralen. The psoralen is applied or taken orally to sensitize the skin, then the skin is exposed to UVA.
Photodermatoses is a skin condition resulting in abnormal skin reactions to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. These abnormal skin reactions may develop into rashes. While reactions to UV radiation is common, true photodermatoses is considered when an abnormal reaction is caused by UV-A rays or radiation between 320 and 400 nm.

Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) presents with itchy red small bumps on sun-exposed skin, particularly face, neck, forearms and legs. It generally appears 30 minutes to a few hours after sun exposure and may last between one and 14 days. The bumps may become small blisters or plaques and may appear bloody,often healing with minimal scarring.

Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout.

Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. The most common and most severe form is systemic lupus erythematosus.

Phytophotodermatitis, also known as berloque dermatitis or margarita photodermatitis, is a cutaneous phototoxic inflammatory reaction resulting from contact with a light-sensitizing botanical agent followed by exposure to ultraviolet light. Symptoms include erythema, edema, blisters, and delayed hyperpigmentation. Heat and moisture tend to exacerbate the reaction.
Chronic actinic dermatitis is a condition where a subject's skin becomes inflamed due to a reaction to sunlight or artificial light; similar to solar urticaria or cholinergic urticaria. Patients often have other related conditions of the skin that cause dermatitis in response to a variety of stimuli.

Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms.

Fluorescent lamps have been suggested to affect human health in various ways.
Heliophobia refers to light sensitivity:











