
Azo compounds are compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.

Acenaphthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of naphthalene with an ethylene bridge connecting positions 1 and 8. It is a colourless solid. Coal tar consists of about 0.3% of this compound.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.

Quinoline Yellow SS is a bright yellow dye with green shade. It is insoluble in water, but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Quinoline yellow is representative of a large class of quinophthalone pigments. It is suggested that quinoline yellow exhibits excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) behavior and the behavior might be the cause of its decent photostability, by recent spectroscopic study.
Arylide yellow, also known as Hansa yellow and monoazo yellow, is a family of organic compounds used as pigments. They are primarily used as industrial colorants including plastics, building paints and inks. They are also used in artistic oil paints, acrylics and watercolors. These pigments are usually semi-transparent and range from orange-yellow to yellow-greens. Related organic pigments are the diarylide pigments. Overall, these pigments have partially displaced the toxic cadmium yellow in the marketplace. Painters such as Alexander Calder and Jackson Pollock are known to have employed arylide yellow in their artworks.

3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity.

Phthalonitrile is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CN)2, which is an off-white crystal solid at room temperature. It is a derivative of benzene, containing two adjacent nitrile groups. The compound has low solubility in water but is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to phthalocyanine and other pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
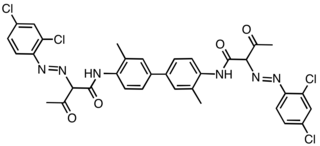
Pigment Yellow 16 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment.
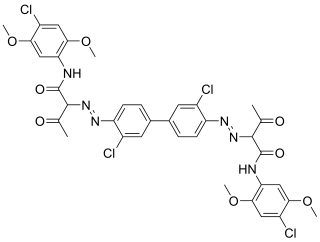
Pigment Yellow 83 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.

Pigment Yellow 81 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.
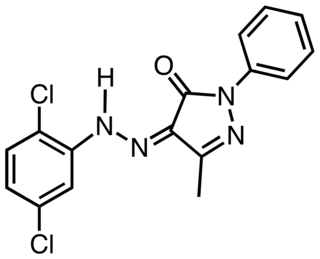
Pigment Yellow 10 is an organic compound that is classified as a Monoazopyrazolone pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant, notably as yellow road marking on highways in the US. The compound is synthesized by coupling the diazonium salt derived from dichloroaniline with the pyrazolone.

Perinone is a class of organic compounds. The parent compound has two isomers, each of which are useful pigments.
Pigment Red 178 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment. Structurally, it is a derivative of perylene, although it is produced from perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by derivatization with 4-aminoazobenzene.

Pigment Red 179 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment. Structurally, it is a derivative of perylene, although it is produced from perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by derivatization with methylamine.
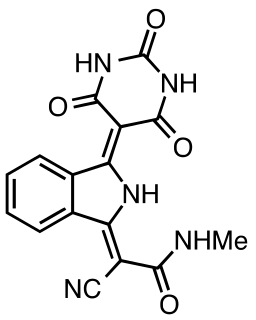
Pigment yellow 185 is an organic compound that is used as a green yellow pigment and optical brightener. It is classified as a derivative of isoindoline. This yellow green compound is prepared by addition of ammonia to o-phthalonitrile to give the diiminoisoindoline, which in turn condenses first with N-methylcyanoacetamide and then with barbituric acid.
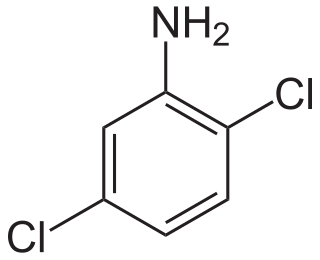
2,5-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2NH2. One of six isomers of dichloroaniline, it is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water. It is produced by hydrogenation of 1,4-dichloro-2-nitrobenzene. It is a precursor to dyes and pigments, e.g., Pigment Yellow 10.
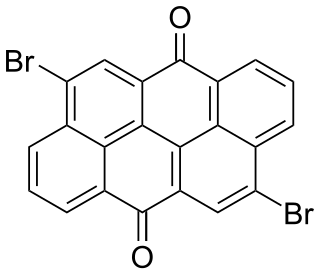
Dibromoanthanthrone is a scarlet or orange-red-hue synthetic organic colourant.
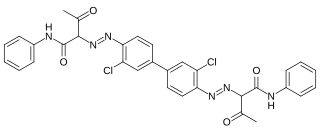
Pigment Yellow 12 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 13, wherein the two phenyl groups are replaced by 2,4-xylyl.
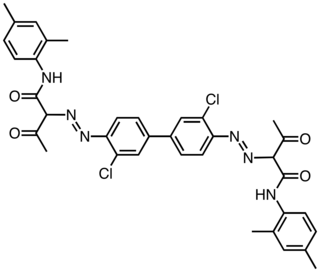
Pigment Yellow 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 12, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by phenyl.
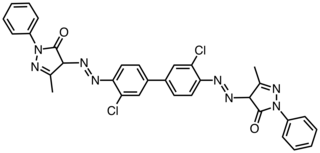
Pigment Orange 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a commercial orange pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Orange 3, wherein the two phenyl groups are replaced by p-tolyl groups.

















