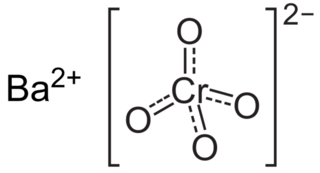A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli.

Oil paint is a type of slow-drying paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in a drying oil, commonly linseed oil. The viscosity of the paint may be modified by the addition of a solvent such as turpentine or white spirit, and varnish may be added to increase the glossiness of the dried oil paint film. The addition of oil or alkyd medium can also be used to modify the viscosity and drying time of oil paint. Oil paints were first used in Asia as early as the 7th century AD and can be seen in examples of Buddhist paintings in Afghanistan. Oil-based paints made their way to Europe by the 12th century and were used for simple decoration, but oil painting did not begin to be adopted as an artistic medium there until the early 15th century. Common modern applications of oil paint are in finishing and protection of wood in buildings and exposed metal structures such as ships and bridges. Its hard-wearing properties and luminous colors make it desirable for both interior and exterior use on wood and metal. Due to its slow-drying properties, it has recently been used in paint-on-glass animation. The thickness of the coat has considerable bearing on the time required for drying: thin coats of oil paint dry relatively quickly.

Azo compounds are compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.

A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the linkage C-N=N-C. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related to azo dyes are azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.
Barium chromate, named barium tetraoxochromate(VI) by the IUPAC, is a yellow sand like powder with the formula BaCrO4. It is a known oxidizing agent and produces a green flame when heated, a result of the barium ions.
Arylide yellow, also known as Hansa yellow and monoazo yellow, is a family of organic compounds used as pigments. They are primarily used as industrial colorants including plastics, building paints and inks. They are also used in artistic oil paints, acrylics and watercolors. These pigments are usually semi-transparent and range from orange-yellow to yellow-greens. Related organic pigments are the diarylide pigments. Overall, these pigments have partially displaced the toxic cadmium yellow in the marketplace. Painters such as Alexander Calder and Jackson Pollock are known to have employed arylide yellow in their artworks.

3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity.

Phthalonitrile is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CN)2, which is an off-white crystal solid at room temperature. It is a derivative of benzene, containing two adjacent nitrile groups. The compound has low solubility in water but is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to phthalocyanine and other pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
Diarylide pigments are organic compounds that are used as pigments in inks and related materials. They often are yellow or yellow-green. To some extent, these organic compounds have displaced cadmium sulfide from the market. They exist as yellow powders of low solubility in water.
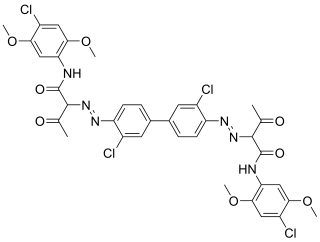
Pigment Yellow 16 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment.

Acetoacetanilide is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2C(O)NHC6H5. It is the acetoacetamide derivative of aniline. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. It and many related compounds (prepared from various aniline derivatives) are used in the production of organic pigments called arylide yellows.

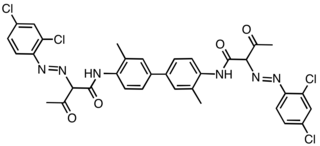
Pigment Yellow 81 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.
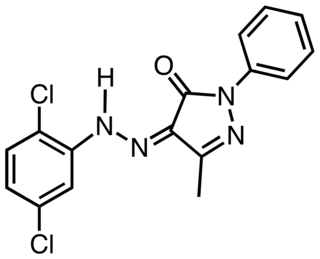
Pigment Yellow 10 is an organic compound that is classified as a Monoazopyrazolone pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant, notably as yellow road marking on highways in the US. The compound is synthesized by coupling the diazonium salt derived from dichloroaniline with the pyrazolone.
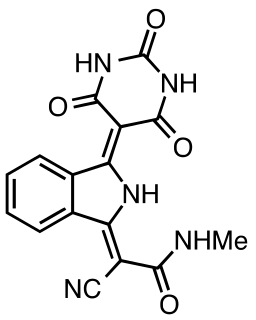
Pigment yellow 185 is an organic compound that is used as a green yellow pigment and optical brightener. It is classified as a derivative of isoindoline. This yellow green compound is prepared by addition of ammonia to o-phthalonitrile to give the diiminoisoindoline, which in turn condenses first with N-methylcyanoacetamide and then with barbituric acid.
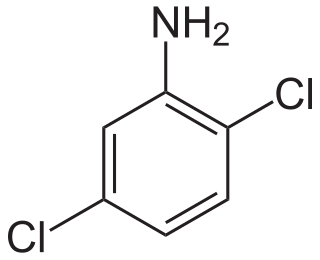
2,5-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2NH2. One of six isomers of dichloroaniline, it is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water. It is produced by hydrogenation of 1,4-dichloro-2-nitrobenzene. It is a precursor to dyes and pigments, e.g., Pigment Yellow 10.
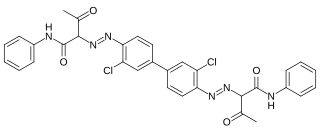
Pigment Yellow 12 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 13, wherein the two phenyl groups are replaced by 2,4-xylyl.
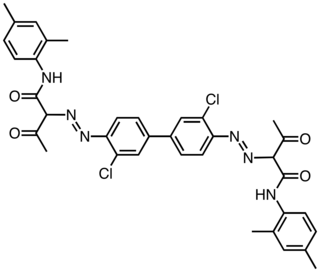
Pigment Yellow 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 12, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by phenyl.

In chemistry, a selenosulfide refers to distinct classes of inorganic and organic compounds containing sulfur and selenium. The organic derivatives contain Se-S bonds, whereas the inorganic derivatives are more variable.