Related Research Articles

Dabbala Rajagopal "Raj" Reddy is an Indian-born American computer scientist and a winner of the Turing Award. He is one of the early pioneers of artificial intelligence and has served on the faculty of Stanford and Carnegie Mellon for over 50 years. He was the founding director of the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University. He was instrumental in helping to create Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies in India, to cater to the educational needs of the low-income, gifted, rural youth. He is the chairman of International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad. He is the first person of Asian origin to receive the Turing Award, in 1994, known as the Nobel Prize of Computer Science, for his work in the field of artificial intelligence.
A cognitive tutor is a particular kind of intelligent tutoring system that utilizes a cognitive model to provide feedback to students as they are working through problems. This feedback will immediately inform students of the correctness, or incorrectness, of their actions in the tutor interface; however, cognitive tutors also have the ability to provide context-sensitive hints and instruction to guide students towards reasonable next steps.

The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching (CFAT) is a U.S.-based education policy and research center. It was founded by Andrew Carnegie in 1905 and chartered in 1906 by an act of the United States Congress. Among its most notable accomplishments are the development of the Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association (TIAA), the Flexner Report on medical education, the Carnegie Unit, the Educational Testing Service, and the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
An intelligent tutoring system (ITS) is a computer system that aims to provide immediate and customized instruction or feedback to learners, usually without requiring intervention from a human teacher. ITSs have the common goal of enabling learning in a meaningful and effective manner by using a variety of computing technologies. There are many examples of ITSs being used in both formal education and professional settings in which they have demonstrated their capabilities and limitations. There is a close relationship between intelligent tutoring, cognitive learning theories and design; and there is ongoing research to improve the effectiveness of ITS. An ITS typically aims to replicate the demonstrated benefits of one-to-one, personalized tutoring, in contexts where students would otherwise have access to one-to-many instruction from a single teacher, or no teacher at all. ITSs are often designed with the goal of providing access to high quality education to each and every student.
Kenneth R. Koedinger is a professor of human–computer interaction and psychology at Carnegie Mellon University. He is the founding and current director of the Pittsburgh Science of Learning Center. He is widely known for his role in the development of the Cognitive Tutor software. He is also widely published in cognitive psychology, intelligent tutoring systems, and educational data mining, and his research group has repeatedly won "Best Paper" awards at scientific conferences in those areas, such as the EDM2008 Best Paper, ITS2006 Best Paper, ITS2004 Best Paper, and ITS2000 Best Paper.
Carnegie Learning, Inc. is a provider of K-12 education services for math, literacy and ELA, world languages, and applied sciences, as well as high-dosage tutoring and professional learning.
The Language Technologies Institute (LTI) is a research institute at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States, and focuses on the area of language technologies. The institute is home to 33 faculty with the primary scholarly research of the institute focused on machine translation, speech recognition, speech synthesis, information retrieval, parsing, information extraction, and multimodal machine learning. Until 1996, the institute existed as the Center for Machine Translation, which was established in 1986. Subsequently, from 1996 onwards, it started awarding degrees, and the name was changed to The Language Technologies Institute. The institute was founded by Professor Jaime Carbonell, who served as director until his death in February 2020. He was followed by Jamie Callan, and then Carolyn Rosé, as interim directors. In August 2023, Mona Diab became the director of the institute.

Subra Suresh is an Indian-born American engineer, materials scientist, and academic leader. He is currently Professor at Large at Brown University and Vannevar Bush Professor of Engineering Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and Dean of the School of Engineering at MIT from 2007 to 2010 before being appointed as Director of the National Science Foundation (NSF) by Barack Obama, where he served from 2010 to 2013. He was the president of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) from 2013 to 2017. Between 2018 and 2022, he was the fourth President of Singapore's Nanyang Technological University (NTU), where he is also the inaugural Distinguished University Professor.
Neil T. Heffernan is a professor of computer science at Worcester Polytechnic Institute. He is known for his role in the development of the ASSISTments online learning tool and app, which assists students with homework and classwork while helping teachers assess where to focus instructional time in mathematics, and is used by over 50,000 students a year in the US. His work gained prominence when a New York Times Magazine story by Annie Murphy Paul featured ASSISTments and Heffernan's research with the tool.
The Tepper School of Business is the business school of Carnegie Mellon University. It is located in the university's 140-acre (0.57 km2) campus in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Albert T. Corbett is an associate research professor emeritus of human–computer interaction at Carnegie Mellon University. He is widely known for his role in the development of the Cognitive Tutor software, leading to one article with over 1,000 citations. Along with John Robert Anderson, he developed the Bayesian Knowledge Tracing algorithm, which is used in Cognitive Tutor software. This work has been particularly influential in the educational data mining community—over half of the EDM conference papers published in 2011 and 2012 cited Bayesian Knowledge-Tracing. Corbett studied psychology at Brown University, and obtained a doctorate in psychology from the University of Oregon. His doctoral advisor was Wayne Wickelgren.
Vincent Aleven is a professor of human-computer interaction and director of the undergraduate program at Carnegie Mellon University's Human–Computer Interaction Institute.

The Ray and Stephanie Lane Computational Biology Department (CBD) is a one of the seven departments within the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Now situated in the Gates-Hillman Center, CBD was established in 2007 as the Lane Center for Computational Biology by founding department head Robert F. Murphy. The establishment was supported by funding from Raymond J. Lane and Stephanie Lane, CBD officially became a department within the School of Computer Science in 2009. In November 2023, Carnegie Mellon named the department as the Ray and Stephanie Lane Computational Biology Department, in recognition of the Lanes' significant investment in computational biology at CMU.

Ryan S. Baker is professor of education and computer science at the University of Pennsylvania, and also directs the Penn Center for Learning Analytics. He is known for his role in establishing the educational data mining scientific community, for the Baker Rodrigo Ocumpaugh Monitoring Protocol (BROMP), and for establishing the first automated detector of student disengagement. He was awarded the Educational Research Award for 2018 by the Council of Scientific Society Presidents.
Michelene (Micki) T. H. Chi is a cognitive and learning scientist known for her work on the development of expertise, benefits of self-explanations, and active learning in the classroom. Chi is the Regents Professor, Dorothy Bray Endowed Professor of Science and Teaching at Arizona State University, where she directs the Learning and Cognition Lab.
Linda Argote is an American academic specializing in industrial and organizational psychology. She is Thomas Lord Professor of Organizational Behavior and Theory in the Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon University, where she directs the Center of Organizational Learning, Innovation and Knowledge.

Bruce Martin McLaren is an American researcher, scientist and author. He is an Associate Research Professor at Carnegie Mellon University and a former President of the International Artificial Intelligence in Education Society (2017-2019).
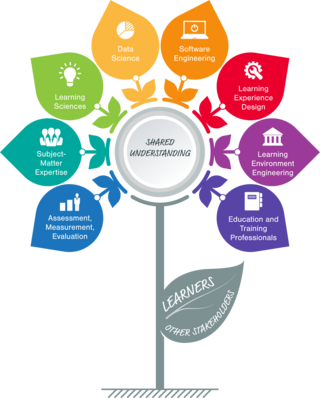
Learning Engineering is the systematic application of evidence-based principles and methods from educational technology and the learning sciences to create engaging and effective learning experiences, support the difficulties and challenges of learners as they learn, and come to better understand learners and learning. It emphasizes the use of a human-centered design approach in conjunction with analyses of rich data sets to iteratively develop and improve those designs to address specific learning needs, opportunities, and problems, often with the help of technology. Working with subject-matter and other experts, the Learning Engineer deftly combines knowledge, tools, and techniques from a variety of technical, pedagogical, empirical, and design-based disciplines to create effective and engaging learning experiences and environments and to evaluate the resulting outcomes. While doing so, the Learning Engineer strives to generate processes and theories that afford generalization of best practices, along with new tools and infrastructures that empower others to create their own learning designs based on those best practices.
Seiji Isotani is a renowned Brazilian scientist specializing in the areas of artificial intelligence applied to education, particularly Intelligent Tutoring Systems, gamification, and educational technologies. He is a Visiting Full Professor in Education at Harvard University and a Full Professor in Computer Science and Educational Technologies at the University of São Paulo. since 2019,
References
- ↑ "Award#0354420 - SLC Center: Pittsburgh Science of Learning Center: Studying Robust Learning with Learning Experiments in Real Classrooms". Nsf.gov. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- ↑ "Carnegie Mellon, University of Pittsburgh receive NSF grant to create Science of Learning Center". Psych Central. 2009-02-21. Archived from the original on 2014-05-13. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- ↑ "Instructional Principles and Hypotheses - Pslc". Learnlab.org. 2011-09-08. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- ↑ "DataShop". 2011-09-08. Retrieved 2020-11-24.
- ↑ "LearnSphere". 2015-01-01. Retrieved 2020-11-24.
- ↑ Koedinger, Kenneth; Corbett, Albert; Perfetti, Charles (2012). "The Knowledge‐Learning‐Instruction framework: Bridging the science‐practice chasm to enhance robust student learning". Cognitive Science. 36 (5): 757–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2012.01245.x . PMID 22486653.

