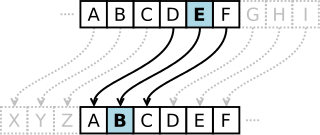
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code, or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
The Sicilian Mafia or Cosa Nostra, also referred to as simply Mafia, is a criminal society originating on the island of Sicily and dates back to the mid-19th century. It is an association of gangs which sell their protection and arbitration services under a common brand. The Mafia's core activities are protection racketeering, the arbitration of disputes between criminals, and the organizing and oversight of illegal agreements and transactions.

Bernardo Provenzano was an Italian mobster and chief of the Sicilian Mafia clan known as the Corleonesi, a Mafia faction that originated in the town of Corleone, and de facto the boss of bosses. His nickname was Binnu u tratturi because, in the words of one informant, "he mows people down". Another nickname was il ragioniere, due to his apparently subtle and low-key approach to running his crime empire, at least in contrast to some of his more violent predecessors.

Benedetto Spera is a member of the Sicilian Mafia and the boss of the Belmonte Mezzagno Mafia family and the mandamento of Belmonte Mezzagno in the province of Palermo, Sicily, southern Italy. He was convicted in absentia for the killing of the two prominent anti-mafia judges Paolo Borsellino and Giovanni Falcone, receiving life sentences.

Matteo Messina Denaro, also known as Diabolik, was a Sicilian Mafia boss from Castelvetrano. He was considered to be one of the new leaders of the Sicilian mob after the arrests of Bernardo Provenzano on 11 April 2006 and Salvatore Lo Piccolo in November 2007. The son of a Mafia boss, Denaro became known nationally on 12 April 2001 when the magazine L'Espresso put him on the cover with the headline: Ecco il nuovo capo della Mafia.
Capo dei capi or capo di tutti i capi or Godfather are terms used mainly by the media, public, fiction writers and law enforcement community to indicate a supremely powerful crime boss in the Sicilian or American Mafia who holds great influence over the whole organization. The term was introduced to the U.S. public by the Kefauver Commission in 1950.

Salvatore Lo Piccolo, also known as "the Baron", is a Sicilian mafioso and one of the most powerful bosses of Palermo, Sicily. Lo Piccolo rose through the ranks of the Palermo mafia throughout the 1980s and he became the capomandamento of the San Lorenzo district in 1993, replacing Salvatore Biondino, who was sent to prison. Lo Piccolo was a fugitive since 1983 and had been running his Mafia affairs in hiding. With the capture of Bernardo Provenzano on 11 April 2006, Lo Piccolo had been cementing his power and rise to the top of the Palermo Mafia until his own arrest on 5 November 2007. It is believed that his family spread across Europe due to rising tensions, settling in England, Portugal, and southern Spain.
Antonino "Nino" Giuffrè is an Italian former mafioso who later became a justice collaborator. The head of the mandamento of Caccamo, he was the second-highest ranked member of Cosa Nostra. He became one of the most important Mafia turncoats, or pentito, after his arrest in April 2002, providing further information about its inner workings.
The Sicilian Mafia Commission, known as Commissione or Cupola, is a body of leading Sicilian Mafia members who decide on important questions concerning the actions of, and settling disputes within the Sicilian Mafia or Cosa Nostra. It is composed of representatives of a mandamento who are called capo mandamento or rappresentante. The Commission is not a central government of the Mafia, but a representative mechanism for consultation of independent Mafia families who decide by consensus. Its primary role is to keep the use of violence among families within limits tolerable to the public and political authorities.

The Corleonesi Mafia clan was a faction within the Corleone family of the Sicilian Mafia, formed in the 1970s. Notable leaders included Luciano Leggio, Salvatore Riina, Bernardo Provenzano, and Leoluca Bagarella.

Domenico "Mimmo" Raccuglia, nicknamed 'u vitirinariu, is a member of the Mafia in Sicily. He was a fugitive and included on Italy's most wanted list since 1996, until his capture on November 15, 2009, near Trapani.

Antonino "Nino" Rotolo is a Sicilian Mafia boss from the Pagliarelli area in Palermo that traditionally was under the control of the Motisi Mafia family. Rotolo was the underboss of Matteo Motisi, but according to some pentiti he was the de facto leader representing the mandamento on the Sicilian Mafia Commission. In 2006, the police deduced that Rotolo — Number 25 in the numbered code of Mafia boss Bernardo Provenzano — had become a key figure in Cosa Nostra's hierarchy.

Giovanni "Gianni" Nicchi is a member of the Sicilian Mafia. Despite his young age – he is nicknamed 'u picciutteddu – he is considered to be one of the leading mafiosi of Cosa Nostra in Palermo. He was on the "most wanted list" of the Italian ministry of the Interior since 2006, until his arrest on 5 December 2009.

Giuseppe Falsone, sometimes spelled as Falzone, is a member of the Sicilian Mafia. He was on the "Most wanted list" of the Italian ministry of the Interior since January 1999, until his arrest in France in June 2010. He is considered to be one of the bosses of Cosa Nostra in the province of Agrigento, jointly with Gerlandino Messina from Porto Empedocle.
Gaspare Pulizzi is a member of the Sicilian Mafia from Carini near Palermo. Pulizzi was one of the right-hand men of Mafia boss Salvatore Lo Piccolo, the capo mandamento of the San Lorenzo area in Palermo.

Giovanni Motisi also known as 'U Pacchiuni, is a member of the Sicilian Mafia in Sicily from the Altarello neighbourhood in Palermo. He has been on the most wanted list of the Italian ministry of the Interior since 1998.

Salvatore Riina, called Totò, was an Italian mobster and chief of the Sicilian Mafia, known for a ruthless murder campaign that reached a peak in the early 1990s with the assassinations of Antimafia Commission prosecutors Giovanni Falcone and Paolo Borsellino, resulting in widespread public outcry and a major crackdown by the authorities. He was also known by the nicknames la belva and il capo dei capi.

Benedetto Capizzi was an Italian mobster and a boss of the Sicilian Mafia, from the Villagrazia area of Palermo. He was nominated to be the head of the new Sicilian Mafia Commission.
Girolamo Di Fazio, is a former Police Commissioner.













