
The blotchy swellshark, or Japanese swellshark, is a common species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. The Blotchy swellshark is found at depths of 90–200 m (300–660 ft) in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, from Japan to Taiwan. It is benthic in nature and favors rocky reefs. Reaching 1.4 m (4.6 ft) in length, this thick-bodied shark has a broad head, large mouth, and two unequally-sized dorsal fins positioned far back past the pelvic fins. It can be identified by its dorsal coloration, consisting of seven brown "saddles" and extensive darker mottling on a light tan background. This species has often been confounded with the draughtsboard shark and the Sarawak pygmy swellshark in scientific literature.

The gecko catshark is a species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae, native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean from southern Japan to Taiwan, and possibly also off Vietnam. It is a common, demersal species found at depths of 100–900 m (330–2,950 ft). Its body is slender, with a pattern of dark saddles and blotches. The dorsal and caudal fins are edged in white, and there is a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of the caudal fin. The gecko catshark is a schooling, opportunistic predator of bony fishes, cephalopods, and crustaceans. It is oviparous, with females producing two vase-shaped egg capsules at a time. This species is captured as bycatch, but does not appear to be threatened by fishery activities at present and has been assessed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
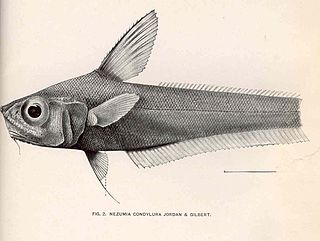
The Japanese pugnose grenadier is a species of rattail fish. It is found at depths of up to 720 m in the waters around southern Japan, northern Taiwan and in the East China Sea.
The arrowtooth grenadier is a species of rattail. This is a deep-water fish found at depths of up to 950 m. It was originally recorded from the waters around Hawaii but has recently also been recorded near Taiwan, which suggests it has a far wider distribution than previously thought.
The plainfin grenadier is a species of rattail. This is a deep-water fish found at depths of up to 772 m. It has a wide distribution in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.
The Palau grenadier is a species of rattail. This is a deep-water fish found at depths of up to 710 m. It has been recorded from many parts of the Pacific Ocean including Hawaii, southern Japan, Palau and northern Taiwan.
Ventrifossa saikaiensis is a species of rattail. This is a deep-water fish found at depths of up to 740 m. It is found in the waters off southern Japan and northern Taiwan.

Plectranthias is a genus of ray-finned fish in the [[subfamily Anthiinae, part of the family Serranidae, the groupers and sea basses. They are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

The comber is a species of marine ray-finned fish from the family Serranidae, the sea basses. It is widely distributed in the eastern North and South Atlantic Oceans and into the southwestern Indian Ocean. It is caught for food and fishmeal in some parts of its range.

The painted comber is a subtropical marine fish, classified in family Serranidae, the groupers and sea basses. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea. Confusingly, a synonym of this species is Perca marina, but that name has incorrectly been used for a separate species, the rose fish.

The blacktip grouper or redbanded grouper, is a species of marine fish in the family Serranidae.

Epinephelus marginatus, the dusky grouper, the yellowbelly rock cod or yellowbelly grouper, is the best known grouper of the Mediterranean Sea and North Africa coast.

The blackfin scad is a species of tropical marine fish of the jack family Carangidae. The species inhabits inshore waters throughout the Indo-Pacific region, although is rare in the western Indian Ocean. It is not a large species, with the largest reported capture being 25 cm, and it is distinguished readily from similar species by the prominent black dorsal fin. It is a predator which feeds on planktonic crustaceans, but little else is known of its biology. The blackfin scad is a minor food fish throughout its range, and is highly valued in Cambodia and Thailand.

The whitefin trevally, also known as the horse trevally, is a species of deep water offshore fish in the jack family Carangidae. The species inhabits the tropical to temperate waters of the Indo-Pacific and central Pacific, ranging from South Africa in the west to Hawaii in the east. The whitefin trevally is a moderate-sized fish, growing to 37 cm, and is distinguished by a number of morphological traits, including fin size, gill raker count, and colour. It inhabits the continental shelf and slope at depths to 200 m over sand and mud substrates, where it preys on fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. Studies in Japan indicate a length at sexual maturity of 17.4 cm on average, with spawning occurring between May and October, with each individual spawning multiple times. Whitefin trevallies are of high importance to fisheries in Japan, where they are taken by trawlers, although the catch numbers have halved since the 1980s. It is of minor importance elsewhere throughout its range, but is considered a good table fish.

The blue trevally, also known as the banded trevally, barred trevally, Ferdau's trevally or Forskaal's jackfish, is a common, widespread species of pelagic marine fish classified in the jack family, Carangidae. The blue trevally is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indo-Pacific and central Pacific regions, ranging from South Africa in the west to Hawaii in the east. It is a moderately large fish, growing to a recorded maximum length of 70 cm, with the number of rays in the second dorsal fin and the colouring serving as diagnostic features of the species. The species inhabits waters to depths of 60 m, generally inhabiting reefs, beaches, lagoons, and areas with sandy substrates. It is a predatory fish, taking other fish, prawns, crabs, and molluscs, and very little is known of the species' reproductive biology. The blue trevally is of varying importance to fisheries throughout its range, with some regions having high catches of the fish. It is considered to be a gamefish, and is sought after for its excellent eating qualities.

Plectropomus laevis, known commonly as the black-saddled coral grouper or saddle grouper, is a species of groupers belonging to the family Serranidae.

Epinephelus spilotoceps, the foursaddle grouper or spotty cod, is a species of marine fish in the family Serranidae.

Lepidoperca is a small genus of fish belonging to the Anthiinae subfamily. It includes ten species.

Liopropoma santi, the spot-tail golden bass, is a golden-coloured fish species which has been collected from deep reefs off Curaçao, southern Caribbean; it is the deepest occurring Liopropoma species in the Atlantic Ocean.

The whitespotted grouper is an Indo-Pacific species of saltwater grouper. The distribution ranges from East Africa, South Africa and the Persian Gulf east to Fiji and Tonga. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".















