| Original author(s) | Robert Maier, Nick Tufillaro |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | GNU Project |
| Stable release | 2.6 / September 27, 2009 |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | gnu |
GNU plotutils is a set of free software command-line tools and software libraries for generating 2D plot graphics based on data sets. It is used in projects such as PSPP and UMLgraph, and in many areas of academic research, [1] [2] [3] and is included in many Linux distributions such as Debian. [4] Windows and Mac OS X versions are also available. The library provides bindings for the C and C++ languages. Its stand-alone command-line tools can generate graphs and perform numerical calculation of spline curves and systems of ordinary differential equations. Plotutils is a GNU package and is distributed under a free software licence, the GPL.
Several utilities were inspired by Unix plotting utilities. A graph utility and various plot filters were present in the first releases of Unix from Bell Laboratories. By the time of Version 7 Unix, graph, plot, spline, and several device-dependent versions of libplot were standard Unix features. The first display device supported by the package was a Tektronix 611 storage scope. By the early 1980s, numerous other devices were supported.
In 1989, the first GNU versions of graph, plot, tek2plot, spline and their respective documentation were written. Richard Stallman further directed development of the programs and documentation. The distribution, as it stood in 1991, was distributed under the name GNU graphics.
In 1995, the package was significantly expanded by writing a device-independent, standalone version of libplot, and by rewriting graph from scratch, turning it into a real-time filter.
Berkeley DB (BDB) is an embedded database software library for key/value data, historically significant in open-source software. Berkeley DB is written in C with API bindings for many other programming languages. BDB stores arbitrary key/data pairs as byte arrays and supports multiple data items for a single key. Berkeley DB is not a relational database, although it has database features including database transactions, multiversion concurrency control and write-ahead logging. BDB runs on a wide variety of operating systems, including most Unix-like and Windows systems, and real-time operating systems.

GNU is an extensive collection of free software, which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operating systems popularly known as Linux. Most of GNU is licensed under the GNU Project's own General Public License (GPL).

A Linux distribution is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro, if distributed on its own, is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers to servers and from embedded devices to supercomputers.

gnuplot is a command-line and GUI program that can generate two- and three-dimensional plots of functions, data, and data fits. The program runs on all major computers and operating systems . Originally released in 1986, its listed authors are Thomas Williams, Colin Kelley, Russell Lang, Dave Kotz, John Campbell, Gershon Elber, Alexander Woo "and many others." Despite its name, this software is not part of the GNU Project.
deb is the format, as well as filename extension of the software package format for the Debian Linux distribution and its derivatives.
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils.

IRAF is a collection of software written at the National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) geared towards the reduction of astronomical images and spectra in pixel array form. This is primarily data taken from imaging array detectors such as CCDs. It is available for all major operating systems for mainframes and desktop computers. IRAF was designed cross-platform, supporting VMS and UNIX-like operating systems. Use on Microsoft Windows was made possible by Cygwin in earlier versions, and can be today done with the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Today, it is primarily used on macOS and Linux.
The GNU Scientific Library is a software library for numerical computations in applied mathematics and science. The GSL is written in C; wrappers are available for other programming languages. The GSL is part of the GNU Project and is distributed under the GNU General Public License.
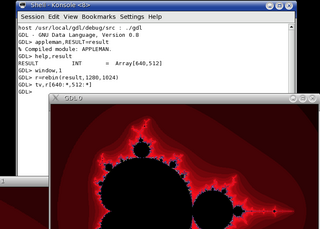
The GNU Data Language (GDL) is a free alternative to IDL, achieving full compatibility with IDL 7 and partial compatibility with IDL 8. Together with its library routines, GDL is developed to serve as a tool for data analysis and visualization in such disciplines as astronomy, geosciences, and medical imaging. GDL is licensed under the GPL. Other open-source numerical data analysis tools similar to GDL include Julia, Jupyter Notebook, GNU Octave, NCAR Command Language (NCL), Perl Data Language (PDL), R, Scilab, SciPy, and Yorick.

Mathomatic is a free, portable, general-purpose computer algebra system (CAS) that can symbolically solve, simplify, combine and compare algebraic equations, and can perform complex number, modular, and polynomial arithmetic, along with standard arithmetic. It can perform symbolic calculus (derivative, extrema, Taylor series, and polynomial integration and Laplace transforms), numerical integration, and can handle all elementary algebra except logarithms. Trigonometric functions can be entered and manipulated using complex exponentials, with the GNU m4 preprocessor. Not currently implemented are general functions such as f(x), arbitrary-precision and interval arithmetic, as well as matrices.

SpareMiNT is a software distribution based on FreeMiNT, which consists of a MiNT-like operating system (OS) and kernel plus GEM compatible AES.
Euler is a free and open-source numerical software package. It contains a matrix language, a graphical notebook style interface, and a plot window. Euler is designed for higher level math such as calculus, optimization, and statistics.

Graphics Layout Engine (GLE) is a graphics scripting language designed for creating publication quality graphs, plots, diagrams, figures and slides. GLE supports various graph types such as function plots, histograms, bar graphs, scatter plots, contour lines, color maps and surface plots through a simple but flexible set of graphing commands. More complex output can be created by relying on GLE's scripting language, which is full featured with subroutines, variables, and logic control. GLE relies on LaTeX for text output and supports mathematical formula in graphs and figures. GLE's output formats include EPS, PS, PDF, JPEG, and PNG.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
XZ Utils is a set of free software command-line lossless data compressors, including the programs lzma and xz, for Unix-like operating systems and, from version 5.0 onwards, Microsoft Windows. For compression/decompression the Lempel–Ziv–Markov chain algorithm (LZMA) is used. XZ Utils started as a Unix port of Igor Pavlov's LZMA-SDK that has been adapted to fit seamlessly into Unix environments and their usual structure and behavior.

lzip is a free, command-line tool for the compression of data; it employs the Lempel–Ziv–Markov chain algorithm (LZMA) with a user interface that is familiar to users of usual Unix compression tools, such as gzip and bzip2.
In Unix, graph is a command-line utility used to draw plots from tabular data.