
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Six subfamilies comprising 15 genera and 54 species are currently recognized.

The Auchenorrhyncha suborder of the Hemiptera contains most of the familiar members of what was called the "Homoptera" – groups such as cicadas, leafhoppers, treehoppers, planthoppers, and spittlebugs. The aphids and scale insects are the other well-known "Homoptera", and they are in the suborder Sternorrhyncha.

The greater lophorina, also known as superb bird-of-paradise or greater superb bird-of-paradise, is a species of the Paradisaeidae (bird-of-paradise) family. It was considered the sole species in the genus until in 2017 it was recognised that there were three species.

A planthopper is any insect in the infraorder Fulgoromorpha, in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, a group exceeding 12,500 described species worldwide. The name comes from their remarkable resemblance to leaves and other plants of their environment and that they often "hop" for quick transportation in a similar way to that of grasshoppers. However, planthoppers generally walk very slowly. Distributed worldwide, all members of this group are plant-feeders, though few are considered pests. The infraorder contains only a single superfamily, Fulgoroidea. Fulgoroids are most reliably distinguished from the other Auchenorrhyncha by two features; the bifurcate (Y-shaped) anal vein in the forewing, and the thickened, three-segmented antennae, with a generally round or egg-shaped second segment (pedicel) that bears a fine filamentous arista.

Siphanta acuta is a species of planthopper in the family Flatidae; this species is native to Australia, but is now found in various other parts of the world. About 10 mm long, they resemble small leaves and are generally found in trees.
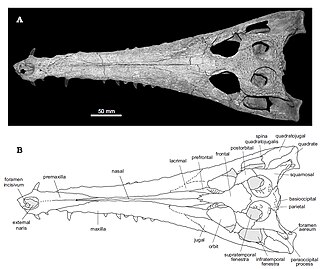
Eosuchus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, traditionally regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian. It might have been among the most basal of all gavialoids, lying crownward of all other known members of the superfamily, including earlier putative members such as Thoracosaurus and Eothoracosaurus. Fossils have been found from France as well as eastern North America in Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. The strata from which specimens have been found date back to the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs.

Trirachodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts. Fossils have been found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in South Africa and the Omingonde Formation of Namibia, dating back to the Early and Middle Triassic.

Oweniasuchus is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Remains have been found from England and Portugal that are Cretaceous in age.

Flatidae are a family of fulgoroid planthoppers. They are cosmopolitan in distribution and are distinguished from others in the superfamily by a combination of characters. Like all other planthoppers, they suck phloem sap of plants. Some species are known to communicate with vibrations through the plant stems. Communication may be with mates, or with ants that tend the nymphs, protecting them and gathering honeydew secretions. Adults of some species have brightly coloured forewings which are tougher and known as tegmina unlike the membranous hindwings which are used for flight. Although a few can be identified by their coloration, most species requires dissection and examination under a microscope with access to literature on already described species.
Oryxa is a genus of planthoppers in the hemipteran family Flatidae. They live on the islands of Borneo and Sumatra, and in Malaysia.

Metcalfa pruinosa, the citrus flatid planthopper, is a species of insect in the Flatidae family of planthoppers first described by Thomas Say in 1830.
Donodon is an extinct genus of mammal from the Ksar Metlili Formation of Talssint, Morocco, which has been dated to the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous epochs. The type species D. perscriptoris was described in 1991 by the palaeontologist Denise Sigogneau-Russell. A second species, D. minor, was named in 2022. Donodon was a member of Cladotheria, a group that includes therian mammals and some of their closest relatives. It differed from dryolestids in having upper molars that were not compressed mesiodistally. Some studies have suggested that it was closely related to various South American cladotherians in the clade Meridiolestida, with specific similarities to Mesungulatum, a herbivorous mesungulatid, being noted. On the other hand, a 2022 phylogenetic analysis found it to be only distantly related to meridiolestidans, and instead closer to crown group therians.

Bythopsyrna circulata is a species of Asian planthoppers belonging to the family Flatidae.
Cromna is a genus of fulgoroid planthoppers in the family Flatidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1857.

Poekilloptera is a genus of South American planthoppers in the subfamily Flatinae and is the sole genus in the tribe Poekillopterini.

The Flatinae are a subfamily of planthoppers, erected by Maximilian Spinola in 1839. Genera have been recorded from all continents except Antarctica: especially in tropical and subtropical regions.
Paraflata is a genus of planthoppers in the family Flatidae. It was first described by Leopold Melichar in 1901. Species in the genus are found on Madagascar.
Flata is the type genus of planthoppers in the family Flatidae and tribe Flatini, erected by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1798. Species are recorded from subtropical and tropical Asia including India, China, Indochina and Malesia.
Neosalurnis is a genus of planthoppers in the family Flatidae, erected by William Lucas Distant in 1910. It was subsequently placed in tribe Flatini, subtribe Phyllyphantina by Metcalf (1957) Records of occurrence are currently from Vietnam and China.

Poekilloptera phalaenoides is a species of planthopper in the family Flatidae. The species can be found in Central America and South America.













