
Located on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington, Puget Sound is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins. As a part of the Salish Sea the sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel.

Poulsbo is a city on Liberty Bay in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is the smallest of the four cities in Kitsap County. The population was 11,970 at the 2020 census and an estimated 10,927 in 2018.

Titchwell Marsh is an English nature reserve owned and managed by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB). Located on the north coast of the county of Norfolk, between the villages of Titchwell and Thornham, about 8 km (5.0 mi) east of the seaside resort of Hunstanton, its 171 hectares include reed beds, saltmarshes, a freshwater lagoon and sandy beach, with a small woodland area near the car park. This internationally important reserve is part of the North Norfolk Coast Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and the Norfolk Coast Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), and is also protected through Natura 2000, Special Protection Area (SPA) and Ramsar listings.

The Duwamish River is the name of the lower 12 miles (19 km) of Washington state's Green River. Its industrialized estuary is known as the Duwamish Waterway. Although heavily polluted, it is an important habitat for the wildlife. Important to the Duwamish people, the Duwamish Longhouse and Cultural Center is on the west bank of the river and several parks have indigenous Lushootseed names.
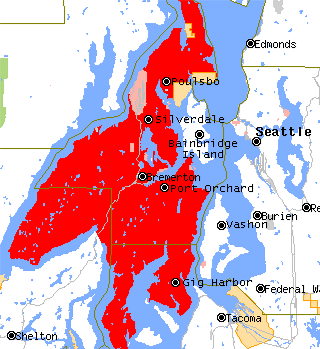
The Kitsap Peninsula lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "Kitsap", encompasses all of Kitsap County except Bainbridge and Blake Islands, as well as the northeastern part of Mason County and the northwestern part of Pierce County. The highest point on the Kitsap Peninsula is Gold Mountain. The U.S. Navy's Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, and Naval Base Kitsap are on the peninsula. Its main city is Bremerton.
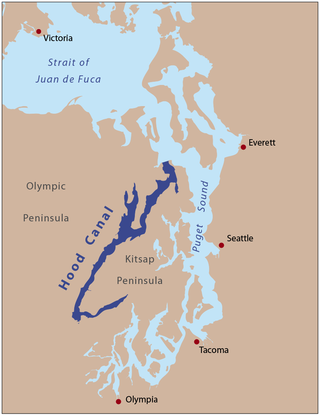
Hood Canal is a fjord-like body of water that lies west of Admiralty Inlet in Washington state that many people consider to be the western lobe and one of the four main basins of Puget Sound. It is one of the minor bodies of water that constitute the Salish Sea. Hood Canal is not a canal in the sense of an artificial waterway— it is a natural feature.

West Point is the westernmost point in Seattle, Washington, United States, jutting into Puget Sound from the Magnolia neighborhood. It also marks the northern extent of Elliott Bay; a line drawn southeastward to Alki Point marks the western extent of the bay. At the point itself is the 1881 West Point Lighthouse, the first staffed light station on Puget Sound. Just to the east is the West Point Treatment Plant, and beyond that, Discovery Park, formerly the U.S. Army's Fort Lawton.

Blake Island is a Puget Sound island in Kitsap County, Washington, United States, that is preserved as Blake Island Marine State Park. The island lies north of Vashon Island, south of Bainbridge Island, and east of Manchester. On the northeast end of the island is Tillicum Village, a tourist attraction based on Northwest Coast Indian arts, culture, and food. The park is managed by the Washington State Parks and Recreation Commission.

The Colvos Passage is a tidal strait within Puget Sound in the American state of Washington running west of Vashon Island between the island and the Kitsap Peninsula. It lies just north of the Dalco Passage. Colvos Passage has a permanent predominantly northbound current, in contrast to the rest of Puget Sound which varies with the tide. The communities of Fragaria, Olalla, Sunrise Beach, Spring Beach, Maplewood, Lisabeula, Paradise Cove and Sylvan Beach are located on Colvos Passage.

The Suquamish Indian Tribe of the Port Madison Reservation is a federally recognized tribe and Indian reservation in the U.S. state of Washington.

Sinclair Inlet is a shallow embayment in the western part of Puget Sound in Kitsap County, Washington, USA. It has a maximum depth of 20 meters. It is the southwestern extension of Port Orchard, and it touches the shores of three of Kitsap County's four incorporated cities: Bremerton, Bainbridge Island, and Port Orchard. It is connected to Dyes Inlet by the Port Washington Narrows and to Puget Sound by Rich Passage. It was named by United States Navy explorer Charles Wilkes for George T. Sinclair, acting master of one of his ship's crews. The Puget Sound Naval Shipyard is located on the north shore of Sinclair Inlet.

The Ythan Estuary is the tidal component of the Ythan River, emptying into the North Sea 19 kilometres (12 mi) north of Aberdeen, Scotland. The estuary’s tidal action extends a 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) inland and has characteristic widths of between 250 metres (820 ft) and 780 metres (2,560 ft). Besides the tidal channel there are interfaces to the upland dunes including mudflats, sand beaches and shingle flats. Reaches of salt marsh occur, but they are primarily near the Waterside Bridge and the mouth of the Tarty Burn, a small tributary river. Based upon the habitat of the moorland bordering the east of the Ythan River near the mouth, this estuary is the most significant coastal moorland in the northern United Kingdom.

Agate Pass or Agate Passage is a high-current tidal strait in Puget Sound connecting Port Madison and mainland Kitsap County in the US state of Washington. It lies between Bainbridge Island and the mainland of the Kitsap Peninsula near Suquamish. It leads south towards Bremerton, extending about one mile (1.6 km) in a straight, southwesterly direction. The depth is about 20 feet (6.1 m). The shores are wooded and fairly steep. The shoreline is mostly rocky and fringed with kelp to Point Bolin. The tidal currents have velocities up to six knots; the flood tide sets southwesterly, and the ebb tide northeasterly.

The Old Man House was the largest winter longhouse in what is now the U.S. state of Washington, once standing on the shore of Puget Sound. It was the center of the Suquamish village of dxʷsəq̓ʷəb on Agate Pass, just south of the present-day town of Suquamish. At one time, it was home to the famous Suquamish chiefs Kitsap and Seattle.

Quartermaster Harbor is a small harbor located in southern Puget Sound, in Vashon Island, Washington state.

Saratoga Passage lies in Puget Sound between Whidbey Island and Camano Island.

Foulweather Bluff is a privately owned protected area and a cliff that lies on the northwest end of the Kitsap Peninsula along Puget Sound, on the east side of the entrance to Hood Canal.

Lee Point refers to a coastal point north of the city of Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia.

Sequalitchew Creek, located in DuPont, Washington emanates from Sequalitchew Lake, Fort Lewis, Washington, was the location of the original Fort Nisqually trading post established in 1833 by the Hudson's Bay Company. The historic, natural flow of Sequalitchew Creek runs from Sequalitchew Lake, through Edmonds Marsh, down the canyon and out to the Puget Sound.

Ketron Island is an island and a census-designated place (CDP) in Pierce County, Washington, United States. The island had a population of 24 persons according to the 2000 census, and 17 persons at the 2010 census.



















