
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.

An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O– alkyl (alkoxy) group, as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils.
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences.
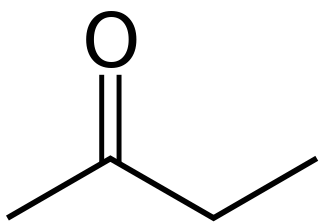
Butanone, also known as ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.

An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds, particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds.
The Robinson annulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for ring formation. It was discovered by Robert Robinson in 1935 as a method to create a six membered ring by forming three new carbon–carbon bonds. The method uses a ketone and a methyl vinyl ketone to form an α,β-unsaturated ketone in a cyclohexane ring by a Michael addition followed by an aldol condensation. This procedure is one of the key methods to form fused ring systems.
The Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl functional group by formaldehyde and a primary or secondary amine or ammonia. The final product is a β-amino-carbonyl compound also known as a Mannich base. Reactions between aldimines and α-methylene carbonyls are also considered Mannich reactions because these imines form between amines and aldehydes. The reaction is named after Carl Mannich.
The Paternò–Büchi reaction, named after Emanuele Paternò and George Büchi, who established its basic utility and form, is a photochemical reaction, specifically a 2+2 photocycloaddition, which forms four-membered oxetane rings from an excited carbonyl and reacting with an alkene.

Cyclododecatrienes are cyclic trienes with the formula C12H18. Four isomers are known for 1,5,9-cyclododecatriene. The trans,trans,cis-isomer is a precursor in the production of nylon-12.

1-Octen-3-ol, octenol for short and also known as mushroom alcohol, is a chemical that attracts biting insects such as mosquitoes. It is contained in human breath and sweat, and it was once believed that insect repellent DEET worked by blocking the insects' octenol odorant receptors. Recent evidence in Anopheles gambiae and Culex quequinfasciatius mosquitoes suggest DEET reduces the volatility of 1-octen-3-ol which can result in a reduction in human attraction. 1-Octen-3-ol is a secondary alcohol derived from 1-octene. It exists in the form of two enantiomers, (R)-(–)-1-octen-3-ol and (S)-(+)-1-octen-3-ol.
Heptanal or heptanaldehyde is an alkyl aldehyde. It is a colourless liquid with a strong fruity odor, which is used as precursor to components in perfumes and lubricants.

2-Heptanone, also known as methyl n-amyl ketone, or Heptan-2-one, is a ketone with the molecular formula C7H14O. It is a colorless, water-like liquid with a banana-like, fruity odor. 2-Heptanone has a neutral formal charge, and is only slightly soluble in water.

Damascenones are a series of closely related chemical compounds that are components of a variety of essential oils. The damascenones belong to a family of chemicals known as rose ketones, which also includes damascones and ionones. beta-Damascenone is a major contributor to the aroma of roses, despite its very low concentration, and is an important fragrance chemical used in perfumery.

2,3-Dihydrothiophene is a heterocyclic compound and an organosulfur compound with the formula SC4H6. It is isomeric with the more symmetrical 2,5-dihydrothiophene. Both isomers of dihydrothiophene are colorless liquids with a thioether-like odor. In terms of their reactivity, both isomers exhibit characteristics of alkenes and thioethers, undergoing addition reactions at carbon and oxidation at sulfur. In contrast, thiophene engages in neither reaction.
Synthetic musks are a class of synthetic aroma compounds to emulate the scent of deer musk and other animal musks. Synthetic musks have a clean, smooth and sweet scent lacking the fecal notes of animal musks. They are used as flavorings and fixatives in cosmetics, detergents, perfumes and foods, supplying the base note of many perfume formulas. Most musk fragrance used in perfumery today is synthetic.

Philip Kraft is a German organic chemist. Since 1996 he has been employed by Givaudan, a leading Flavor and Fragrance company, where he designs captive odorants for use in perfumes. He has lectured at the University of Bern, the University of Zurich, and the ETH Zurich.
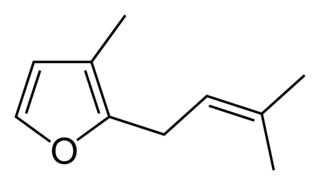
Rosefuran (3-methyl-2-prenylfuran) is a liquid boiling at 103-104 °C, with a density of 0.9089 g/cm3, less than that of water. It is an aroma chemical which is a minor constituent of the aroma of the rose. Rosefuran is a 2,3-disubstituted furan. It has an odor threshold of 200 ppb and constitutes 0.16% of Bulgarian rose oil. Rosefuran has been established as a female sex pheromone of an acarid mite, Caloglyphus sp. Concentrations of less than 100 ng of synthetic rosefuran caused sexual excitation in males of the species.
Decenoic acid is any mono-carboxylic acid with an unbranched chain of ten carbons connected by eight single bonds and one double bond; that is, a chemical compound with formula HO(O=)C–(CH
2)
k–CH=CH–(CH
2)
7-k–H, where k is between 0 and 7 inclusive.
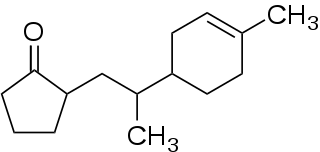
2-[2-(4-Methyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)propyl]cyclopentanone is an organic compound belonging to the group of ketones and cycloalkanes. The compound is used as a fragrance.














