
The 1996 United States presidential election was the 53rd quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 5, 1996. Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton defeated former Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole, the Republican nominee, and Ross Perot, the Reform Party nominee.
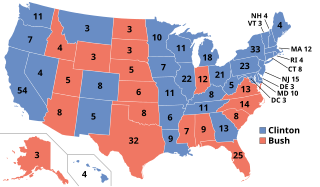
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush, independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas, and a number of minor candidates.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the nineteenth quadrennial presidential election to select the President and Vice President of the United States. The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin emerged triumphant. The election of Lincoln served as the primary catalyst of the American Civil War.

The United States presidential election of 1888 was the 26th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1888. Republican nominee Benjamin Harrison, a former Senator from Indiana, defeated incumbent Democratic President Grover Cleveland of New York. It was the third of five U.S. presidential elections in which the winner did not win a plurality of the national popular vote.
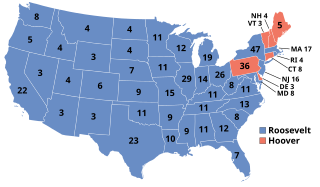
The United States presidential election of 1932 was the thirty-seventh quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. Incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the Governor of New York. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans.

The 1944 United States presidential election was the 40th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 7, 1944. The election took place during World War II. Incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Thomas E. Dewey to win an unprecedented fourth term.

The 1972 United States presidential election was the 47th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican President Richard Nixon defeated Democratic Senator George McGovern of South Dakota.
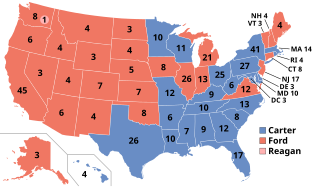
The 1976 United States presidential election was the 48th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 1976. Democrat Jimmy Carter of Georgia defeated incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford from Michigan. Carter's win represented the lone Democratic victory in a presidential election held between 1968 and 1988.

The 1980 United States presidential election was the 49th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 1980. Republican nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democrat Jimmy Carter. Due to the rise of conservativism following Reagan's victory, some historians consider the election to be a realigning election that marked the start of the "Reagan Era".

The 1984 United States presidential election was the 50th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1984. Incumbent Republican President Ronald Reagan defeated former Vice President Walter Mondale, the Democratic candidate.

The United States Electoral College is a body of electors established by the United States Constitution, constituted every four years for the sole purpose of electing the president and vice president of the United States. The Electoral College consists of 538 electors, and an absolute majority of 270 electoral votes is required to win an election. Pursuant to Article II, Section 1, Clause 2, the legislature of each state determines the manner by which its electors are chosen. Each state's number of electors is equal to the combined total of the state's membership in the Senate and House of Representatives; currently there are 100 senators and 435 representatives. Additionally, the Twenty-third Amendment provides that the District of Columbia (D.C.) is entitled to a number of electors no greater than that of the least populous state.

The 1929 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 30 May 1929, and resulted in a hung parliament. It was the second of four general elections under the secret ballot and the first of three under universal suffrage in which a party lost the popular vote but gained a plurality of seats—the others of the four being 1874, 1951 and February 1974. In 1929 that party was Ramsay MacDonald's Labour Party, which won the most seats in the House of Commons for the first time, but failed to get an overall majority. The Liberal Party led by David Lloyd George regained some of the ground it had lost in the 1924 election, and held the balance of power.

The Canadian federal election of 1953 was held on August 10 to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 22nd Parliament of Canada. Prime Minister Louis St. Laurent led his Liberal Party of Canada to its fifth consecutive majority government, although the party lost seats to the other parties.

All Ceylon Tamil Congress, is the oldest Tamil political party in Sri Lanka.

Elections for Barking and Dagenham London Borough Council were held on Thursday 4 May 2006. The whole council was up for election. Barking and Dagenham is split up into 17 wards, each electing 3 councillors, so a total of 51 seats are up for election.

The 2012 United States presidential election was the 57th quadrennial American presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 2012. The Democratic nominee, President Barack Obama, and his running mate, Vice President Joe Biden, were elected to a second term. They defeated the Republican ticket of businessman and former Governor Mitt Romney of Massachusetts and Representative Paul Ryan of Wisconsin.

The election of president and vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the 50 U.S. states or in Washington, D.C. cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the U.S. Electoral College, known as electors. These electors then in turn cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for President, the House of Representatives chooses the winner; if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for Vice President, then the Senate chooses the winner.

The 1892 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania took place on November 8, 1892, as part of the 1892 United States presidential election. Voters chose 32 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

There have been five United States presidential elections in which the winner lost the popular vote including the 1824 election, which was the first U.S. presidential election where the popular vote was recorded. Losing the popular vote means securing less of the national popular vote than the person who received either a majority or a plurality of the vote.




















