Legislative Assembly of the Republic of El Salvador Asamblea Legislativa de la República de El Salvador | |
|---|---|
| XIV Legislative Assembly | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1824 [1] |
New session started | 1 May 2024 |
| Leadership | |
First Vice President | Suecy Callejas (Nuevas Ideas) since 1 May 2021 |
Second Vice President | Rodrigo Ayala(Nuevas Ideas) since 1 May 2021 |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 60 deputies |
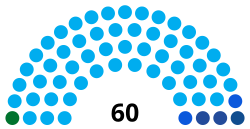 | |
Political groups | Government (57)
Opposition (3) |
| Committees | 8 |
Length of term | 3 years |
| Elections | |
Last election | 4 February 2024 |
Next election | 2027 |
| Motto | |
| Puesta Nuestra Fe En Dios (English: We Put Our Faith In God) | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Salon Azul, San Salvador | |
| Website | |
| www | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of El Salvador | |
 |
|---|
The Legislative Assembly (Spanish : Asamblea Legislativa) is the legislative branch of the government of El Salvador.



