 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Porphyrin [1] | |
| Other names Porphin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.690 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
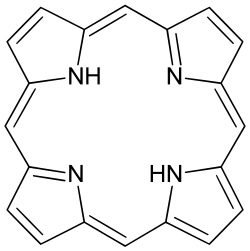
| C20H14N4 | |
| Molar mass | 310.35196 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red, shiny leaflets |
| Melting point | N/A |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Porphine or porphin is an organic compound of empirical formula C20H14N4. It is heterocyclic and aromatic. The molecule is a flat macrocycle, consisting of four pyrrole-like rings joined by four methine bridges, which makes it the simplest of the tetrapyrroles. [2]
Contents
The nonpolar tetrapyrrolic ring structure of porphine means it is poorly soluble in most organic solvents and hardly water soluble. [3] As a result, porphine is mostly of theoretical interest. It has been detected in GC-MS of certain fractions of Piper betle . [4]



