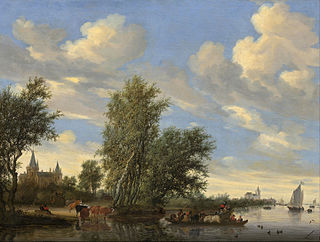Joseph Mallord William Turner, known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbulent, often violent marine paintings. He left behind more than 550 oil paintings, 2,000 watercolours, and 30,000 works on paper. He was championed by the leading English art critic John Ruskin from 1840, and is today regarded as having elevated landscape painting to an eminence rivalling history painting.
The Norwich School of painters was the first provincial art movement established in Britain, active in the early 19th century. Artists of the school were inspired by the natural environment of the Norfolk landscape and owed some influence to the work of landscape painters of the Dutch Golden Age such as Hobbema and Ruisdael.

Salomon van Ruysdael was a Dutch Golden Age landscape painter. He was the uncle of Jacob van Ruisdael.

Meindert Lubbertszoon Hobbema was a Dutch Golden Age painter of landscapes, specializing in views of woodland, although his most famous painting, The Avenue at Middelharnis, shows a different type of scene.

Jacob Isaackszoon van Ruisdael was a Dutch painter, draughtsman, and etcher. He is generally considered the pre-eminent landscape painter of the Dutch Golden Age, a period of great wealth and cultural achievement when Dutch painting became highly popular.

Cornelis Hendriksz Vroom was a Dutch Golden Age landscape painter.
Ruisdael or Ruysdael is a Dutch surname. Notable persons with that name include:

Marine art or maritime art is a form of figurative art that portrays or draws its main inspiration from the sea. Maritime painting is a genre that depicts ships and the sea—a genre particularly strong from the 17th to 19th centuries. In practice the term often covers art showing shipping on rivers and estuaries, beach scenes and all art showing boats, without any rigid distinction - for practical reasons subjects that can be drawn or painted from dry land in fact feature strongly in the genre. Strictly speaking "maritime art" should always include some element of human seafaring, whereas "marine art" would also include pure seascapes with no human element, though this distinction may not be observed in practice.

Paul Huet was a French painter and printmaker born in Paris. He studied under Gros and Guerin. He met the English painter Richard Parkes Bonington in the studio of Gros, where he studied irregularly from 1819 to 1822. Bonington's example influenced Huet to reject neoclassicism and instead paint landscapes based on close observation of nature. The British landscape paintings exhibited in the Salon of 1824 were a revelation to Huet, who said of Constable's work: "It was the first time perhaps that one felt the freshness, that one saw a luxuriant, verdant nature, without blackness, crudity or mannerism." Huet's subsequent work combined emulation of the English style with inspiration derived from Dutch and Flemish old masters such as Rubens, Jacob van Ruisdael, and Meindert Hobbema.

Isaack van Ruisdael was a Dutch Golden Age painter, brother to Salomon van Ruysdael and the father of the landscape painter Jacob van Ruisdael.
Jacob Salomonsz. van Ruysdael, was a Dutch Golden Age landscape painter who was the son of Salomon van Ruysdael and the cousin of the more famous Jacob Isaakszoon van Ruisdael.

The Windmill of Wijk bij Duurstede is an oil-on-canvas painting by the Dutch painter Jacob van Ruisdael. It is an example of Dutch Golden Age painting and is now in the collection of the Amsterdam Museum, on loan to the Rijksmuseum.

A Waterfall in a Rocky Landscape is an oil painting on canvas by the Dutch landscape painter Jacob van Ruisdael. It is an example of Dutch Golden Age painting and is now in the collection of the National Gallery.

Haerlempjes refer to a specific genre of landscape painting that includes a view of Haarlem. It is used most often to refer to Jacob van Ruisdael's panoramic views of the city, but the term is derived from mentions in Haarlem archives as a type of painting included in household inventories. The diminutive suffix "pje" would denote a small, cabinet-sized painting, but even the largest landscapes may be referred to as Haerlempjes today.
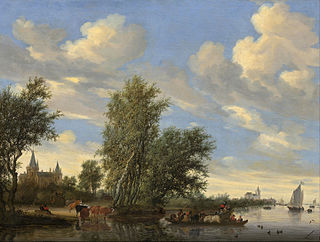
River Landscape with Ferry (1649) is an oil on canvas painting by the Dutch landscape painter Salomon van Ruysdael. It is an example of Dutch Golden Age painting and is now in the collection of the National Gallery of Art in Washington D.C.. This painting was owned by Jacques Goudstikker and was restituted to his heirs in 2006.

Wooded Dunes, also known as Dune Landscape, Peasant Cottage in a Landscape, Wooded Dunes and Cottage in a Grove is a 1646 oil-on-panel painting by the Dutch Golden Age painter Jacob van Ruisdael. It is in the collection of the Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg.

Grainfield at the Edge of a Wood, also known as The Cornfield, is a 1648 etching by the Dutch Golden Age artist Jacob van Ruisdael. There are five versions known about the etching. The first state is at the British Museum in London. The second state, in which a few lines in the sky have been added, is at the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. On the later states "JvRuysdael" has been added by another hand than Jacob's.
van Ruisdael can refer to

Landscape with a Windmill is an oil-on-panel painting executed by the Dutch artist Jacob van Ruisdael in 1646, early in his career. It is now in the Cleveland Museum of Art in Ohio. It had initially been loaned to them by the Mr and Mrs William H. Marlatt fund, who had bought it in 1967 from Kunsthandlung F. Kleinberger & Co, a New York art dealer, who had in turn bought it at the auction of the Cook collection at Christie's in London on 25 November 1966.

Peace – Burial at Sea is a painting in oils on canvas by the English Romantic artist J. M. W. Turner (1775–1851), first exhibited in 1842. The work is a memorial tribute to Turner's contemporary the Scottish painter Sir David Wilkie (1786–1841). The canvas depicts Wilkie's burial at sea. This work was intended as a companion piece to War. The Exile and the Rock Limpet which alludes to the sordid demise of the former Emperor of France Napoleon Bonaparte. The two works are characterized by sharply contrasting colors and tones: War utilizes a strident yellow and red while Peace is painted a cool blend of white, blue and black.