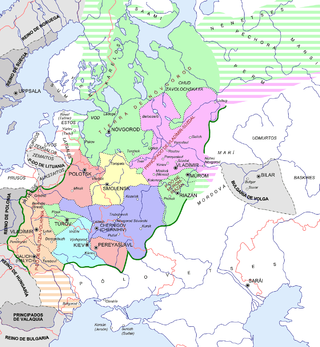
| Ruler | Born | Reign | Ruling part | Consort | Death | Notes |
|---|
Vladimir I the Great
Vladimir Basil Sviatoslavich
(Володимир Великий/Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь)
Old Norse: Valdamarr Sveinaldsson |  | c.958
Budiatychi
Son of Sviatoslav I of Kyiv and Malusha/Malfrida | 980 – 15 July 1015 | Kyivan Rus' | Olava/Allogia
c.977
at least one son
A Greek nun
(widow of his brother)
c.980
at least one son
Rogneda of Polotsk
c.978
(possibly in bigamy)
eight children
Adela (of Bulgaria?)
at least two children (maximum four)
Malfrida (of Bohemia?)
Before 1000
two children
Anna Porphyrogenita of Byzantium
988
Cherson
three children
Regelindis (?) of Saxony (granddaughter of Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor)
After 1011
one or two daughters
Unknown
two children | 15 July 1015
Berestove
(now part of Kyiv)
aged 57–58 | His early rule is characterized by a staunch pagan reaction but in 988 he was baptized into Orthodoxy and successfully converted Kyivan Rus' to Christianity. |
Iziaslav I
(Ізяслаў) |  | c.978
Kyiv
First son of Vladimir I the Great and Rogneda of Polotsk | 988 – 1001 | Polotsk | Unknown
two children | 1001
Polotsk
aged 22–23 | Polotsk splits rapidly from Kyivan Rus. As the eldest son of his mother, Iziaslav ruled in Polotsk alongside her. |
Vseslav I
(Усяслаў) | | c.990
Polotsk
First son of Iziaslav I | 1001-1003 | Polotsk | Unmarried | 1003
Polotsk
aged 12–13? | His succession to his father consolidated the family's possession of Polotsk. Died without descendants. |
Briacheslav I
(Брачыслаў) |  | c.990
Polotsk
Second son of Iziaslav I | 1003-1044 | Polotsk | Unknown
one child | 1044
Polotsk
aged 53–54 | |
Sviatopolk I the Accursed
Sviatopolk Yaropolkovich
(Святополк Окаянний)
Old Norse: Sveinpolk Iaropolksson |  | c.980
Kyiv
Son of Sviatoslav I of Kyiv and Predslava | 15 July 1015 – 1019 | Kyivan Rus' | Unknown name
(daughter of Bolesław I of Poland)
no children | 1019
Brest
aged 38–39 | |
Yaroslav I the Wise
Yaroslav George Vladimirovich
(Яросла́в Му́дрий)
Old Norse: Jarizleifr Valdamarrsson [6] |  | c.978
Third son of Vladimir I the Great and Rogneda of Polotsk | 1019 – 20 February 1054 | Kyivan Rus' | Ingigerda of Sweden
1019
Novgorod
eight or nine children | 20 February 1054
Vyshhorod
aged 75–76 | Prince of Rostov, Prince of Novgorod, and Grand Prince of Kyiv; during his reign Kyivan Rus' reached the pinnacle of its power. |
Iziaslav I
Iziaslav Demetrius Yaroslavich
(Ізяслав Ярославич)
Old Norse: Izjasleifr(?) Jarizleifsson |  | c.1024
Second son of Yaroslav I and Ingigerda of Sweden | 20 February 1054 – 14 September 1068
April 1069 – 22 May 1073
15 July 1076 – 3 October 1078 | Kyivan Rus' | Gertrude of Poland
1043
three children | 3 October 1078
Nizhyn
aged 53–54 | Reigned three times, threatened by the power of his relatives Vseslav of Polotsk (1068–69) and Sviatoslav II of Kyiv (1073–76). First ruler titled King of Rus' , as Pope Gregory VII sent him a crown from Rome in 1075. |
Vseslav II the Seer
Vseslav Basil Bryacheslavich
(Всеслав Брячиславич) |  | c.1039
Polotsk
Son of Briacheslav I | 1044 – 24 April 1101 | Polotsk | Unknown
six children | 24 April 1101
Polotsk
aged 61–62 | |
| 14 September 1068 – April 1069 | Kyivan Rus' |
Sviatoslav II
Sviatoslav Nicholas Yaroslavich
(Святослав Ярославич)
Old Norse: Sveinald Jarizleifsson |  | c.1027
Kyiv
Third son of Yaroslav I and Ingigerda of Sweden | 22 May 1073 – 15 July 1076 | Kyivan Rus' | Cecilia of DithmarschenBetween 1043 and 1047
five children
Oda of Stade (Nordmark)
c.1065
one son | 27 December 1076
Kyiv
aged 48–49 | A brief ruler during his brother Iziaslav's official reign. |
| Saint Yaropolk Iziaslavich |  | c.1043
First son of Iziaslav I and Gertrude of Poland | 3 October 1078 – 22 November 1087 | Turov-Pinsk | Kunigunde of Meissen
c.1071
four children | 22 November 1087
Zvenyhorod
aged 62–63 | His rule splits Turov-Pinsk from Kyiv authority. |
| Sviatopolk Iziaslavich |  | 8 November 1050
Second son of Iziaslav I and Gertrude of Poland | 22 November 1087 – 13 April 1093 | Turov-Pinsk | Unknown name
(daughter of Spytihněv II of Bohemia) [7]
c.1085
three children
Olenna of the Kipchaks
c.1094
four children | 26 April 1113
Vyshhorod
aged 62 | In 1093, he ascended to Kyivan throne. |
| Viacheslav Yaropolkovich | | c.1075?
Second son of Yaropolk Iziaslavich and Kunigunde of Meissen | 13 April 1093 – 1104 | Turov-Pinsk | Unknown | 1104
aged 28–29? | |
Rogvolod II Boris I
(Брачыслаў) |  | c.1060?
Polotsk
First son of Vseslav II | 24 April 1101 - 1129 | Polotsk | Unknown
three children | 1129
Polotsk
aged 68–69? | Children of Vseslav II, divided the principality between the three. |
| 24 April 1101 - 1127 | Drutsk |
Gleb Vseslavich
(Глеб Усяславіч) |  | c.1060?
Polotsk
Second son of Vseslav II | 24 April 1101 - 13 September 1119 | Minsk | Anastasia Yaropolkovna of Turov-Pinsk
1090
four children | 13 September 1119
Kyiv
aged 58–59? |
| Minsk briefly annexed to Kyiv (1119-1146) |
Sviatoslav Vseslavich
(Святаслаў Усяславіч) |  | c.1060?
Polotsk
Sixth son of Vseslav II | 24 April 1101 - c.1129 | Vitebsk | Sophia
five children | c.1129
Vitebsk
aged 68–69? |
| Vitebsk briefly annexed to Kyiv (1129-1132) |
| Vladimir Vsevolodovich Monomakh |  | 1053
Son of Vsevolod I of Kyiv and Anastasia of Byzantium | 1104 – 19 May 1125 | Turov-Pinsk | Gytha of Wessex
c.1074
five or six children
Euphemia of Byzantium
c.1100
six or seven children
Unknown name
(daughter of Aepa Ocenevich, Khan in Cumania)
After 1107
no known children | 19 May 1125
Kyiv
aged 71–72 | Also Grand Prince of Kyiv. From his reign, the succession in Turov-Pinsk echoed the distant Kyivan disputes for the throne. |
| Viacheslav Vladimirovich |  | 1083
Chernihiv
Sixth son of Vladimir Vladimirovich and Gytha of Wessex | 19 May 1125 – 14 April 1132
1134 - 1136
1136 - 1142
1146 | Turov-Pinsk | Unknown
before 1139
one child | 2 February 1154
Kyiv
aged 70–71 | Also Grand Prince of Kyiv. |
David
(Давыд) |  | c.1060?
Polotsk
Fourth son of Vseslav II | 1129 | Polotsk | Unknown
three children | 1129
Polotsk
aged 68–69? | |
| Iziaslav II |  | 1096 [8]
Novgorod
First son of Mstislav I of Kyiv and Christina of Sweden | 1129 - 14 April 1132 | Polotsk
(with Drutsk) | Agnes of Hohenstaufen
before 1151
five children
Rusudan of Georgia [8]
1154
no children | 13 November 1154 [8]
Kyiv
aged 57–58 | Also Grand Prince of Kyiv. |
14 April 1132 - 1134
1136 | Turov-Pinsk |
| Sviatopolk |  | 1114
Fourth son of Mstislav I of Kyiv and Christina of Sweden | 24 April 1132 – 1132 | Polotsk
(with Drutsk) | Euphemia of Olomouc [9]
1143 or 1144
no children | 20 February 1154 | Also Prince of Volhynia. |
Vasilko I
(Васілька) |  | c.1080
Polotsk
First son of Sviatoslav Vseslavich and Sophia | 1132 - 1144 | Polotsk
(with Vitebsk and Drutsk) | Unknown
five children | 1144
Vitebsk
aged 63–64 | While also ruling in the senior principality of Polotsk, Vasilko managed to restore the sovereignty of his father's principality. |
| Sviatoslav Vsevolodovich |  | 1123
Chernihiv
First son of Vsevolod II of Kyiv and Maria Mstislavna of Kyiv
| 1142-1146
1154 | Turov-Pinsk | Maria Vasilkovna of Polotsk
1143
eight children | 25 July 1194
Brest
aged 70–71 | Also Prince of Chernihiv and Grand Prince of Kyiv. |
Rogvolod III Basil
(Рагвалод-Васіль) |  | c.1110
Polotsk
Second son of Rogvolod II Boris | 1127-1129
1140-1144
1158-1159
1162-1170 | Drutsk | ? Iziaslavna of Kyiv
(daughter of Iziaslav II of Kyiv)
five children | 1170
Polotsk
aged 59–60? | |
1144-1151
1159-1162 | Polotsk |
| Gleb Rogvolodovich | | c.1130?
Polotsk
First son of Rogvolod III Basil | 1144-1151
1159-1162
1170-1186 | Drutsk | Unknown | 1186
Drutsk
aged 55–56? | |
| Yaroslav Iziaslavich |  | 1132
Second son of Iziaslav Mstislavich and Agnes of Hohenstaufen
| 1146-1148 | Turov-Pinsk | Richeza of Bohemia
1149
four children | 1180
Lutsk
aged 47–48 | Also Grand Prince of Kyiv. |
| Yuri Yaroslavich | | c.1112
Son of Yaroslav Sviatopolkovich, Prince of Volhynia | 1148-1150
1151-1154
1157-1168 | Turov-Pinsk | Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno
seven children | 1168
Bogolyubovo
aged 55–56 | His last reign marked the end of Kyiv involvement in the government; the principality passed directly to Yuri's children. |
| Andrey Yurievich Bogolyubsky |  | 1111
Rostov
Third son of Yuri of Kyiv and ? of Cumania | 1150-1151 | Turov-Pinsk | Yulita Stepanovna
four children | 29 June 1174
Bogolyubovo
aged 62–63 | Also Grand Prince of Vladimir. |
Rostislav
(Расціслаў) |  | c.1110
Polotsk
First son of Gleb Vseslavich, Prince of Minsk and Anastasia Yaropolkovna of Turov-Pinsk | 1146-1151
1159-1165 | Minsk | Unknown
two children | 1165
Minsk
aged 64–65? | |
| 1151-1159 | Polotsk |
| Gleb Rostislavich |  | c.1130?
Polotsk
Son of Rostislav | 1151-1158 | Drutsk | Unknown | 1163
Drutsk
aged 69–70? | |
| Boris Yurievich |  | c.1120?
Seventh son of Yuri of Kyiv and ? of Cumania | 1154-1157 | Turov-Pinsk | Maria
one child | 2 May 1159
Suzdal
aged 38–39? | |
| Vseslav III | | c.1110
Polotsk
First son of Vasilko I | 1144-1162
1176-1178
1182-1186 | Vitebsk | ? Rostislavna of Smolensk
c.1160
one child | 1186
Polotsk
aged 69–70? | |
1162-1167
1167-1180 | Polotsk |
Roman Viacheslavich
(Раман) | | c.1130?
Son of Viacheslav Rostislavich and ? Viacheslavna of Kyiv | 1162-1165 | Vitebsk | Unknown
two children | 1165
Vitebsk
aged 34–35? | Great-grandson of Vseslav I. |
| David Sviatoslavich | | c.1110?
Second son of Sviatoslav Vseslavich and Sophia | 1165-1167 | Vitebsk | Unknown
one child | 1173
Vitebsk
aged 62–63? | |
Volodar
(Валадар) | | c.1120
Polotsk
Second son of Gleb Vseslavich, Prince of Minsk and Anastasia Yaropolkovna of Turov-Pinsk | 1151-1159
1165-1177 | Minsk | Richeza of Poland
18 June 1136
(annulled c.1150)
four children | 1180
Minsk
aged 59–60? | |
| 1167 | Polotsk |
| Viacheslav Sviatoslavich | | c.1110?
Third son of Sviatoslav Vseslavich and Sophia | 1167-1168 | Vitebsk | Unknown
two children | 1168
Vitebsk
aged 57–58? | |
| Ivan Yurievich | | c.1140?
First son of Yuri Yaroslavich and Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno | 1168-c.1170 | Turov-Pinsk | Unknown
one child | c.1180?
Turov
aged 39–40? | Retired from government in 1170. After that, his brothers divided the principality. |
| Briacheslav Vasilkovich | | c.1140
Vitebsk
First son of Vasilko I | 1168-1176
1178-1182 | Vitebsk | Unknown
two children | 1186
Vitebsk
aged 45–46 | |
| Sviatopolk Yurievich | | c.1140?
Second son of Yuri Yaroslavich and Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno | c.1170 - 19 April 1190 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Turov) | Unknown
two children | 19 April 1190
Turov
aged 49–50? | Brothers of Ivan Yurievich, divided the principality in halves. |
| Yaroslav Yurievich | | c.1140?
Third son of Yuri Yaroslavich and Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno | c.1170 - 1190 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown
one child | c.1190
Pinsk
aged 49–50? |
| Boris II | | c.1140?
Son of David Sviatoslavich, Prince of Vitebsk | 1180-1185 | Polotsk | Unknown
one child | 1185
Vitebsk
aged 44–45? | |
Vladimir II
(Уладзімір) |  | c.1140
Polotsk
First son of Volodar and Richeza of Poland | 1177-1216 | Minsk | Unmarried | 1216
Polotsk
aged 75–76? | Children of Volodar, ruled jointly in Minsk, but succeeded each other in Polotsk. |
| 1185-1216 | Polotsk |
| Vasilko II | | c.1140
Polotsk
Second son of Volodar and Richeza of Poland | 1177-1216 | Minsk | ? Davidovna of Smolensk
(daughter of Davyd Rostislavich)
at least one child | 1222
Polotsk
aged 75–76? |
| 1216-1222 | Polotsk |
| Minsk annexed to Lithuania |
| Polotsk briefly annexed to Smolensk [10] |
| Vasilko Briacheslavich | | c.1150?
Vitebsk
Son of Briacheslav Vasilkovich | 1186-1221 | Vitebsk | Unknown
two children | 1221
Vitebsk
aged 70–71? | |
| Boris Rogvolodovich |  | c.1140?
Polotsk
Second son of Rogvolod III Basil | 1186-c.1200 | Drutsk | Unknown | c.1200
Drutsk
aged 59–60? | Brothers of Gleb Rogvolodovich, possibly ruled jointly. |
| Vseslav Rogvolodovich | | c.1140?
Polotsk
Third son of Rogvolod III Basil | c.1200
Drutsk
aged 59–60? |
| Drutsk annexed to Vitebsk |
| Gleb Yurievich | | c.1140?
Fourth son of Yuri Yaroslavich and Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno | 19 April 1190 - 1195 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Turov) | Unknown
three children | 1195
Turov
aged 54–55? | |
| Yaropolk Yurievich | | c.1140?
Fifth son of Yuri Yaroslavich and Anna Vsevolodovna of Grodno | c.1190-1204 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown
one child | 1204
Pinsk
aged 63–64? | |
| Andrey Ivanovich | | c.1170?
Son of Ivan Yurievich | 1195 - 1 June 1223 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Turov) | Unknown
one child | 1 June 1223
aged 52–53? | |
| Vladimir Sviatopolkovich | | c.1170?
First son of Sviatopolk Yurievich | 1204-1228 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk; also in Turov since 1223) | Unknown
one child | 1228
Turov
aged 57–58? | |
| Briacheslav Vasilkovich | | c.1190
Vitebsk
Son of Vasilko Briacheslavich | 1221-1232 | Vitebsk | Unknown
two children | 1232
Vitebsk
aged 41–42 | |
| Rostislav Sviatopolkovich | | c.1170?
Second son of Sviatopolk Yurievich | 1228-1232 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown | 1232
Pinsk
aged 61–62? | |
| Yuri Andreyevich | | c.1170?
Son of Andrey Ivanovich | 1228-c.1280? | Turov-Pinsk
(at Turov) | Unknown
one child | 1 June 1223
aged 52–53? | |
| Briacheslav II | | c.1190
Polotsk
Son of Vasilko II and ? Davidovna of Smolensk | 1232-1256 | Polotsk | Unknown
five children | 1256
Polotsk
aged 65–66? | |
| Iziaslav Briacheslavich | | c.1210?
Vitebsk
Second son of Briacheslav Vasilkovich | 1232-1262
1264 | Vitebsk | Unknown | 1264
Vitebsk
aged 53–54? | |
| Michael Vladimirovich | | c.1190?
First son of Vladimir Sviatopolkovich | 1232-1247 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown | 1247
Pinsk
aged 56–57? | |
| Feodor Vladimirovich | | c.1200?
Second son of Vladimir Sviatopolkovich | 1247-1262 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown | 1262
Pinsk
aged 61–62? | |
| Constantine the Armless |  | c.1230
Polotsk
Son of Briacheslav II | 1256-1258
1268-1274 | Polotsk | ? Alexandrovna of Vladimir-Suzdal
(daughter of Alexander Nevsky)
two children | 1292
aged 61–62? | He probably used the title rex Ruthenorum . His reign coincided with a civil war between various claimants to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It is known that he renounced the right to the land of Lotigola in favor of the Livonian Order. |
| 1262-1263 | Vitebsk |
| Polotsk annexed to Lithuania (1256-58 and from 1274) |
| Yuri Vladimirovich | | c.1220?
Third son of Vladimir Sviatopolkovich | 1262-1290 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown
at least one child | 1290
Pinsk
aged 69–70? | |
| Michael Kostantinovich | | c.1250?
Vitebsk
Son of Constantine and ? Alexandrovna of Vladimir-Suzdal | 1264-1287 | Vitebsk | Unknown | 1307
Vitebsk
aged 56–57? | |
| Semyon Yurievich | | c.1250?
Son of Yuri Andreyevich | c.1280?-1320 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Turov) | Unknown | 1320?
aged 69–70? | After his death Turov was absorbed by Lithuania. |
| Turov annexed to Lithuania |
| Vasilko Briacheslavich | | c.1220?
Vitebsk
Third son of Briacheslav Vasilkovich | 1287-1297 | Vitebsk | Unknown
at least one child | 1297
Vitebsk
aged 76–77? | |
| Demid Vladimirovich | | c.1220?
Fourth son of Vladimir Sviatopolkovich | 1290-1292 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown | 1292
Pinsk
aged 71–72? | |
| Yaroslav Yurievich | | c.1270?
Son of Yuri Vladimirovich | 1292-c.1300? | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown
at least one child | c.1300?
Pinsk
aged 31–32? | |
| Yaroslav Vasilkovich | | c.1250?
Vitebsk
Son of Vasilko Briacheslavich | 1297-1320 | Vitebsk | Unknown
one child | 1320
Vitebsk
aged 69–70? | |
| Vasily Yaroslavich | | c.1290?
Fourth son of Yaroslav Yurievich | c.1300-1320 | Turov-Pinsk
(at Pinsk) | Unknown | c.1320?
Pinsk
aged 29–30? | After his death Pinsk was absorbed by Lithuania. |
| Pinsk annexed to Lithuania |
| Maria Yaroslavna |  | c.1300
Vitebsk
Daughter of Yaroslav Vasilkovich | 1320-1346 | Vitebsk | Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania
1317
seven children | 1346
aged 45–46 | The only heir to the Principality, [11] she may have ruled with her husband. Vitebsk was then annexed to Lithuania. |
| Vitebsk annexed to Lithuania |