External links
- Zimmerman, Elwood C. (1958). Insects of Hawaii. 7 Macrolepidoptera. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu. hdl:10125/7336.
| This Larentiinae moth related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| Progonostola caustoscia | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | P. caustoscia |
| Binomial name | |
| Progonostola caustoscia Meyrick, 1899 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Progonostola caustoscia is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1899. It is endemic to the Hawaiian islands of Maui and Lanai.
In color, size and pattern, this species is similar to Progonostola cremnopis , but it is easily separated, in the male at least, by its bipectinate (comb-like on both sides) antennae.
| This Larentiinae moth related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

Hawaii is a U.S. state located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the only state outside North America, the only island state, and the only state in the tropics. Hawaii is also one of a handful of U.S. states to have once been an independent nation.

Honolulu is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is located in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oʻahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for international business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by an eclectic mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, as reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions.
Hawaiian is a Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the State of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840.

Oceania is a geographic region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, Oceania has a land area of 8,525,989 square kilometres (3,291,903 sq mi) and a population of over 41 million. When compared to continents, the region of Oceania is the smallest in land area and the second smallest in population after Antarctica.

Oahu, also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—about two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island lies within Honolulu County and the state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast.
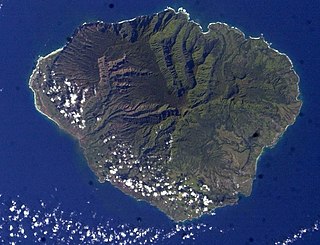
Kauaʻi, anglicized as Kauai, is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island in the United States. Known also as the "Garden Isle", Kauaʻi lies 105 miles (169 km) across the Kauaʻi Channel, northwest of Oʻahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park.

Hawaiʻi is the largest island located in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It is the largest and the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of volcanic islands in the North Pacific Ocean. With an area of 4,028 square miles (10,430 km2), it has 63% of the Hawaiian archipelago's combined landmass, and is the largest island in the United States. However, it has only 13% of Hawaiʻi's people. The island of Hawaiʻi is the third largest island in Polynesia, behind the two main islands of New Zealand.
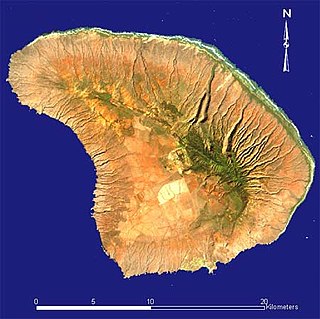
Lanai is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands and the smallest publicly accessible inhabited island in the chain. It is colloquially known as the Pineapple Island because of its past as an island-wide pineapple plantation. The island's only settlement of note is the small town of Lanai City. As of 2012, the island was 98% owned by Larry Ellison, founder and chairman of Oracle Corporation, with the remaining 2% owned by the state of Hawaii and privately owned homes.

Hawaiian Airlines is the flag carrier and the largest airline in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It is the tenth-largest commercial airline in the US, and is based in Honolulu, Hawaii. The airline operates its main hub at Daniel K. Inouye International Airport on the island of Oʻahu and a secondary hub out of Kahului Airport on the island of Maui. The airline also maintained a crew base at Los Angeles International Airport. Hawaiian Airlines operates flights to Asia, American Samoa, Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Zealand, and the United States mainland. Hawaiian Airlines is owned by Hawaiian Holdings, Inc. of which Peter R. Ingram is the current President and Chief Executive Officer.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly the group was known to Europeans and Americans as the Sandwich Islands, a name that James Cook chose in honor of the then First Lord of the Admiralty John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich. The contemporary name, dating from the 1840s, is derived from the name of the largest island, Hawaiʻi Island. The islands were first known to Europeans after the expedition of Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón in 1527.

The University of Hawaiʻi system, formally the University of Hawaiʻi and popularly known as UH, is a public college and university system that confers associate, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees through three university campuses, seven community college campuses, an employment training center, three university centers, four education centers and various other research facilities distributed across six islands throughout the state of Hawaiʻi in the United States. All schools of the University of Hawaiʻi system are accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges. The U.H. system's main administrative offices are located on the property of the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa in Honolulu CDP.

Israel Kaʻanoʻi Kamakawiwoʻole, Hawaiian of the fearless eye, the bold face; May 20, 1959 – June 26, 1997), also called Bruddah Iz or IZ, was a Hawaiian singer-lyricist, musician, and Hawaiian sovereignty activist.

The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900 until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding Palmyra Island, was admitted to the Union as the fiftieth U.S. state, the State of Hawaii. The Hawaii Admission Act specified that the State of Hawaii would not include Palmyra Island, the Midway Islands, Kingman Reef, and Johnston Atoll, which includes Johnston Island and Sand Island.

Native Hawaiians are the aboriginal people of the Hawaiian Islands or their descendants who trace their ancestry back to the original Polynesian settlers of Hawaiʻi. The traditional name of the Hawaiian people is Kanaka Maoli.

Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It has been long visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. Its surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, promptly led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II.
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, originated in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi, and Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauaʻi and Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.
Progonostola is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae, native to Hawaii.

Tulsi Gabbard is an American politician and United States Army Reserve officer who serves as the U.S. Representative for Hawaii's 2nd congressional district. Elected in 2012, she is the first Hindu member of Congress and also the first Samoan-American voting member of Congress. In early February 2019 she announced her candidacy for the Democratic nomination in the 2020 United States presidential election.

Hawaii Five-0 is an American action police procedural television series that centers around a special police major crimes task force operating at the behest of the governor of Hawaii. It is a reboot of the 1968–1980 series Hawaii Five-O, which also aired on CBS. The series was produced by K/O Paper Products and 101st Street Entertainment, initially in association with CBS Productions, then CBS Television Studios starting in season three. The show received praise for its modern take on the original series.
Progonostola cremnopis is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1899. It is endemic to the Hawaiian islands of Kauai, Oahu, Molokai and Hawaii.