
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts specifically to foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.

B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules; however, these antibodies are not secreted. Rather, they are inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed.

A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the immune system of jawed vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte".

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruising, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.
Auer rods are large, crystalline cytoplasmic inclusion bodies sometimes observed in myeloid blast cells during acute myeloid leukemia, acute promyelocytic leukemia, and high-grade myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders. Composed of fused lysosomes and rich in lysosomal enzymes, Auer rods are azurophilic and can resemble needles, commas, diamonds, rectangles, corkscrews, or rarely granules.

A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24 hours for three to five days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each clone sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as plasma cells, cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells.
Marek's disease is a highly contagious viral neoplastic disease in chickens. It is named after József Marek, a Hungarian veterinarian who described it in 1907. Marek's disease is caused by an alphaherpesvirus known as "Marek's disease virus" (MDV) or Gallid alphaherpesvirus 2 (GaHV-2). The disease is characterized by the presence of T cell lymphoma as well as infiltration of nerves and organs by lymphocytes. Viruses related to MDV appear to be benign and can be used as vaccine strains to prevent Marek's disease. For example, the related herpesvirus found in turkeys (HVT), causes no apparent disease in the birds, and continues to be used as a vaccine strain for prevention of Marek's disease.
Lymphokines are a subset of cytokines that are produced by a type of immune cell known as a lymphocyte. They are protein mediators typically produced by T cells to direct the immune system response by signaling between its cells. Lymphokines have many roles, including the attraction of other immune cells, including macrophages and other lymphocytes, to an infected site and their subsequent activation to prepare them to mount an immune response. Circulating lymphocytes can detect a very small concentration of lymphokine and then move up the concentration gradient towards where the immune response is required. Lymphokines aid B cells to produce antibodies.
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is a type of cancer made up of B-cells that replace the normal architecture of the white pulp of the spleen. The neoplastic cells are both small lymphocytes and larger, transformed lymphoblasts, and they invade the mantle zone of splenic follicles and erode the marginal zone, ultimately invading the red pulp of the spleen. Frequently, the bone marrow and splenic hilar lymph nodes are involved along with the peripheral blood. The neoplastic cells circulating in the peripheral blood are termed villous lymphocytes due to their characteristic appearance.
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.
CD58, or lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3), is a cell adhesion molecule expressed on Antigen Presenting Cells (APC), particularly macrophages.

B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, referred to as B-PLL, is a rare blood cancer. It is a more aggressive, but still treatable, form of leukemia.

In dermatologic pathology, a dermal cylindroma, also dermal eccrine cylindroma or cutaneous cylindroma) and cylindroma, is a benign adnexal tumor that occurs on the scalp and forehead.

CD48 antigen also known as B-lymphocyte activation marker (BLAST-1) or signaling lymphocytic activation molecule 2 (SLAMF2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD48 gene.
T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, previously labeled precursor T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is a form of lymphoid leukemia and lymphoma in which too many T-cell lymphoblasts are found in the blood, bone marrow, and tissues, particularly mediastinal lymph nodes. Labeling as leukemia or lymphoma depends on which feature is more pronounced in a given situation, but has no biological or treatment implication.
In cell biology, a precursor cell, also called a blast cell or simply blast, is a partially differentiated cell, usually referred to as a unipotent cell that has lost most of its stem cell properties. A precursor cell is also known as a progenitor cell but progenitor cells are multipotent. Precursor cells are known as the intermediate cell before they become differentiated after being a stem cell.
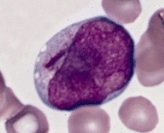
Lutzner cells were discovered by Marvin A. Lutzner, Lucien-Marie Pautrier, and Albert Sézary. These cells are described as the smaller forms of Sézary cells, or Sézary-Lutzner cells, and the two variants are recognised as being morphologically different. Aggregates of these cells in mycosis fungoides are known as a Pautrier's microabscesses. They are a form of T-lymphocytes that has been mutated This atypical form of T-lymphocytes contains T-cell receptors on the surface and is found in both the dermis and epidermis layers of the skin. Since Lutzner cells are a mutated form of T-lymphocytes, they develop in bone marrow and are transported to the thymus is order to mature. The production and maturation stages occur before the cell has developed a mutation. Lutzner cells can form cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, which is a form of skin cancer.

White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system.

Theileria parva is a species of parasites, named in honour of Arnold Theiler, that causes East Coast fever (theileriosis) in cattle, a costly disease in Africa. The main vector for T. parva is the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. Theiler found that East Coast fever was not the same as redwater, but caused by a different protozoan.

Raji is the first continuous human cell line of hematopoietic origin. The Raji cell line is widely used as a transfection host.














