
Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 validly described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae, and P. graminis.

Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.
Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprotrophic soil bacterium.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes.

Pseudomonas syringae is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from international culture collections such as the NCPPB, ICMP, and others.
Pseudomonas moraviensis is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. It is named after Moravia, the region of the Czech Republic where it was first isolated. The type strain is CCM 7280T.
Pseudomonas lutea is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, non-spore-forming, motile, rod-shaped bacterium originally isolated from the rhizosphere of grasses in Spain. The type strain is LMG 21974.
Pseudomonas grimontii is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, fluorescent, motile bacterium isolated from natural springs in France. The type strain is CIP 106645.
Pseudomonas palleroniana is a Gram-negative bacterium that infects rice. The type strain is CFBP 4389.
Pseudomonas trivialis is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grasses. The type strain is DSM 14937.
Pseudomonas poae is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grasses. The type strain is DSM 14936.
Pseudomonas congelans is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grasses. The type strain is DSM 14939.
Pseudomonas knackmussii is a Gram-negative, polarly flagellated, motile, short rod bacterium isolated from a sewage treatment plant in Göttingen, Germany. It is the first bacterium used to study the degradation of haloaromatic compounds. It is named after Hans-Joachim Knackmuss. The type strain is DSM 6978.
Pseudomonas koreensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile, multiple polar flagellated, yellow-white, rod bacterium isolated from farming soil in Korea. The type strain is LMG 21318.
Pseudomonas umsongensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile, single polar-flagellated, yellow-white, rod-shaped bacterium isolated from the soil in the Umsong region of Korea. The type strain is LMG 21317.
Pseudomonas costantinii is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes brown blotch disease in cultivated mushrooms. It demonstrates hemolytic activity. The type strain is CFBP 5705.
Pseudomonas indica is a Gram-negative, butane-using bacterium first isolated in India. The type strain is MTCC 3713.
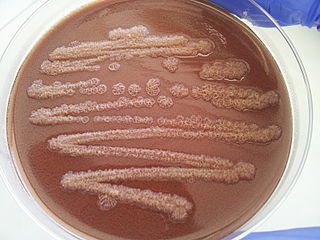
Pseudomonas stutzeri is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that is motile, has a single polar flagellum, and is classified as bacillus, or rod-shaped. While this bacterium was first isolated from human spinal fluid, it has since been found in many different environments due to its various characteristics and metabolic capabilities. P. stutzeri is an opportunistic pathogen in clinical settings, although infections are rare. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, this bacterium has been placed in the P. stutzeri group, to which it lends its name.

Cefsulodin is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and was discovered by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in 1977.
Turicella otitidis is a Coryneform Gram-positive bacterium first isolated from patients with otitis media.





