
Pseudorhabdosynochus regius is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the mottled grouper .

Pseudorhabdosynochus americanus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of groupers. It was described as Diplectanum americanum by Price in 1937 and transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky and Beverley-Burton in 1986. The species was redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus yucatanensis is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the red grouper, Epinephelus morio. It was described by Vidal-Martínez, Aguirre-Macedo & Mendoza-Franco in 1997 and redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus justinella is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the red grouper, Epinephelus morio. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus kritskyi is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the gag, Mycteroperca microlepis. The species has been described by Dyer, Williams and Bunkley-Williams in 1995 and redescribed successively by Yang, Gibson and Zeng in 2005 and by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015. The name of the species honours the American parasitologist Delane C. Kritsky.

Pseudorhabdosynochus capurroi is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Black grouper, Mycteroperca bonaci. It was described by Vidal-Martínez and Mendoza-Franco in 1998 and redescribed successively by Yang, Gibson and Zeng in 2005 and by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus sulamericanus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the snowy grouper, Epinephelus niveatus, the Warsaw grouper, Epinephelus nigritus and the Haifa grouper, Epinephelus haifensis. It has been described by Santos, Buchmann & Gibson in 2000, redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015. and again redescribed by Chaabane, Justine, Gey, Bakenhaster & Neifar in 2016.

Pseudorhabdosynochus firmicoleatus is a diplectanid monogenean parasite on the gills of the Yellowedge grouper, Epinephelus flavolimbatus and the Snowy grouper, Epinephelus niveatus. It was described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.
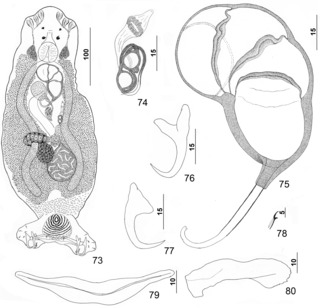
Pseudorhabdosynochus mcmichaeli is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the scamp, Mycteroperca phenax. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus meganmarieae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Graysby, Cephalopholis cruentata. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus vascellum is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the scamp, Mycteroperca phenax. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus contubernalis is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Scamp, Mycteroperca phenax. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.
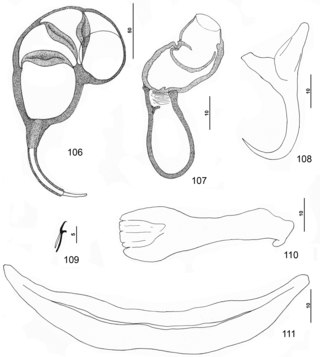
Pseudorhabdosynochus monaensis is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the rock hind, Epinephelus adscensionis. It has been described by Dyer, Williams & Bunkley-Williams in 1994 and redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus mycteropercae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the tiger grouper, Mycteroperca tigris (Serranidae). It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus williamsi is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the rock hind, Epinephelus adscensionis. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus mizellei is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the red hind, Epinephelus guttatus. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015. The species was named Diplectanum epinepheli by Mizelle & Wood but this name was not published and is a nomen nudum according to Kritsky, Bakenhaster & Adams (2015).

Pseudorhabdosynochus bunkleywilliamsae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Nassau grouper, Epinephelus striatus. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus woodi is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the red hind, Epinephelus guttatus. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus tumeovagina is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the speckled hind, Epinephelus drummondhayi. It has been described by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.

Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus. It has been described by Guy Oliver in 1984 as Cycloplectanum beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Oliver in 1987, transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky & Beverley-Burton in 1986 as Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015, and redescribed in 2016 by Chaabane, Neifar, Gey & Justine.





















