
Amstrad was a British consumer electronics company, founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar. During the 1980s, the company was known for its home computers beginning with the Amstrad CPC and later also the ZX Spectrum range after the Sinclair deal, which led it to have a substantial share of the PC market in Britain. In the following decade it shifted focus towards communication technologies, and its main business during the 2000s was the manufacture of satellite television set-top boxes for Sky, which Amstrad had started in 1989 as the then sole supplier of the emerging Sky TV service.

Psion PLC was a designer and manufacturer of mobile handheld computers for commercial and industrial uses. The company was headquartered in London, England, with major operations in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, and other company offices in Europe, the United States, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. It was a public company listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

The Psion Series 5 was a personal digital assistant (PDA) from Psion. It came in two main variants, the Series 5 and the Series 5mx (1999), the latter having a faster processor, clearer liquid crystal display (LCD), and updated software. There was also a rare Series 5mx Pro, which differed only in having the operating system (OS) loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and hence upgradeable. Ericsson marketed a version of the Series 5mx renamed as MC218.

A netbook is a small and inexpensive laptop designed primarily as a means of accessing the Internet. Netbooks were sold from 2007 until around 2013, when the widespread advent of smartphones and tablets eclipsed their popularity.
The Psion Series 7 is a subnotebook computer from Psion that was released in 2000. In size it is fairly original: larger than a palmtop or handheld machine, but smaller than a laptop computer. It was the first and last of the Psion series to have a full color electronic visual display. It has a leather-bound clamshell design, with a touch-sensitive, Video Graphics Array (VGA) resolution liquid-crystal display (LCD) and QWERTY computer keyboard. Internally it has a 132.71 MHz StrongARM SA-1100 processor, 16 megabyte (MB) of random-access memory (RAM) and 16 MB of internal read-only memory (ROM).

Xbox Linux was a project that ported the Linux operating system to the Xbox video game console. Because the Xbox uses a digital signature system to prevent the public from running unsigned code, one must either use a modchip, or a softmod. Originally, modchips were the only option; however, it was later demonstrated that the TSOP chip on which the Xbox's BIOS is held may be reflashed. This way, one may flash on the "Cromwell" BIOS, which was developed legally by the Xbox Linux project. Catalyzed by a large cash prize for the first team to provide the possibility of booting Linux on an Xbox without the need of a hardware hack, numerous software-only hacks were also found. For example, a buffer overflow was found in the game 007: Agent Under Fire that allowed the booting of a Linux loader ("xbeboot") straight from a save game.
The Intel Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) is a series of integrated graphics processors introduced in 2004 by Intel, replacing the earlier Intel Extreme Graphics series and being succeeded by the Intel HD and Iris Graphics series.

An ultra-mobile PC, or ultra-mobile personal computer (UMPC), is a miniature version of a pen computer, a class of laptop whose specifications were launched by Microsoft and Intel in Spring 2006. Sony had already made a first attempt in this direction in 2004 with its Vaio U series, which was only sold in Asia. UMPCs are generally smaller than subnotebooks, have a TFT display measuring (diagonally) about 12.7 to 17.8 centimetres, are operated like tablet PCs using a touchscreen or a stylus, and can also have a physical keyboard. There is no clear boundary between subnotebooks and ultra-mobile PCs, but UMPCs commonly have major features not found in the common clamshell laptop design, such as small keys on either side of the screen, or a slide-out keyboard.
Jiangsu Lemote Tech Co., Ltd or Lemote is a computer company established as a joint venture between the Jiangsu Menglan Group and the Chinese Institute of Computing Technology, involved in computer hardware and software products, services, and projects.
The Classmate PC, formerly known as Eduwise, is Intel's entry into the market for low-cost personal computers for children in the developing world. It is in some respects similar to the One Laptop Per Child (OLPC) trade association's Children's Machine (XO), which has a similar target market. Although made for profit, the Classmate PC is considered an Information and Communication Technologies for Development project (ICT4D). Introduced in 2006, the device falls into the then popular category of netbooks.

Efika is a line of power efficient ARM architecture and Power ISA based computers manufactured by Genesi.

The ASUS Eee PC is a netbook computer line from Asus, and a part of the ASUS Eee product family. At the time of its introduction in late 2007, it was noted for its combination of a lightweight, Linux-based operating system, solid-state drive (SSD), and relatively low cost. Newer models added the options of Microsoft Windows operating system and rotating media hard disk drives (HDD), and initially retailed for up to 500 euros.

The A110 is a netbook computer by One. It is built on a reference design by Quanta Computer and was announced to run Linpus Linux. However, some or all of the first batch have actually been delivered with a modified Ubuntu Linux installed, using SquashFS to fit the system in the 2 GB Flash memory.
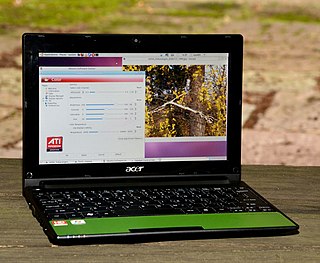
Acer Aspire One is a line of netbooks first released in July 2008 by Acer Inc.
Nvidia Ion was a product line of Nvidia Corporation intended for motherboards of low-cost portable computers. It used graphics processing units and chipsets intended for small products.
The Dell Inspiron Mini Series is a line of subnotebook/netbook computers designed by Dell. The series was introduced in September 2008 amidst the growing popularity of low-cost netbook computers introduced by competitors.
Psion Teklogix Inc. was the operational business of Psion.

The Nokia Booklet 3G was a netbook produced by the Finnish company Nokia. It was announced on 24 August 2009.

HP Mini is a former line of small computers categorized as netbooks manufactured by Hewlett-Packard. They either contained a custom version of Ubuntu Linux, Windows XP Home Edition, or Windows 7 Starter operating system. Like most netbooks, they were not built with CD/DVD drives.

The IdeaPad S Series is a series of notebook computers launched by Lenovo in October 2008. The IdeaPad S10 was initially scheduled for launch in September, but its release was delayed in the United States until October.












