
Scyliorhinus is a genus of catsharks in the family Scyliorhinidae. This genus is known in the fossil records from the Cretaceous period, late Albian age to the Pliocene epoch.

The Decapoda or decapods are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossil decapod is the Devonian Palaeopalaemon.

James Wood-Mason was an English zoologist. He was the director of the Indian Museum at Calcutta, after John Anderson. He collected marine animals and lepidoptera, but is best known for his work on two other groups of insects, phasmids and mantids.

Xanthidae is a family of crabs known as gorilla crabs, mud crabs, pebble crabs or rubble crabs. Xanthid crabs are often brightly coloured and are highly poisonous, containing toxins which are not destroyed by cooking and for which no antidote is known. The toxins are similar to the tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin produced by puffer fish, and may be produced by bacteria in the genus Vibrio living in symbiosis with the crabs, mostly V. alginolyticus and V. parahaemolyticus.

Calappa is a genus of crabs known commonly as box crabs or shame-faced crabs. The name box crab comes from their distinctly bulky carapace, and the name shame-faced is from anthropomorphising the way the crab's chelae (claws) fold up and cover its face, as if it were hiding its face in shame.

The Bythograeidae are a small family of blind crabs which live around hydrothermal vents. The family contains 16 species in six genera. Their relationships to other crabs are unclear. They are believed to eat bacteria and other vent organisms.

Metanephrops is a genus of lobsters, commonly known as scampi. Important species for fishery include Metanephrops australiensis and Metanephrops challengeri. It differs from other lobsters such as Homarus and Nephrops norvegicus in that its two main claws are of equal size, rather than being differentiated into a crusher and a pincher. There are 18 extant species recognised in the genus:

Comitas is a genus of medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Pseudomelatomidae.
Mioceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish in the family Neoceratodontidae, which also contains the extant Queensland lungfish. It is known only from Oligocene and Miocene-aged sediments in Australia, although phylogenetic evidence supports it having first diverged from its closest relative, Neoceratodus, during the Late Jurassic or Early Cretaceous period.

Paraceratodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric lungfish. Only one species, P. germaini, is known from the latest Permian or earliest Triassic period of Madagascar. Phylogenetic evidence supports it being the most basal member of the suborder Ceratodontoidei, which contains modern lungfish, and as with the rest of the order it likely diverged during the late Carboniferous.

Latirus is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Fasciolariidae, the spindle snails, the tulip snails and their allies.

Metapenaeopsis, the velvet shrimps, is a prawn genus in the family Penaeidae. It contains these species:
The family Homolidae, known as carrier crabs or porter crabs, contains 14 genera of marine crabs. They mostly live on the continental slope and continental shelf, and are rarely encountered. Members of the Homolidae have their fifth pereiopods in a sub-dorsal position, which allows them to hold objects in place over the rear half of the carapace. The objects carried include sponges, black corals and gorgonians, and this behaviour may be a defence mechanism against predators. Some species have been observed carrying living sea urchins in a symbiotic relationship which allows them to benefit from the protection of the urchin's dangerous spikes.
Dictyaster is a small genus of starfish in the family Echinasteridae in the order Spinulosida.

Borsonia symbiotes is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Borsoniidae.
Chilobrachys is a genus of Asian tarantulas that was first described by Ferdinand Anton Franz Karsch in 1892.
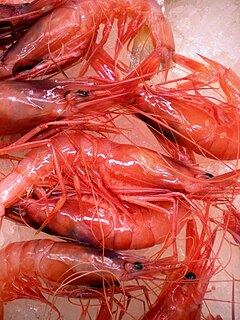
Aristeidae is a family of Dendrobranchiata decapod crustaceans known as deep-sea shrimps, gamba prawns or gamba shrimps. Some species are subject to commercial fisheries.

Solenoceridae is a family of decapods, containing 10 genera. They are marine, inhabiting shallow and offshore waters from the mid-continental shelf, ranging from depths to 1000 meters deep, and are sometimes confused with other commercial shrimp species.
Acanthephyra is a genus of shrimp in the family Acanthephyridae, with species that live at depths from 0 to more than 5000 meters deep below the ocean surface.
Bairdemys is an extinct genus of side-necked turtles in the family Podocnemididae. The genus existed from the Late Oligocene to Late Miocene and its fossils have been found in South Carolina, Puerto Rico, Panama and Venezuela. The genus was described in 2002 by Gaffney & Wood and the type species is B. hartsteini.














