Related Research Articles

The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Yareta or llareta is a velvety, chartreuse cushion plant in the family Apiaceae which is native to South America. It grows in the Puna grasslands of the Andes in Peru, Bolivia, northern Chile and western Argentina at altitudes between 3,200 and 5,250 metres.

Pterobranchia is a class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are Rhabdopleura, Cephalodiscus, and Atubaria. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period.
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons.
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It lies caudal to the substantia nigra and adjacent to the superior cerebellar peduncle. It has two divisions of subnuclei; the pars compacta containing mainly cholinergic neurons, and the pars dissipata containing mainly glutamatergic neurons and some non-cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine nucleus is one of the main components of the reticular activating system. It was first described in 1909 by Louis Jacobsohn-Lask, a German neuroanatomist.

Impact is a sans-serif typeface in the industrial or grotesk style designed by Geoffrey Lee in 1965 and released by the Stephenson Blake foundry of Sheffield. It is well known for having been included in the core fonts for the Web package and distributed with Microsoft Windows since Windows 98. In the 2010s, it gained popularity for its use in image macros and other internet memes.
The pars compacta (SNpc) is one of two subdivisions of the substantia nigra of the midbrain ; it is situated medial to the pars reticulata. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons. It projects to the striatum and portions of the cerebral cortex. It is functionally involved in fine motor control.

Leptoxis compacta, the oblong rocksnail, is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Pleuroceridae.

Victaphanta compacta, common name the Otway black snail, is a species of carnivorous air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Rhytididae. The Otway Black Snail Victaphanta compacta is only found in cool temperate rainforests in the Otway Ranges, Victoria, Australia. It is one of four species of the carnivorous land snails in the genus Victaphanta and is endemic to the Otway Ranges.

Ayenia compacta is a species of shrub in the mallow family known by the common name California ayenia.
Compacta is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. The genus was erected by Hans Georg Amsel in 1956.
Compacta, a Latin adjective for compact, may refer to:

Compacta is a condensed sans-serif typeface designed by Fred Lambert for Letraset in 1963. It is visually similar to the typefaces Impact and Haettenschweiler, though Compacta has a distinctively square shape in comparison. Letraset was a dry transfer system, widely used by amateur or small-scale lettering projects, although many professional designers used it as well. Compacta was Letraset's first original typeface design, and proved widely popular. Rights to it were acquired by Linotype and others, leading to it becoming available in other formats such as digitally.
P. compacta may refer to:
In mathematics, the Farrell–Markushevich theorem, proved independently by O. J. Farrell (1899–1981) and A. I. Markushevich (1908–1979) in 1934, is a result concerning the approximation in mean square of holomorphic functions on a bounded open set in the complex plane by complex polynomials. It states that complex polynomials form a dense subspace of the Bergman space of a domain bounded by a simple closed Jordan curve. The Gram–Schmidt process can be used to construct an orthonormal basis in the Bergman space and hence an explicit form of the Bergman kernel, which in turn yields an explicit Riemann mapping function for the domain.
Cyclophora compacta is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found on the Kei Islands and in New Guinea and Queensland.

Pterolophia is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
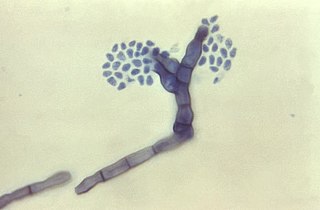
Fonsecaea compacta is a saprophytic fungal species found in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It is a rare etiological agent of chromoblastomycosis, with low rates of correspondence observed from reports. The main active components of F. compacta are glycolipids, yet very little is known about its composition. F. compacta is widely regarded as a dysplastic variety of Fonsecaea pedrosoi, its morphological precursor. The genus Fonsecaea presently contains two species, F. pedrosoi and F. compacta. Over 100 strains of F. pedrosoi have been isolated but only two of F. compacta.

Cuscuta compacta, the compact dodder, is a parasitic plant that specializes on woody plants. This species is distributed across the Eastern and Midwestern USA, Eastern Canada, and Mexico.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Pterolophia compacta. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.