
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country in Mainland Southeast Asia, and has a population of about 54 million as of 2017. Myanmar is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (Rangoon).

Cymbopogon, also known as lemongrass, barbed wire grass, silky heads, Cochin grass, Malabar grass, oily heads, citronella grass or fever grass, is a genus of Asian, African, Australian, and tropical island plants in the grass family. Some species are commonly cultivated as culinary and medicinal herbs because of their scent, resembling that of lemons . The name cymbopogon derives from the Greek words kymbe and pogon "which mean [that] in most species, the hairy spikelets project from boat-shaped spathes." Lemongrass and its oil are believed to possess therapeutic properties.

The Burmese python is one of the largest species of snakes. It is native to a large area of Southeast Asia and is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Until 2009, it was considered a subspecies of Python molurus, but is now recognized as a distinct species. It is an invasive species in Florida as a result of the pet trade.

Rhopalosomatidae is a family of Hymenoptera containing about 68 extant species in four genera that are found worldwide. Three fossil genera are known.

Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, or biting midges, generally 1–3 millimetres in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic.

Ripiphoridae is a cosmopolitan family of some 450 described species of beetles sometimes called "wedge-shaped beetles". Ripiphoridae are unusual among beetle families in that many species are hypermetamorphic parasitoids, an attribute that they share with the Meloidae. Members of the family differ in their choice of hosts, but most attack various species of bees or wasps, while some others attack cockroaches. Many species of Ripiphoridae have abbreviated elytra, and flabellate or pectinate antennae.

Tetrablemmidae, sometimes called armored spiders, is a family of tropical araneomorph spiders first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1873. It contains 126 described species in 29 genera from southeast Asia, with a few that occur in Africa and Central and South America. Pacullidae was incorporated into this family in 1981, but was later restored as a separate family in a 2016 phylogenetic study.

Archaeidae, also known as assassin spiders and pelican spiders, is a spider family with about ninety described species in five genera. It contains small spiders, ranging from 2 to 8 millimetres long, that prey exclusively on other spiders. They are unusual in that they have "necks", ranging from long and slender to short and fat. The name "pelican spider" refers to these elongated jaws and necks used to catch their prey. Living species of Archaeidae occur in South Africa, Madagascar and Australia, with the sister family Mecysmaucheniidae occurring in southern South America and New Zealand.

The Platycnemididae are a family of damselflies. They are known commonly as white-legged damselflies. There are over 400 species native to the Old World. The family is divided into several subfamilies.
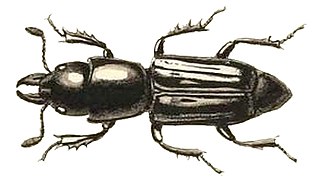
Syntelia is a genus of middle-sized beetles described by John O. Westwood in 1864. It is the only genus in the family Synteliidae erected by George Lewis in 1882.

Lepicerus is a genus of myxophagan beetles containing three described species in the family Lepiceridae; it is the only extant genus in the family, with another genus, Lepiceratus only known from fossils. Extant species occur in the Neotropics, from Mexico south to Venezuela and Ecuador. Fossils referrable to the genus are known from the early Late Cretaceous of Southeast Asia.

Kateretidae is a family of short-winged flower beetles in the suborder Polyphaga. There are about 11 genera and at least 40 described species in Kateretidae. They are found worldwide except in New Zealand. Adults are anthophagous, feeding on flowers, while the larvae are spermatophagous inside the flower corolla.
Ironomyiidae is a small family of flies in the order Diptera. Historically, they had been included in the family Platypezidae, and includes three extant species within the single extant genus Ironomyia endemic to Australia and a number of extinct fossil genera from North America and Asia extending back to the Early Cretaceous.

Eucnemidae, or false click beetles, are a family of polyphagan beetles including about 1700 species distributed worldwide.
Crocidura cranbrooki is a species of shrew from Northern Myanmar.

Burmese amber, also known as Burmite or Kachin amber, is amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar. The amber is dated to around 100 million years ago, during the latest Albian to earliest Cenomanian ages of the mid-Cretaceous period. The amber is of significant palaeontological interest due to the diversity of flora and fauna contained as inclusions, particularly arthropods including insects and arachnids but also birds, lizards, snakes, frogs and fragmentary dinosaur remains. The amber has been known and commercially exploited since the first century AD, and has been known to science since the mid-nineteenth century. Research on the deposit has attracted controversy due to its alleged role in funding internal conflict in Myanmar and hazardous working conditions in the mines where it is collected.
The Amphipithecidae were simian primates that lived in Late Eocene and Early Oligocene. Fossils have been found in Myanmar, Thailand, and Pakistan. The limited fossil evidence is consistent with, but not exclusive to, arboreal quadrupedalism. In other words, the species may have moved about in trees on four legs, but not with regular leaping as seen in later simians.

Throscidae is a family of small false click beetles in the order Coleoptera. In North America, there are 3 genera and 20 described species.

Cyclaxyridae are a family of beetles in the superfamily Cucujoidea. The only living genus is Cyclaxyra, with two species endemic to New Zealand. Other species have been named from fossils. They are also known as sooty mould beetles due to the association of Cyclaxyra with sooty mould. The extant species are mycophagous, feeding on spores, conidia, and hyphae.
Valeseguyidae is a family of flies, belonging to Scatopsoidea. It contains only one known extant species, Valeseguya rieki, known from a single male specimen found in Victoria, Australia, described in 1990. It was initially classified as a member of the wood gnat family Mycetobiidae, but was later given its own family in 2006. Two fossil species are known, including another species of Valeseguya, V. disjuncta, which is known from Miocene aged Dominican amber from the Caribbean, and Cretoseguya, containing the single species C. burmitica, which is known from the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber of Myanmar, dating to around 100 million years ago.















