Related Research Articles

CountryLink was a passenger rail and road service brand that operated in regional areas of New South Wales, and to and from Canberra, Brisbane and Melbourne. Originally created as a business unit of the State Rail Authority of New South Wales, it later became a subsidiary of RailCorp. CountryLink operated rail services using XPT and Xplorer rolling stock, with connecting coach services operated under contract by private operators.
Traffic signal preemption is a system that allows an operator to override the normal operation of traffic lights. The most common use of these systems manipulates traffic signals in the path of an emergency vehicle, halting conflicting traffic and allowing the emergency vehicle right-of-way, thereby reducing response times and enhancing traffic safety. Signal preemption can also be used on tram, light-rail and bus rapid transit systems, to allow public transportation priority access through intersections, and by railroad systems at crossings to prevent collisions.
The Sydney Coordinated Adaptive Traffic System, abbreviated SCATS, is an intelligent transportation system that manages the dynamic timing of signal phases at traffic signals, meaning that it tries to find the best phasing for a traffic situation. SCATS is based on the automatic plan selection from a library in response to the data derived from loop detectors or other road traffic sensors.
NightRide is a network of bus routes in operation between midnight and 4.30am in Sydney, Australia. The sixteen routes are run by bus operators as listed below and allow for a nightly shutdown of the Sydney Trains commuter rail network. The NightRide network was established in mid-1989 as low-patronage late-night train services were progressively withdrawn. Services follow major roads, and some stops are some distance from the railway stations they replace. In addition, some routes serve stations on multiple railway lines. In the city, most services depart from George Street, above Town Hall station.

Albury Airport is a regional airport located 2 nautical miles northeast of Albury, New South Wales, Australia. The airport, which also serves Albury's adjacent twin city of Wodonga, Victoria, was the fifth busiest in New South Wales as of 2016–17, handling 257,769 passengers. However, like most Australian airports, the impacts of travel restrictions and state border closures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a significant reduction in revenue passengers. ABX handled 107,934 passengers in the 2021–22 financial year and was the 32nd busiest airport in Australia. In addition to regular public transport flights, Albury airport handles a relatively large number of charter, freight, agricultural, and general aviation aircraft movements and hosts the official weather station for Albury–Wodonga.

Albury railway station is a heritage-listed railway station at Railway Place, Albury, New South Wales, Australia, adjacent to the border with Victoria, in Australia. It was designed under the direction of John Whitton and built from 1880 to 1881. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register in 1999.

A passenger information system, or passenger information display system, is an automated system for supplying users of public transport with information about the nature and the state of a public transport service through visual, voice or other media. It is also known as a customer information system or an operational information system. Among the information provided by such systems, a distinction can be drawn between:
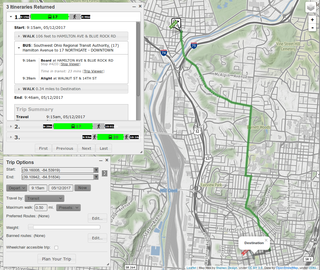
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialized search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimized on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained, for example, to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, which is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as cycling, driving, or walking, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or journey planning, in contrast, would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimize it so as to minimize the waiting time incurred for each leg. In European Standards such as Transmodel, trip planning is used specifically to describe the planning of a route for a passenger, to avoid confusion with the completely separate process of planning the operational journeys to be made by public transport vehicles on which such trips are made.
The Sydney–Melbourne rail corridor is an approximately 953-kilometre (592 mi) standard gauge railway corridor that runs between Melbourne (Victoria) and Sydney, the two largest cities in Australia. Freight and passenger services operate along the route, such as the NSW TrainLink XPT passenger service. The XPT offers a day and night service in each direction.

Busabout Wagga Wagga, formerly Fearnes Coaches, is an Australian bus company with depots in Wagga Wagga and Harden, New South Wales.

iBus is an Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) system to improve London's buses using technology installed by Siemens. The system tracks all London's buses, providing passengers with audio-visual announcements and improved information on bus arrivals, with plans to trigger priority at traffic lights.
Cycling in the Australian state of New South Wales is a common form of recreation. In 2009, cycling was the fifth-most popular sports/physical activity in NSW.

Sydney bus route 190X is a peak-hour express bus service operated by Keolis Downer Northern Beaches between Avalon and Wynyard station. The route and its predecessors are well known for its ocean scenery along the journey and have been popular with hikers planning to walk from Palm Beach back towards Sydney. For many years the route was also the longest commuter bus route in metropolitan Sydney at 42 kilometres (26 mi) when operating from Palm Beach. In March 2013 Australian diecast model company Transit Graphics released a 1:76 scale model of a Mercedes-Benz O305 bus operating on route L90.
Moovit is an Israel-based mobility as a service provider and journey planner app. It has been owned by Intel through the Israeli subsidiary Mobileye since 2020. Moovit uses both crowdsourced and official public transit data to provide route planning to users as well as transit data APIs to transit companies, cities, and transit agencies. Because Moovit integrates crowdsourced data, it can provide transit information for areas where no data is officially available.

NSW TrainLink is a train and coach operator in Australia, providing services throughout New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, along with limited interstate services into Victoria, Queensland and South Australia. Its primary intercity and regional services are spread throughout five major rail lines, operating out of Sydney's Central railway station.

Premier Transport Group is an Australian operator of bus and coach services in New South Wales and Queensland. Its origins can be traced back to December 1987 when John King purchased Nowra Coaches. It has since expanded through a number of acquisitions.
Sydney, Australia is served by a number of bus operators, with Busways the largest privately owned operator in New South Wales as of January 2022 when the company took-over the NSW government's State Transit Authority. Other major operators include CDC, Transdev and Transit Systems. Most services are provided as part of the city's integrated public transport system, with routes, fares, service levels, fleet specifications and customer service standards determined by Transport for NSW. A small number of services operate outside of this network.
BRIDJ is a SaaS platform designed to support ‘demand responsive’ or ‘on demand’ public transport providers. The platform allows a user to optimise an on-road service and digitise work processes, and includes an optimisation engine, traveller app, driver app and client portal. The traveller app allows passengers to book, pay and track a service between two locations within a service area. The optimisation engine consumes pre-planned and real-time bookings and then allocates passengers to the available vehicles to create the optimal trips for the given service objectives. The optimisation engine is designed to handle large numbers of passengers and vehicles of both small capacities and high capacity (6-50+). BRIDJ technology is currently deployed on public transport services in both Sydney and Adelaide, Australia and for transfer services Singapore.
Bustimes.org is a transportation information website created to take advantage of Bus Services Act 2017 requirement for bus operators in England to provide bus timetables, fares and vehicle locations in an open data format, which can be utilised by app and website developers. This DfT service is called the Bus Open Data Service.

U-Go Mobility is a bus company in Sydney, Australia, that operates services in Region 10, which serves South Western Sydney, and Sutherland Shire. It is a 50:50 joint venture between UGL and Go-Ahead Group.
References
- Sample of Realtime Data Government of New South Wales
- Contract ID: PTIPS Roads & Traffic Authority Retrieved on 16 April 2007.
- Priority bus green lights scrapped Sydney Morning Herald Retrieved on 16 April 2007.
- ↑ New apps with real time bus information Sydney Buses 18 December 2012
- ↑ PTIPS Electronic Bus Priority Trial in Sydney Smart Urban Transport
- ↑ NSW, Transport for (23 July 2020). "Real-time bus tracking new reality for regional NSW". www.transport.nsw.gov.au. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- ↑ Real-time trip updates and digital timetables for Albury, Greater Nowra and Tamworth Transport for NSW 29 March 2022