
Parkin is a 465-amino acid residue E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that in humans and mice is encoded by the PARK2 gene. Parkin plays a critical role in ubiquitination – the process whereby molecules are covalently labelled with ubiquitin (Ub) and directed towards degradation in proteasomes or lysosomes. Ubiquitination involves the sequential action of three enzymes. First, an E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme binds to inactive Ub in eukaryotic cells via a thioester bond and mobilises it in an ATP-dependent process. Ub is then transferred to an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme before being conjugated to the target protein via an E3 ubiquitin ligase. There exists a multitude of E3 ligases, which differ in structure and substrate specificity to allow selective targeting of proteins to intracellular degradation.

ITCH is a HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligase that is ablated in non-agouti-lethal 18H mice. Itchy mice develop a severe immunological phenotype after birth that includes hyperplasia of lymphoid and hematopoietic cells, and stomach and lung inflammation. In humans ITCH deficiency causes altered physical growth, craniofacial morphology defects, defective muscle development, and aberrant immune system function. ITCH contains a C2 domain, proline-rich region, WW domains, HECT domain, and multiple amino acids that are phosphorylated and ubiquitinated.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4, also known as neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 4 is an enzyme that is, in humans, encoded by the NEDD4 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RING2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNF2 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2D2 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HUWE1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HUWE1 gene.
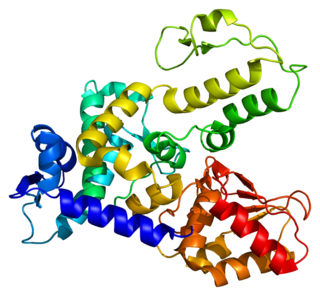
NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WWP1 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2D3 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMURF2 gene which is located at chromosome 17q23.3-q24.1.

Ubiquitin/ISG15-conjugating enzyme E2 L6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2L6 gene.

The human gene UBR1 encodes the enzyme ubiquitin-protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 1.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2C gene.

RING finger protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNF11 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM32 gene. Since its discovery in 1995, TRIM32 has been shown to be implicated in a number of diverse biological pathways.
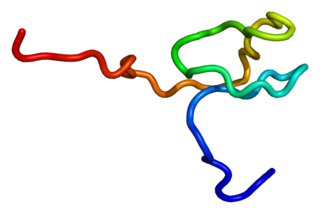
RanBP-type and C3HC4-type zinc finger-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBCK1 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UBR2 gene.

Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3C is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UBE3C gene.

Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (MUL1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MUL1 gene on chromosome 1. This enzyme localizes to the outer mitochondrial membrane, where it regulates mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis through multiple pathways, including the Akt, JNK, and NF-κB. Its proapoptotic function thus implicates it in cancer and Parkinson’s disease.

HECT domain and ankyrin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HACE1 gene.
Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) is a multi-protein complex and the only known E3 ubiquitin ligase able to conjugate ubiquitin in a head-to-tail manner to generate linear (M1-linked) polyubiquitin chains. The complex is currently known to be composed of three proteins: heme-oxidized IRP2 ubiquitin ligase 1 (HOIL-1), HOIL-1-interacting protein (HOIP), and Shank-associated RH domain-interacting protein (SHARPIN),,. HOIL-1 and HOIP are both E3 ubiquitin ligases, however, the specific linear ubiquitin-ligating activity is enacted by HOIP. Mice deficient in HOIP are embryonically lethal. Two cases of mutated HOIP have been detected in humans. These patients presented with autoinflammation and immunodeficiency,. HOIL-1 is required for LUBAC assembly and stability as demonstrated by embryonic lethality in HOIL-1 deficient mice. Recently, it has been noted, that HOIL-1 is also able to catalyze formation of oxyester bonds between the C-terminus of ubiquitin and serine/threonine of substrate protein in TLR signaling. SHARPIN exhibits a significant sequence similarity to HOIL-1 and is important for LUBAC stability. Spontaneous point mutation in the Sharpin gene in mice leads to development of chronic proliferative dermatitis (cpdm),. Both HOIL-1 and SHARPIN bind to HOIP through their ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain,. LUBAC consisting of either HOIP-HOIL-1 or HOIP-SHARPIN is functional in vitro, however the greatest activity of the complex has been observed in the presence of all three components.





















