Related Research Articles
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide.

Radium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rather than oxygen) upon exposure to air, forming a black surface layer of radium nitride (Ra3N2). All isotopes of radium are radioactive, the most stable isotope being radium-226 with a half-life of 1,600 years. When radium decays, it emits ionizing radiation as a by-product, which can excite fluorescent chemicals and cause radioluminescence.

The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.
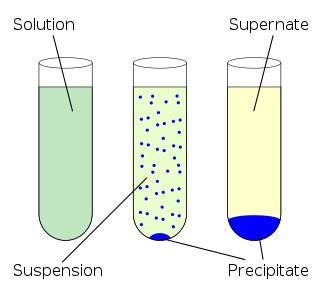
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a supersaturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant.

Radium chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula RaCl2. It is a radium salt of hydrogen chloride. It was the first radium compound isolated in a pure state. Marie Curie and André-Louis Debierne used it in their original separation of radium from barium. The first preparation of radium metal was by the electrolysis of a solution of this salt using a mercury cathode.

Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (x = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O.

Silver is a relatively unreactive metal, although it can form several compounds. The common oxidation states of silver are (in order of commonness): +1 (the most stable state; for example, silver nitrate, AgNO3); +2 (highly oxidising; for example, silver(II) fluoride, AgF2); and even very rarely +3 (extreme oxidising; for example, potassium tetrafluoroargentate(III), KAgF4). The +3 state requires very strong oxidising agents to attain, such as fluorine or peroxodisulfate, and some silver(III) compounds react with atmospheric moisture and attack glass. Indeed, silver(III) fluoride is usually obtained by reacting silver or silver monofluoride with the strongest known oxidizing agent, krypton difluoride.

Radium bromide is the bromide salt of radium, with the formula RaBr2. It is produced during the process of separating radium from uranium ore. This inorganic compound was discovered by Pierre and Marie Curie in 1898, and the discovery sparked a huge interest in radiochemistry and radiotherapy. Since elemental radium oxidizes readily in air and water, radium salts are the preferred chemical form of radium to work with. Even though it is more stable than elemental radium, radium bromide is still extremely toxic, and can explode under certain conditions.

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. It is ionic and hygroscopic in nature.

Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes.

Compounds of lead exist with lead in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.

Actinide chemistry is one of the main branches of nuclear chemistry that investigates the processes and molecular systems of the actinides. The actinides derive their name from the group 3 element actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide. All but one of the actinides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 5f electron shell; lawrencium, a d-block element, is also generally considered an actinide. In comparison with the lanthanides, also mostly f-block elements, the actinides show much more variable valence. The actinide series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.
Radium carbonate is a compound of radium, carbon, and oxygen. This salt is a highly radioactive, amorphous, white powder that has potential applications in medicine. It is notable for forming disordered crystals at room temperature and for being approximately 10 times more soluble than the corresponding barium carbonate - witherite. Radium carbonate is one of a few radium compounds which has significantly different properties from corresponding barium compounds. Moreover, radium is the only alkaline-earth metal which forms disordered crystals in its carbonate phase. Even though radium carbonate has very low solubility in water, it is soluble in dilute mineral acids and concentrated ammonium carbonate.
Radium nitrate is a radioactive salt with the formula Ra(NO3)2. It is a white solid, but old samples appear yellowish-grey. It has a lower solubility than barium nitrate. It decomposes at 280 °C to radium oxide.
Francium compounds are compounds containing the element francium (Fr). Due to francium being very unstable, its salts are only known to a small extent. Francium coprecipitates with several caesium salts, such as caesium perchlorate, which results in small amounts of francium perchlorate. This coprecipitation can be used to isolate francium, by adapting the radiocaesium coprecipitation method of Lawrence E. Glendenin and C. M. Nelson. It will additionally coprecipitate with many other caesium salts, including the iodate, the picrate, the tartrate, the chloroplatinate, and the silicotungstate. It also coprecipitates with silicotungstic acid, and with perchloric acid, without another alkali metal as a carrier, which leads to other methods of separation.
References
- ↑ Kirby et al., p. 4
- ↑ Kirby et al., p. 8
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kirby et al., pp. 4–8
- ↑ US 1655184, Hahn, Otto,"Radium preparation and process of making same",published 1928-01-03
- ↑ Kirby et al., pp. 8–9
- ↑ Kirby et al., p. 12
- ↑ Keller, Cornelius; Wolf, Walter; Shani, Jashovam. "Radionuclides, 2. Radioactive Elements and Artificial Radionuclides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 97–98. doi:10.1002/14356007.o22_o15. ISBN 978-3527306732.