Related Research Articles
The MAPK/ERK pathway is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell.

RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase, also known as proto-oncogene c-RAF or simply c-Raf or even Raf-1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RAF1 gene. The c-Raf protein is part of the ERK1/2 pathway as a MAP kinase (MAP3K) that functions downstream of the Ras subfamily of membrane associated GTPases. C-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases, from the TKL (Tyrosine-kinase-like) group of kinases.

Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-R) are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family. PDGF subunits -A and -B are important factors regulating cell proliferation, cellular differentiation, cell growth, development and many diseases including cancer. There are two forms of the PDGF-R, alpha and beta each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor is bound, PDGF-R homo- or heterodimerizes.
In cell signalling, Son of Sevenless (SOS) refers to a set of genes encoding guanine nucleotide exchange factors that act on the Ras subfamily of small GTPases.

Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase.
Zalutumumab is a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed towards the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). It is a product developed by Genmab in Utrecht, the Netherlands. Specifically, zalutumumab is designed for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN), a type of cancer.
Rap GTP-binding protein also known as Ras-related proteins or simply RAP is a type of small GTPase, similar in structure to Ras.

BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf.

ETS Like-1 protein Elk-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELK1. Elk-1 functions as a transcription activator. It is classified as a ternary complex factor (TCF), a subclass of the ETS family, which is characterized by a common protein domain that regulates DNA binding to target sequences. Elk1 plays important roles in various contexts, including long-term memory formation, drug addiction, Alzheimer's disease, Down syndrome, breast cancer, and depression.

Ras-related protein Rap-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAP1A gene.
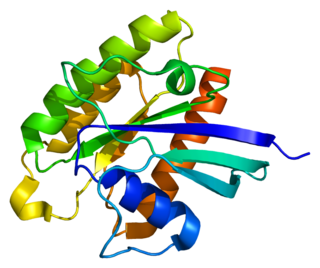
RHEB also known as Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB) is a GTP-binding protein that is ubiquitously expressed in humans and other mammals. The protein is largely involved in the mTOR pathway and the regulation of the cell cycle.

Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) are protein structural domains or the proteins that contain these domains, that function to activate the GTPase activity of heterotrimeric G-protein α-subunits.

Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) also known as p195 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that in humans is encoded by the IQGAP1 gene. IQGAP1 is a scaffold protein involved in regulating various cellular processes ranging from organization of the actin cytoskeleton, transcription, and cellular adhesion to regulating the cell cycle.

Ras-related protein R-Ras is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RRAS gene.
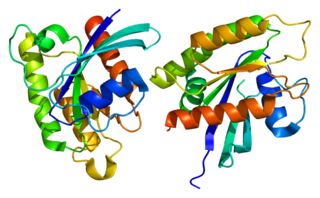
Ras-related protein R-Ras2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RRAS2 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS12 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS14 gene.

Connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of ras 2, also known as CNK homolog protein 2 (CNK2) or MAGUIN, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CNKSR2 gene.

GoLoco motif is a protein structural motif. In heterotrimeric G-protein signalling, cell surface receptors (GPCRs) are coupled to membrane-associated heterotrimers comprising a GTP-hydrolyzing subunit G-alpha and a G-beta/G-gamma dimer. The inactive form contains the alpha subunit bound to GDP and complexes with the beta and gamma subunit. When the ligand is associated to the receptor, GDP is displaced from G-alpha and GTP is bound. The GTP/G-alpha complex dissociates from the trimer and associates to an effector until the intrinsic GTPase activity of G-alpha returns the protein to GDP bound form. Reassociation of GDP-bound G-alpha with G-beta/G-gamma dimer terminates the signal. Several mechanisms regulate the signal output at different stage of the G-protein cascade. Two classes of intracellular proteins act as inhibitors of G protein activation: GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), which enhance GTP hydrolysis, and guanine dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which inhibit GDP dissociation. The GoLoco or G-protein regulatory (GPR) motif found in various G-protein regulators. acts as a GDI on G-alpha(i).

Ras association domain-containing protein 9 (RASSF9), also known as PAM COOH-terminal interactor protein 1 (PCIP1) or peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase COOH-terminal interactor (PAMCI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASSF9 gene.
References
- ↑ Ponting CP (October 1999). "Raf-like Ras/Rap-binding domains in RGS12- and still-life-like signalling proteins". Journal of Molecular Medicine. 77 (10): 695–8. doi:10.1007/s001099900054. PMID 10606204. S2CID 22667367.