
The cutlassfishes are about 45 species of predatory ray-finned fish in the family Trichiuridae of the order Scombriformes found in seas throughout the world. Fish of this family are long, slender, and generally steely blue or silver in colour, giving rise to their name. They have reduced or absent pelvic and caudal fins, giving them an eel-like appearance, and large fang-like teeth.
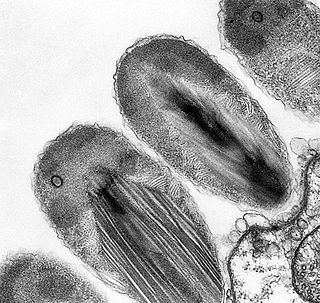
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes from genus Xiphinema, residing in their gametes. The verrucomicrobial bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila is a human intestinal symbiotic bacterium that is considered as a promising probiotic.
Quadrigyridae is the only family within Gyracanthocephala, an order of parasitic worms of class Eoacanthocephala. This family contains two subfamilies, ten genera and about 92 species.
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
Centrorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms. Three species of these thorny-headed worms in the genus Centrorhynchus were found to parasitize birds of prey and owls Slovakia. These hosts include Buteo buteo, Buteo rufinus, Falco tinnunculus, Asio otus, Strix aluco, Strix uralensis and Tyto alba.

Pomphorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Leptorhynchoididae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.
Propalticidae is a family of beetles, in the suborder Polyphaga. It contains two genera with the following species:

Silvanidae, "silvan flat bark beetles", is a family of beetles in the superfamily Cucujoidea, consisting of 68 described genera and about 500 described species. The family is represented on all continents except Antarctica, and is most diverse at both the generic and species levels in the Old World tropics.

Neoechinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Neoechinorhynchida.

Rhadinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Wanda Wesołowska is a Polish zoologist known for her work with jumping spiders. She has described more species of jumping spider than any contemporary writer, and is second only to Eugène Simon in the history of arachnology. Originally a student of ornithology, she developed an interest in jumping spiders while still a student at the Siedlce University of Natural Sciences and Humanities in the 1970s.

Helicometra is a genus of trematodes in the class Opecoelidae. It is synonymous with AllostenoperaBaeva, 1968, MetahelicometraYamaguti, 1971, and StenoperaManter, 1933. Its type species is H. fasciata(Rudolphi, 1819). They are distinguished by their unique spiral uterus, from which their name is derived.
Lobotrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on fish. The type-species is Lobotrema madrasiTripathi, 1959.
Paradiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on marine perciform fishes of the family Sillaginidae.
Acanthogyrus is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Quadrigyridae. The species of this genus are found in Africa.
Cleaveius is a genus of worms belonging to the family Rhadinorhynchidae.
Isthomosacanthidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed worms.

Neoechinorhynchus is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Neoechinorhynchidae.
Halopseudomonas is a genus of pseudomonad bacteria.








