This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(February 2026) |
| Redlichia takooensis | |
|---|---|
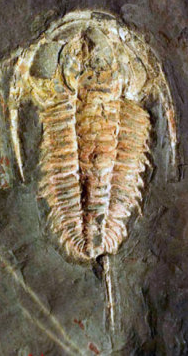 | |
| Redlichia takooensis (Lower Cambrian Emu Shale, Kangaroo Island, South Australia) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Clade: | † Artiopoda |
| Class: | † Trilobita |
| Order: | † Redlichiida |
| Family: | † Redlichiidae |
| Genus: | † Redlichia |
| Species: | †R. takooensis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Redlichia takooensis (Lu, 1950) | |
Redlichia takooensis is a species of redlichiid trilobite from the lower Cambrian-aged Emu Shale of Kangaroo Island, Australia.