
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae, are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places. In southern Africa the genus Palystes are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related.

Philodromidae, also known as philodromid crab spiders and running crab spiders, is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Tord Tamerlan Teodor Thorell in 1870. It contains over 600 species in thirty genera. Most are dull colored- brown, gray, yellowish or mottled with a leaf-like cardiac mark on the anterior dorsal abdomen, and seldom reach above 10 millimetres (0.39 in) long. None of the species build webs, but they do use silk for draglines and egg sacs.

Sphaeroceridae are a family of true flies in the order Diptera, often called small dung flies, lesser dung flies or lesser corpse flies due to their saprophagous habits. They belong to the typical fly suborder Brachycera as can be seen by their short antennae, and more precisely they are members of the section Schizophora. There are over 1,300 species and about 125 genera accepted as valid today, but new taxa are still being described.
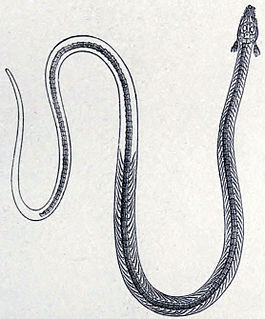
Phlegethontia is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibian from the Carboniferous and Permian periods of Europe and North America.

Menemerus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1868. They are 4 to 10 millimetres long, flattened in shape, and very hairy, usually with brown and grayish hairs. Most species have white edges on the thorax. The abdomen is often oval, or sometimes elongated or rounded.

The Celyphidae, commonly known as beetle flies or beetle-backed flies, are a family of flies. About 115 species in about 9 genera are known chiefly from the Oriental and Afrotropic biogeographic regions with one lineage in the New World.

Hydrophorus is a genus of flies in the family Dolichopodidae.

Idiops is a genus of armored trapdoor spiders that was first described by Josef Anton Maximilian Perty in 1833. It is the type genus of the spurred trapdoor spiders, Idiopidae. Idiops is also the most species-rich genus of the family, and is found at widely separated locations in the Neotropics, Afrotropics, Indomalaya and the Middle East. Females live in tubular burrows lined with a thick layer of white silk. These typically have a D-shaped lid that fits into the entrance like a cork, and some burrows have two entrances. The lid may consist of mud, moss or lichen, which is bound below by a thick layer of silk. As in all genera of this family, the anterior lateral eyes (ALE) are situated near the clypeal margin, far in front of the remaining six eyes, which are arranged in a tight group. The males which are smaller in size, wander about or occasionally live in burrows. Like other mygalomorphs, they are relatively large and long-lived. Forest clearance and agricultural practices that loosen the soil and enhance erosion, besides soil removal for brick making have been pointed out as serious threats to some Indian species. Species ranges are poorly known – in India for instance, most species are known only from their type localities.

Epicauta is a genus of beetles in the blister beetle family, Meloidae. The genus was first scientifically described in 1834 by Pierre François Marie Auguste Dejean. Epicauta is distributed nearly worldwide, with species native to all continents except Australia and Antarctica. Surveys have found the genus to be particularly diverse in northern Arizona in the United States. Few species occur in the Arctic, with none farther north than the southern Northwest Territory of Canada.

The Sepidiini is a tribe of ground-dwelling darkling beetles (Tenebrionidae), that occurs across Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Arabian Peninsula and Mesopotamia. It is composed of many hundreds of species. The larvae of some species are known to damage crops.

Lytta is a genus of blister beetles in the family Meloidae. There are about 70 described species in North America, and over 100 species worldwide.

The Tok-tok beetles are ground-dwelling, Afrotropical beetles in the family Tenebrionidae. They are stout in shape and typically black or dark rufous in colour. They average about 2.6 cm in body length, but the Spindle toktokkie has an elongate body shape and measures 5.3 cm, while P. sulcicollis reaches 6 to 8 cm, and is the largest Tenebrionid in the world. Like the related genus Dichtha, the adults tap out a rhythm on the ground to attract and locate mates. Habitats are varied, from coastal forest to ridges, koppies, woodland and desert sand.

Trachelidae is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1897 as a subfamily called "Tracheleae". The Trachelidae family, also known as "ground sac spiders", is within the group of spiders known as the RTA clade, which includes mostly wandering spiders that do not use webs. Spiders in the Trachelidae family are characterized as being 3-10mm long and having a red cephalothorax and a yellow/tan abdomen. They are commonly found indoors. It was placed in the family Clubionidae, then later in Corinnidae when the Clubionidae were split up. The first study that suggested Trachelidae should be considered its own family was done by Deeleman-reinhold in 2001 as part of an analysis of RTA Clade spiders. An analysis by Martín J. Ramírez in 2014 suggested that it was not closely related to other members of the Corinnidae, and was better treated as a separate family. It was then placed in the CTC clade of spiders, or the Claw Tuft Clasper clade, which is a group of spiders that have two tarsal claws with tufts of hair.
Colaspoides is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Eumolpinae. It is one of the largest genera in the subfamily, containing over 100 species worldwide. It is an extant genus but there is at least one species, C. eocenicus, found in Baltic amber from the Upper Eocene of Russia, and the genus has also been reported from the Miocene of the Dominican Republic.

Renatiella reticulata is a species of diurnal, herbivorous beetle that is native to East and southern Africa. It has rather long legs, and is the most widespread, apomorphic and polytypic species of its genus.
Spintherophyta is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Eumolpinae. Most species in the genus are found in Central and South America, but there are also a few North American species.
Nerissus is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Eumolpinae. It is known from Africa.

Stenocara is a genus of darkling beetles which is native to southern Africa. Several species are endemic to Namibia.
Nycterodina is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Eumolpinae. It is known from South America.















