
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera, in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Some others also have unusual characteristics, such as fireflies, which use a light-emitting organ for mating and communication purposes.

Stag beetles are a family of about 1,200 species of beetles in the family Lucanidae, currently classified in four subfamilies. Some species grow to over 12 centimetres, but most to about 5 cm (2 in).

The Japanese beetle is a species of scarab beetle. Due to the presence of natural predators, the Japanese beetle is not considered a pest in its native Japan, but in North America and some regions of Europe, it is a noted pest to roughly 300 species of plants. Some of these plants include rose bushes, grapes, hops, canna, crape myrtles, birch trees, linden trees, and others.

The longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), also known as long-horned or longicorns, are a large family of beetles, with over 35,000 species described.

Harmonia axyridis is a large lady beetle or ladybug species that is most commonly known as the harlequin, Asian, or multicoloured Asian lady beetle. This is one of the most variable species in the world, with an exceptionally wide range of colour forms. It is native to eastern Asia, but has been artificially introduced to North America and Europe to control aphids and scale insects. It is now common, well known, and spreading in those regions, and has also established in Africa and widely across South America. This species is conspicuous in North America, where it may locally be known as the Halloween beetle, as it often invades homes during October to overwinter.

Dung beetles are beetles that feed on feces. Some species of dung beetles can bury dung 250 times their own mass in one night.

Histeridae is a family of beetles commonly known as clown beetles or hister beetles. This very diverse group of beetles contains 3,900 species found worldwide. They can be easily identified by their shortened elytra that leaves two of the seven tergites exposed, and their geniculate (elbowed) antennae with clubbed ends. These predatory feeders are most active at night and will fake death if they feel threatened. This family of beetles will occupy almost any kind of niche throughout the world. Hister beetles have proved useful during forensic investigations to help in time of death estimation. Also, certain species are used in the control of livestock pests that infest dung and to control houseflies. Because they are predacious and will even eat other hister beetles, they must be isolated when collected.

Dermestidae are a family of Coleoptera that are commonly referred to as skin beetles. Other common names include larder beetle, hide or leather beetles, carpet beetles, and khapra beetles. There are over 1,800 species described.

A bark beetle is the common name for the subfamily of beetles Scolytinae. Previously, this was considered a distinct family (Scolytidae), but is now understood to be a specialized clade of the "true weevil" family (Curculionidae). Although the term "bark beetle" refers to the fact that many species feed in the inner bark (phloem) layer of trees, the subfamily also has many species with other lifestyles, including some that bore into wood, feed in fruit and seeds, or tunnel into herbaceous plants. Well-known species are members of the type genus Scolytus, namely the European elm bark beetle S. multistriatus and the large elm bark beetle S. scolytus, which like the American elm bark beetle Hylurgopinus rufipes, transmit Dutch elm disease fungi (Ophiostoma). The mountain pine beetle Dendroctonus ponderosae, southern pine beetle Dendroctonus frontalis, and their near relatives are major pests of conifer forests in North America. A similarly aggressive species in Europe is the spruce ips Ips typographus. A tiny bark beetle, the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei is a major pest on coffee plantations around the world.
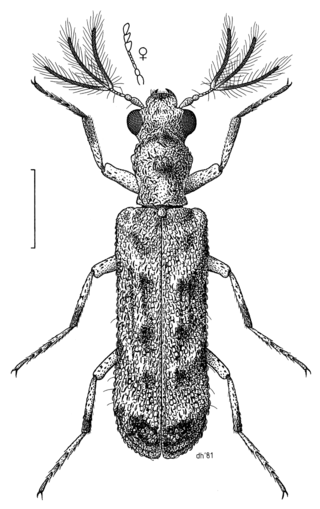
The Bostrichidae are a family of beetles with more than 700 described species. They are commonly called auger beetles, false powderpost beetles, or horned powderpost beetles. The head of most auger beetles cannot be seen from above, as it is downwardly directed and hidden by the thorax. Exceptions are the powderpost beetles, and members of the subfamily Psoinae.

Antonio Bertoloni was an Italian physician and botanist who made extensive studies of Italian plants. He also collected notable samples of Central American flora.

Ophrys bertolonii, commonly known as Bertoloni's bee orchid, is a species of orchid native to the western and central Mediterranean.
The basil-thyme case-bearer moth is a moth of the family Coleophoridae found in Europe. It was first described by the 6th Baron Walsingham in 1899.

Viola bertolonii is a species of violet known by the common name Bertoloni's pansy, belonging to the Violaceae family.

Sternocera orissa, the giant jewel beetle, is a species of beetles belonging to the Buprestidae family.
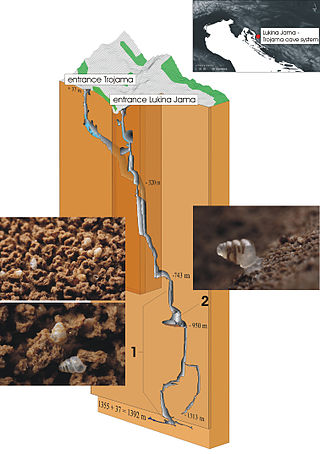
Biospeleology, also known as cave biology, is a branch of biology dedicated to the study of organisms that live in caves and are collectively referred to as troglofauna.

Rhamphorrhina splendens, commonly known as the regal fruit chafer, is a large beetle of the family Scarabaeidae which can grow to 30mm long.

Tragiscoschema is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:

Tragiscoschema bertolonii is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1857. It is known from Tanzania, South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe.
Rhamphorrhina is a genus of beetles belonging to the subfamily Cetoniinae.

















