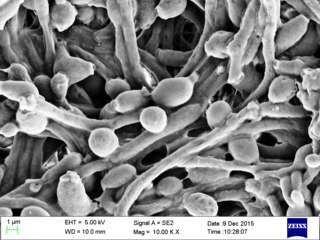
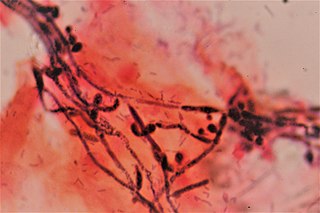
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood–brain barrier in mice.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeasts.

Oral candidiasis (Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis),which is also known as oral thrush, among other names, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis (yeast/fungal infection) of Candida species on the mucous membranes of the mouth.

The corpus albicans is the regressed form of the corpus luteum. As the corpus luteum is being broken down by macrophages, fibroblasts lay down type I collagen, forming the corpus albicans. This process is called "luteolysis". The remains of the corpus albicans may persist as a scar on the surface of the ovary.

A chlamydospore is the thick-walled large resting spore of several kinds of fungi, including Ascomycota such as Candida, Basidiomycota such as Panus, and various Mortierellales species. It is the life-stage which survives in unfavourable conditions, such as dry or hot seasons. Fusarium oxysporum which causes the plant disease Fusarium wilt is one which forms chlamydospores in response to stresses like nutrient depletion. Mycelia of the pathogen can survive in this manner and germinate in favorable conditions.

Iris albicans, also known as the cemetery iris, white cemetery iris, or the white flag iris, is a species of iris which was planted on graves in Muslim regions and grows in many countries throughout the Middle East and northern Africa. It was later introduced to Spain, and then other European countries. It is a natural hybrid.

A dimorphic fungus is a fungus that can exist in the form of both mold and yeast. As this is usually brought about by a change in temperature, this fungus type is also described as a thermally dimorphic fungus. An example is Talaromyces marneffei, a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature.
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.

Rhaphiptera is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Rhaphiptera candicans is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Gounelle in 1908. It is known from Brazil.
Rhaphiptera gahani is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Gounelle in 1908. It is known from Brazil.
Rhaphiptera rixator is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1868. It is known from French Guiana and Brazil.
Rhaphiptera scrutator is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1868. It is known from Peru, Panama and French Guiana.
Rhaphiptera melzeri is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by S. A. Fragoso and Miguel A. Monné in 1984. It is known from Brazil.
Rhaphiptera apeara is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 2011.
Rhaphiptera avicenniae is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Dalens and Tavakilian in 2007. It is known from French Guiana and Brazil.
Rhaphiptera boliviana is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 2007. It is known from Bolivia.
Rhaphiptera durantoni is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Tavakilian and Touroult in 2007. It is known from French Guiana.
Rhaphiptera elegans is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1961. It is known from Brazil.
Rhaphiptera lavaissierorum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Dalens and Tavakilian in 2007. It is known from French Guiana.








