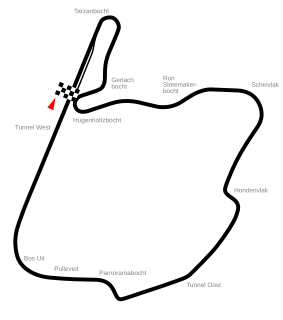
The 1984 Dutch Grand Prix was a Formula One motor race held at Zandvoort on 26 August 1984. It was the thirteenth race of the 1984 Formula One World Championship.

Acronicta is a genus of noctuid moths containing about 150 species distributed mainly in the temperate Holarctic, with some in adjacent subtropical regions. The genus was erected by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. Caterpillars of most Acronicta species are unmistakable, with brightly colored hairy spikes, and often feed quite visibly on common foliate trees. The hairy spikes may contain poison, which cause itchy, painful, swollen rash in humans on contact. The larva of the smeared dagger moth is unusually hairy even for this genus. Acronicta species are generally known as dagger moths, as most have one or more black dagger-shaped markings on their forewing uppersides. But some species have a conspicuous dark ring marking instead.

Crambinae is a large subfamily of the lepidopteran family Crambidae, the crambid snout moths. It currently includes over 1,800 species worldwide. The larvae are root feeders or stem borers, mostly on grasses. A few species are pests of sod grasses, maize, sugar cane, rice, and other Poaceae. The monophyly of this group is supported by the structure of the tympanal organs and the phallus attached medially to the juxta.
Burtia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1866.

Carathis is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1866.

Grammia is a genus of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was described by Rambur in 1866.

Robinsonia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1866.

Virbia is a genus of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Pyrausta is a speciose genus of moths of the family Crambidae. The genus was erected by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1802.

Gabara is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1866.

Heliomata is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae.
Drasteria pallescens, the cowhead arches, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote and Coleman Townsend Robinson in 1866. It is found in North America from Alberta and Saskatchewan south to Texas and Baja California.

Datana is a genus of moths of the family Notodontidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1855.

Euteliidae is a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family was erected by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1882.
Harriet Grote (1792–1878) was an English biographer. As the wife of George Grote, she played host to the English philosophical radicals of the earlier 19th century.
The Grote Chair of the Philosophy of Mind and Logic is an endowed chair at University College London's Department of Philosophy.

The Chrysauginae are a subfamily of snout moths. They are primarily Neotropical and include about 400 described species.

The Epipaschiinae are a subfamily of snout moths. Almost 600 species are known today, which are found mainly in the tropics and subtropics. Some occur in temperate regions, but the subfamily is apparently completely absent from Europe, at least as native species. A few Epipaschiinae are crop pests that may occasionally become economically significant.
Robinsonia is the scientific name of two genera of organisms and may refer to:














