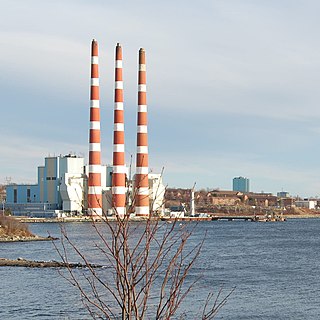A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a Combined Cycle Gas Turbine (CCGT) plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs.
Puget Sound Energy (PSE) is a Washington state energy utility providing electrical power and natural gas primarily in the Puget Sound region of the northwest United States. The utility serves electricity to more than 1.1 million customers in Island, King, Kitsap, Kittitas, Pierce, Skagit, Thurston, and Whatcom counties; and provides natural gas to 750,000 customers in King, Kittitas, Lewis, Pierce, Snohomish and Thurston counties. The company has a 6,000-square-mile (16,000 km2) electric and natural gas service area.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from expanding gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

A thermal power station is a power station in which heat energy is converted to electric power. In most places the turbine is steam-driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine the steam is condensed in a condenser and recycled to where it was heated. This is known as a Rankine cycle. The greatest variation in the design of thermal power stations is due to the different heat sources; fossil fuel power generation, though nuclear heat energy, solar heat energy, biofuels, and waste incineration are also used. Some prefer to use the term energy center because such facilities convert forms of heat energy into electrical energy. Certain thermal power stations are also designed to produce heat for industrial purposes, for district heating, or desalination of water, in addition to generating electrical power.
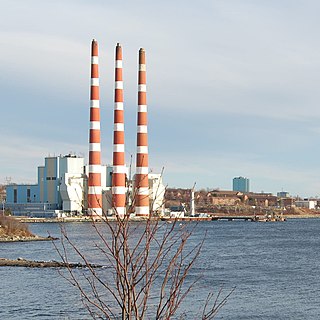
Tufts Cove Generating Station is a Canadian electrical generating station located in the Dartmouth neighbourhood of Tufts Cove in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality.

Littlebrook Power Station was a series of four oil and coal-fired power stations situated on the south bank of the River Thames, next to the Queen Elizabeth 2 Bridge and the Dartford Tunnel in Dartford, Kent. The final power station, Littlebrook D, ceased operating in March 2015, and has now been demolished.
The Dickerson Generating Station is an 853 MW electric generating plant owned by NRG Energy, located approximately two miles west of Dickerson, Maryland.

Riverside Energy Center is an electrical power station located north of Beloit, Wisconsin in the Town of Beloit, just west of the Rock River. The facility is owned and operated by Alliant Energy.

RockGen Energy Center is a 503 megawatt duel fuel fired peaking power plant located near Rockdale, Wisconsin. According to ihipowerplants, it was the largest peaking plant in Wisconsin at the time it was constructed.

Edgewater Generating Station is a 380 megawatt (MW) coal power plant located in Sheboygan, Wisconsin. It provides electricity for customers in the northeastern part of Alliant Energy's Wisconsin Power & Light service area and service to several local municipal utilities. In 2009, it was the seventh largest generating station in Wisconsin, with a net summer capacity of 767 MW.
Paris Generating Station is a natural gas fired, electrical peaking power plant located in the town of Paris in Kenosha County, south east of Union Grove, Wisconsin. It is a four unit, 100 MW each, natural gas or #2 fuel oil combustion turbine facility. There is a 1.5 million gallon fuel tank at the site for the fuel oil, and natural gas is transported to the facility via pipeline.
Concord Generating Station is a natural gas fired, electrical peaking power plant located in the town of Watertown in Jefferson County, Wisconsin. It is a four unit natural gas or #2 fuel oil combustion turbine facility. Two units are 100 MW each and the other two are 94 MW each.

The Saint Clair Power Plant is a major coal- and oil-fired power plant owned by Detroit Edison, a subsidiary of DTE Energy. It is located in St. Clair County, Michigan, on the west bank of St. Clair River. The plant is across M-29 from the newer Belle River Power Plant in East China, Michigan. The first four units of St. Clair were built in 1953–1954. Since then, three more generating units have been added to the plant. The St. Clair Power Plant generates 1982 megawatts in total. It is Detroit Edison's second largest power producer. The power plant has a large impact on the local economy, employing about 300 workers.

The Gould Street Generating Station is a 100 MW electric generating plant operated by Exelon that is located on Gould Street in south Baltimore, Maryland, USA. The plant is adjacent to an elevated section of freeway I-95 and is south of the Riverside neighborhood and west of the Locust Point neighborhood of Baltimore. The plant site, located on the shore of the Middle Branch of the Patapsco River, has been used for the generation of electric power for over one hundred years.

The Wilton power station refers to a series of coal, oil, gas and biomass fired CHP power stations which provide electricity and heat for the Wilton International Complex, with excess electricity being sold to the National Grid. It is located on the Wilton site in Redcar and Cleveland, south of the town of Middlesbrough in North East England. The station has provided for the site since opening in 1952, when it was operated by ICI. The station is currently owned and operated by SembCorp Industries.

The Riverside Generating Station is a 261 MW electric generating station operated by Exelon that is located at 4000 Broening Highway in Dundalk, Maryland. The station is on Sollers Point on the Patapsco River.

The West Springfield Generating Station, also known by its corporate name EP Energy Massachusetts, LLC, is a fossil-fuel-fired power plant located in West Springfield, Massachusetts. The station is a "peaking" facility, meaning that it primarily operates during peak electrical demand. The facility consists of two 49-megawatt (MW) combustion turbine generators fueled by natural gas or ultra low-sulphur diesel fuel, one 18 MW jet turbine that is fueled by kerosene, and one 107 MW simple-cycle steam boiler unit burning no. 6 fuel oil, ULSD or natural gas. The station also has a small auxiliary boiler for process and building heat and an emergency back-up generator. The station's management also operates several small remote power generators including two other jet turbines identical to West Springfield 10 which are the Doreen Street unit in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, and Woodland Road unit in Lee, Massachusetts as well as five run-of-river hydroelectric power stations located on the Chicopee and Deerfield Rivers.
The Russell City Energy Center (RCEC) is a 619-megawatt natural gas-fired power station, which began operating in August 2013. It is operated by Calpine, and is located in Hayward, California. It is named for Russell City and is built on that community's former landfill site.