
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main, is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 763,380 inhabitants as of 31 December 2019 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. On the river Main, it forms a continuous conurbation with the neighbouring city of Offenbach am Main and its urban area has a population of over 2.3 million. The city is the heart of the larger Rhine-Main metropolitan region, which has a population of more than 5.6 million and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region. Frankfurt's central business district lies about 90 km (56 mi) northwest of the geographic center of the EU at Gadheim, Lower Franconia. Like France and Franconia, the city is named after the Franks. Frankfurt is the largest city in the Rhine Franconian dialect area.

Honolulu is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is located in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southwest coast of the island of Oʻahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for international business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, as reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions.

Stockholm is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Outside the city to the east, and along the coast, is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the county seat of Stockholm County.
The Swedish Armed Forces is the government agency that forms the armed forces of Sweden, tasked with the defense of the country as well as with promoting Sweden's wider interests, supporting international peacekeeping, and providing humanitarian aid. It consists of the Swedish Army, the Swedish Air Force and the Swedish Navy, as well as a military reserve force, the Home Guard. Since 1994, all Swedish military branches are organized within a single unified government agency, headed by the Supreme Commander, even though the individual services maintain their distinct identities.
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck, wrist, at the groin, behind the knee, near the ankle joint, and on foot. Pulse is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart is used to nullify the effect of the ulnar pulse as the two arteries are connected via the palmar arches. The study of the pulse is known as sphygmology.
A capital or capital city is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the government's offices and meeting places; the status as capital is often designated by its law or constitution. In some jurisdictions, including several countries, different branches of government are in different settlements. In some cases, a distinction is made between the official (constitutional) capital and the seat of government, which is in another place.

Brisbane is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Queensland, and the third-most populous city in Australia, as well as Oceania, with a population of around 2.6 million, It lies at the centre of the South East Queensland metropolitan region, which encompasses a population of around 3.8 million. The Brisbane central business district is situated within a peninsula of the Brisbane River about 15 km (9 mi) from its mouth at Moreton Bay, a bay of the Coral Sea. Geographically Australia's largest metropolitan area, Brisbane extends in all directions along the hilly floodplain of the Brisbane River Valley between Moreton Bay and the Taylor and D'Aguilar mountain ranges. It sprawls across several of Australia's most populous local government areas, most centrally the City of Brisbane, Australia's most populous local government area. The demonym of Brisbane is "Brisbanite".

Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the Chrysler Building, the Hudson Yards Redevelopment Project, the headquarters of the United Nations, Grand Central Terminal, and Rockefeller Center, as well as tourist destinations such as Broadway and Times Square.

Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Eight seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.

The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones located to the north and south of the Tropics. Geographically part of the North and South temperate zones, they cover the latitudes from 23°26′11.0″ (or 23.43639°) to approximately 45° in the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The horse latitudes lie within this range.

The North American Central Time Zone (CT) is a time zone in parts of Canada, the United States, Mexico, Central America, some Caribbean Islands, and part of the Eastern Pacific Ocean.

An ice field is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation for them to form. The higher peaks of the underlying mountain rock that protrude through the icefields are known as nunataks. Ice fields are larger than alpine glaciers, but smaller than ice caps and ice sheets. The topography of ice fields is determined by the shape of the surrounding landforms, while ice caps have their own forms overriding underlying shapes.
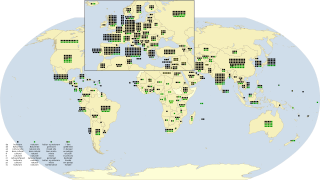
As of July 2021, there are a total of 1,154 World Heritage Sites located in 167 States Parties, of which 897 are cultural, 218 are natural and 39 are mixed properties. The countries have been divided by the World Heritage Committee into five geographic zones: Africa, Middle East, Asia and the Pacific, Europe and North America, and Latin America and the Caribbean. Italy, with 58 entries, has the highest number of World Heritage Sites. 27 state parties have no properties inscribed on the World Heritage List: Bahamas, Bhutan, Brunei, Burundi, Comoros, Cook Islands, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eswatini, Grenada, Guinea-Bissau, Guyana, Kuwait, Liberia, Maldives, Monaco, Niue, Rwanda, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Samoa, São Tomé and Príncipe, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Timor-Leste, Tonga, and Trinidad and Tobago.
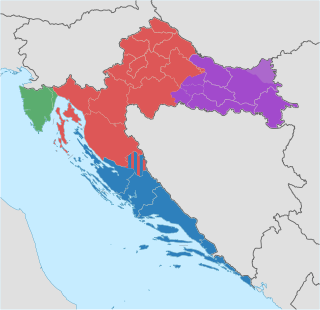
The Republic of Croatia is administratively organised into twenty counties, and is also traditionally divided into four historical and cultural regions: Croatia Proper, Dalmatia, Istria, and Slavonia. These are further divided into other, smaller regions.
The layout of a motorised vehicle such as a car is often defined by the location of the engine and drive wheels.

Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country located in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region; and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the Lachin corridor under a Russian peacekeeping force, and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the capital and largest city.
Semmencherry is a neighbourhood in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is situated in Chennai district, located south of the city about 18 km from the city centre, along the Old Mahabalipuram Road a.k.a. Rajiv Gandhi Salai. Semmencherry is located between Sholinganallur and Navalur. The suburb has experienced rapid development with the advent of IT companies along the Old Mahabalipuram Road.

Zürich is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 434,335 inhabitants, the urban area 1.315 million (2009), and the Zürich metropolitan area 1.83 million (2011). Zürich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zurich Airport and Zürich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country.

Kaliningrad, until 1946 known as Königsberg, is the largest city and the administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an exclave sandwiched between Lithuania and Poland. The city is situated on the Pregolya River, at the head of the Vistula Lagoon on the Baltic Sea, and is the only ice-free port of Russia and the Baltic states on the Baltic Sea. Its population in 2020 is 489,359 with up to 800,000 residents in the urban agglomeration. Kaliningrad is the second-largest city in the Northwestern Federal District, after Saint Petersburg, the third-largest city in the Baltic region, and the seventh-largest city on the Baltic Sea.















