
Celtic music is a broad grouping of music genres that evolved out of the folk music traditions of the Celtic people of Northwestern Europe. It refers to both orally-transmitted traditional music and recorded music and the styles vary considerably to include everything from traditional music to a wide range of hybrids.
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.

Loch is the Scottish Gaelic, Scots and Irish word for a lake or sea inlet. It is cognate with the Manx lough, Cornish logh, and one of the Welsh words for lake, llwch.

Scottish Gaelic, also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names.

Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving surfaces covered with "card clothing", a firm flexible material embedded with metal pins. It breaks up locks and unorganised clumps of fibre and then aligns the individual fibres to be parallel with each other. In preparing wool fibre for spinning, carding is the step that comes after teasing.
In early medieval Scotland, a mormaer was the Gaelic name for a regional or provincial ruler, theoretically second only to the King of Scots, and the senior of a Toísech (chieftain). Mormaers were equivalent to English earls or Continental counts, and the term is often translated into English as 'earl'.

A paper machine is an industrial machine which is used in the pulp and paper industry to create paper in large quantities at high speed. Modern paper-making machines are based on the principles of the Fourdrinier Machine, which uses a moving woven mesh to create a continuous paper web by filtering out the fibres held in a paper stock and producing a continuously moving wet mat of fibre. This is dried in the machine to produce a strong paper web.
Teuchter is a Lowland Scots word commonly used to describe a Scottish Highlander, in particular a Gaelic-speaking Highlander. Like most such cultural epithets, it can be seen as offensive, but is often seen as amusing by the speaker. The term is contemptuous, essentially describing someone seen to be uncouth and rural.

A machair is a fertile low-lying grassy plain found on part of the northwest coastlines of Ireland and Scotland, in particular the Outer Hebrides. The best examples are found on North and South Uist, Harris and Lewis.
A cant is the jargon or language of a group, often employed to exclude or mislead people outside the group. It may also be called a cryptolect, argot, pseudo-language, anti-language or secret language. Each term differs slightly in meaning; their use is inconsistent.

A mòd is an Eisteddfod-inspired festival of Scottish Gaelic song, arts and culture. Historically, the Gaelic word mòd, which came from Old Norse mót, refers to a Viking Age Thing or a similar kind of assembly. There are both local mòds, and an annual national mòd, the Royal National Mòd. Mòds are run under the auspices of An Comunn Gàidhealach. The term comes from a Gaelic word for a parliament or congress in common use during the Lordship of the Isles.

A croft is a fenced or enclosed area of land, usually small and arable, and usually, but not always, with a crofter's dwelling thereon. A crofter is one who has tenure and use of the land, typically as a tenant farmer, especially in rural areas.

Irish clans are traditional kinship groups sharing a common surname and heritage and existing in a lineage-based society, originating prior to the 17th century. A clan included the chief and his patrilineal relatives; however Irish clans also included unrelated clients of the chief.
Gaelic type is a family of Insular script typefaces devised for printing Classical Gaelic. It was widely used from the 16th until the mid-18th century (Scotland) or the mid-20th century (Ireland) but is now rarely used. Sometimes, all Gaelic typefaces are called Celtic or uncial although most Gaelic types are not uncials. The "Anglo-Saxon" types of the 17th century are included in this category because both the Anglo-Saxon types and the Gaelic/Irish types derive from the insular manuscript hand.

The languages of Scotland are the languages spoken or once spoken in Scotland. Each of the numerous languages spoken in Scotland during its recorded linguistic history falls into either the Germanic or Celtic language families. The classification of the Pictish language was once controversial, but it is now generally considered a Celtic language. Today, the main language spoken in Scotland is English, while Scots and Scottish Gaelic are minority languages. The dialect of English spoken in Scotland is referred to as Scottish English.
This article describes the grammar of the Scottish Gaelic language.

Long draw is the spinning technique used to create woolen yarns. It is spun from carded rolags. It is generally spun from shorter stapled fibers. Long draw spun yarns are light, lofty, stretchy, soft, and full of air, thus they are good insulators, and make good knitting yarns.
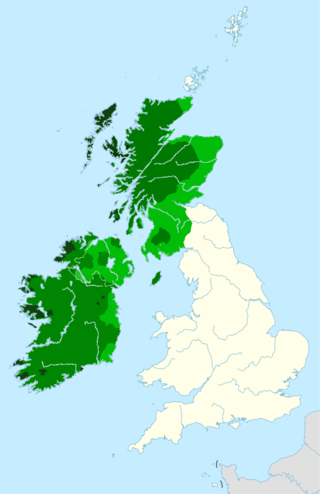
The Gaels are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic.

Alba is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term Alba and the Manx term Nalbin, the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish and Welsh, both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses Bro-Skos, meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion.

The Scots are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic-speaking peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who founded the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century. In the following two centuries, the Celtic-speaking Cumbrians of Strathclyde and the Germanic-speaking Angles of north Northumbria became part of Scotland. In the High Middle Ages, during the 12th-century Davidian Revolution, small numbers of Norman nobles migrated to the Lowlands. In the 13th century, the Norse-Gaels of the Western Isles became part of Scotland, followed by the Norse of the Northern Isles in the 15th century.















