Related Research Articles
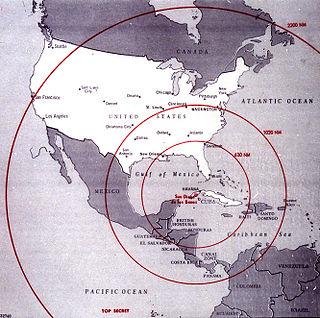
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis in Cuba, or the Caribbean Crisis, was a 13-day confrontation between the governments of the United States and the Soviet Union, when American deployments of nuclear missiles in Italy and Turkey were matched by Soviet deployments of nuclear missiles in Cuba. The crisis lasted from 16 to 28 October 1962. The confrontation is widely considered the closest the Cold War came to escalating into full-scale nuclear war.
Operation Anadyr was the code name used by the Soviet Union for its Cold War secret operation in 1962 of deploying ballistic missiles, medium-range bombers, and a division of mechanized infantry to Cuba to create an army group that would be able to prevent an invasion of the island by United States forces. The plan was to deploy approximately 60,000 personnel in support of the main missile force, which consisted of three R-12 missile regiments and two R-14 missile regiments. However, part of it was foiled when the United States discovered the plan, prompting the Cuban Missile Crisis.

Brinkmanship or brinksmanship is the practice of trying to achieve an advantageous outcome by pushing dangerous events to the brink of active conflict. The maneuver of pushing a situation with the opponent to the brink succeeds by forcing the opponent to back down and make concessions rather than risk engaging in a conflict that would no longer be beneficial to either side. That might be achieved through diplomatic maneuvers, by creating the impression that one is willing to use extreme methods rather than concede. The tactic occurs in international politics, foreign policy, labor relations, contemporary military strategy, terrorism, and high-stakes litigation.

Oleg Vladimirovich Penkovsky, codenamed Hero and Yoga was a Soviet military intelligence (GRU) colonel during the late 1950s and early 1960s. Penkovsky informed the United States and the United Kingdom about Soviet military secrets, including the appearance and footprint of Soviet intermediate-range ballistic missile installations and the weakness of the Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) program. This information was decisive in allowing the US to recognize that the Soviets were placing missiles in Cuba before most of them were operational. It also gave US President John F. Kennedy, during the Cuban Missile Crisis that followed, valuable information about Soviet weakness that allowed him to face down Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev and resolve the crisis without a nuclear war.

Roger Lindsey Donaldson is an Australian and New Zealand film director, screenwriter, and producer. His 1977 debut film, Sleeping Dogs, is considered landmark work of New Zealand cinema, as one of the country’s first films to attract large-scale critical and commercial success. He has subsequently directed 17 feature films, working in Hollywood and the United Kingdom, as well as his native country.

Thirteen Days is a 2000 American historical political thriller film directed by Roger Donaldson. It dramatizes the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, seen from the perspective of the US political leadership. Kevin Costner stars as top White House assistant Kenneth P. O'Donnell, with Bruce Greenwood featured as President John F. Kennedy, Steven Culp as Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy, and Dylan Baker as Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara.

The Fog of War: Eleven Lessons from the Life of Robert S. McNamara is a 2003 American documentary film about the life and times of former U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara, illustrating his observations of the nature of modern warfare. It was directed by Errol Morris and features an original score by Philip Glass. The title derives from the military concept of the "fog of war", which refers to the difficulty of making decisions in the midst of conflict.
In the United States, during the Cold War, the missile gap was the perceived superiority of the number and power of the USSR's missiles in comparison with those of the U.S., causing a lack of military parity. The gap in the ballistic missile arsenals did not exist except in exaggerated estimates, made by the Gaither Committee in 1957 and in United States Air Force (USAF) figures. Even the contradictory CIA figures for the USSR's weaponry, which showed a clear advantage for the US, were far above the actual count. Like the bomber gap of only a few years earlier, it was soon demonstrated that the gap was entirely fictional.
Thirteen Days: A Memoir of the Cuban Missile Crisis is Robert F. Kennedy's account of the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962. The book was released in 1969, the year after his assassination.
A Trollope ploy is a negotiation technique named after an incident from an Anthony Trollope novel, in which a woman interprets a casual romantic gesture, such as squeezing her hand, as a marriage proposal.

Llewellyn E. "Tommy" Thompson Jr. was an American diplomat. He served in Sri Lanka, Austria, and for a lengthy period in the Soviet Union, where his tenure saw some of the most significant events of the Cold War. He was a key advisor to President John F. Kennedy during the Cuban Missile Crisis. A 2019 assessment described him as "arguably the most influential figure who ever advised U.S. presidents about policy toward the Soviet Union during the Cold War."

After the establishment of diplomatic ties with the Soviet Union after the Cuban Revolution of 1959, Cuba became increasingly dependent on Soviet markets and military aid and was an ally of the Soviet Union during the Cold War. In 1972 Cuba joined the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon), an economic organization of states designed to create co-operation among the communist planned economies, which was dominated by its largest economy, the Soviet Union. Moscow kept in regular contact with Havana and shared varying close relations until the end of the Soviet Union in 1991. Cuba then entered an era of serious economic hardship, the Special Period.

The Missiles of October is a 1974 docudrama made-for-television play about the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962. The title evokes the 1962 book The Guns of August by Barbara Tuchman about the missteps amongst the great powers and the failed chances to give an opponent a graceful way out, which led to World War I.

William Ecker was a United States Navy officer.
John Barbour is a Canadian actor, comedian, and television host who has worked extensively in the United States. Barbour is the only performer in TV to win Emmys for both entertainment and news shows. Barbour is known as one of the hosts of the NBC reality television series Real People, for which he was also a creator and co-producer.

Mikhail Rachyanovich Sagatelyan was a Soviet journalist, author and KGB agent. He was head of the TASS news agency's United States bureau from 1959 to 1965, making him an important conduit of information between the United States and the Soviet Union during that period of the Cold War.

A Tour of the White House with Mrs. John F. Kennedy was a television special featuring the first lady of the United States, Jacqueline Kennedy, on a tour of the recently renovated White House. It was broadcast on Valentine's Day, February 14, 1962, on both CBS and NBC, and broadcast four days later on ABC. The program was the first televised tour of the White House by a first lady and is considered the first prime-time documentary specifically designed to appeal to a female audience.

The Bomb is a 2015 American documentary film about the history of nuclear weapons, from theoretical scientific considerations at the very beginning, to their first use on August 6, 1945, to their global political implications in the present day. The film was written and directed by Rushmore DeNooyer for PBS. The project took a year and a half to complete, since much of the film footage and images were only recently declassified by the United States Department of Defense.
Robert F. Kennedy, the 64th United States Attorney General, a U.S. senator from New York, and the brother of United States president John F. Kennedy, has frequently been depicted or referenced in works of popular culture.
References
- ↑ Thirteen Days DVD cover, 2000