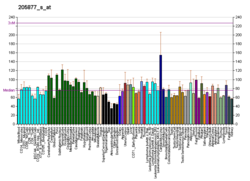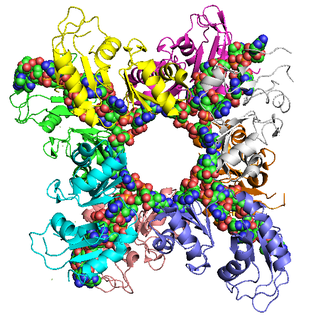
Poly(A)-binding protein is an RNA-binding protein which triggers the binding of eukaryotic initiation factor 4 complex (eIF4G) directly to the poly(A) tail of mRNA which is 200-250 nucleotides long. The poly(A) tail is located on the 3' end of mRNA and was discovered by Mary Edmonds, who also characterized the poly-A polymerase enzyme that generates the poly(a) tail. The binding protein is also involved in mRNA precursors by helping polyadenylate polymerase add the poly(A) nucleotide tail to the pre-mRNA before translation. The nuclear isoform selectively binds to around 50 nucleotides and stimulates the activity of polyadenylate polymerase by increasing its affinity towards RNA. Poly(A)-binding protein is also present during stages of mRNA metabolism including nonsense-mediated decay and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. The poly(A)-binding protein may also protect the tail from degradation and regulate mRNA production. Without these two proteins in-tandem, then the poly(A) tail would not be added and the RNA would degrade quickly.

Rotavirus translation, the process of translating mRNA into proteins, occurs in a different way in Rotaviruses. Unlike the vast majority of cellular proteins in other organisms, in Rotaviruses the proteins are translated from capped but nonpolyadenylated mRNAs. The viral nonstructural protein NSP3 specifically binds the 3'-end consensus sequence of viral mRNAs and interacts with the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4G. The Rotavirus replication cycle occurs entirely in the cytoplasm. Upon virus entry, the viral transcriptase synthesizes capped but nonpolyadenylated mRNA The viral mRNAs bear 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTR) of variable length and are flanked by two different sequences common to all genes.

Rotavirus protein NSP3 (NS34) is bound to the 3' end consensus sequence of viral mRNAs in infected cells.

Tristetraprolin (TTP), also known as zinc finger protein 36 homolog (ZFP36), is a protein that in humans, mice and rats is encoded by the ZFP36 gene. It is a member of the TIS11 family, along with butyrate response factors 1 and 2.

Required for meiotic nuclear division 5 homolog B , also known as RMND5B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RMND5B gene. It has a zinc finger domain and is highly conserved throughout many eukaryotic organisms.
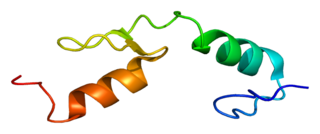
Zinc finger protein 40 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIVEP1 gene.

Mitochondrial import receptor subunit TOM34 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOMM34 gene.

Zinc finger protein 655 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF655 gene.

SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH3TC2 gene. It is believed to be expressed in the Schwann cells that wrap the myelin sheath around nerves.

Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZC3H13 gene.

Zinc finger CCCH-type antiviral protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZC3HAV1 gene.

Zinc finger protein 161 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB14 gene.

Zinc finger protein 330 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF330 gene.

Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTC1 gene.

Zinc finger protein 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF19 gene.

Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 35 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTC35 gene.

PHD finger protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHF1 gene.

Zinc finger protein 193 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF193 gene.

Zinc finger CCCH-type with G patch domain-containing protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZGPAT gene.

ZC3H12B, also known as CXorf32 or MCPIP2, is a protein encoded by gene ZC3H12B located on chromosome Xq12 in humans.