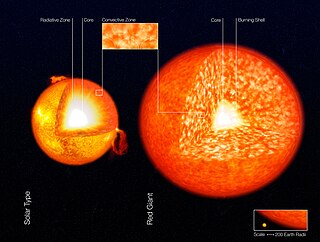
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported by convection in such a region. In a radiation zone, energy is transported by radiation and conduction.

The Arches Cluster is the densest known star cluster in the Milky Way, about 100 light-years from its center in the constellation Sagittarius, 25,000 light-years from Earth. Its discovery was reported by Nagata et al. in 1995, and independently by Cotera et al. in 1996. Due to extremely heavy optical extinction by dust in this region, the cluster is obscured in the visual bands, and is observed in the X-ray, infrared and radio bands. It contains approximately 135 young, very hot stars that are many times larger and more massive than the Sun, plus many thousands of less massive stars.
36 Ursae Majoris is a double star in the northern constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.8, it can be seen with the naked eye in suitable dark skies. Based upon parallax measurements, this binary lies at a distance of 42 light-years from Earth.

In astronomy Westerhout 49 also known as W49, is a strong galactic thermal radio source characteristic of an HII region. It was discovered by Gart Westerhout in 1958.

Cygnus OB2 is an OB association that is home to some of the most massive and most luminous stars known, including suspected Luminous blue variable Cyg OB2 #12. It also includes one of the largest known stars, NML Cygni. The region is embedded within a wider one of star formation known as Cygnus X, which is one of the most luminous objects in the sky at radio wavelengths. The region is approximately 1,570 parsecs from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.

R136c is a star located in R136, a tight knot of stars at the centre of NGC 2070, an open cluster weighing 450,000 solar masses and containing 10,000 stars. At 142 M☉ and 3.8 million L☉, it is the one of the most massive stars known and one of the most luminous, along with being one of the hottest, at over 40,000 K. It was first resolved and named by Feitzinger in 1980, along with R136a and R136b.
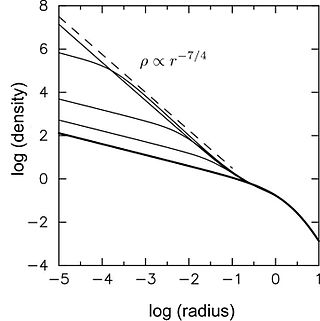
Bahcall–Wolf cusp refers to a particular distribution of stars around a massive black hole at the center of a galaxy or globular cluster. If the nucleus containing the black hole is sufficiently old, exchange of orbital energy between stars drives their distribution toward a characteristic form, such that the density of stars, ρ, varies with distance from the black hole, r, as

S Muscae is a classical (δ) Cepheid variable star in the constellation Musca about 2,600 light years away.

MY Camelopardalis is a binary star system located in the Alicante 1 open cluster, some 13 kly (4.0 kpc) away in the constellation Camelopardalis. It is one of the most massive known binary star systems and a leading candidate for a massive star merger. MY Cam is the brightest star in Alicante 1.
HD 82514, also known as HR 3790, is a solitary, orange-hued star located in the southern constellation Antlia. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.86, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, it is estimated to be 279 light years away from the Solar System. However, it is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 14.3 km/s.

XX Persei is a semiregular variable red supergiant star in the constellation Perseus, between the Double Cluster and the border with Andromeda.

NGC 4103 is an open cluster in the constellation Crux. It was discovered by James Dunlop in 1826. It is located approximately 5,000 light years away from Earth, in the Carina-Sagittarius arm.

DH Cephei is a variable binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus, positioned about two degrees to the east of the star system Delta Cephei. With an apparent visual magnitude of 8.61, it is too faint to be visible without a telescope. Based on parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of approximately 9.6 kilolight-years from the Sun. At present it is moving closer to the Earth with a radial velocity of −33 km/s.
WASP-57 is a single G-type main-sequence star about 1310 light-years away. WASP-57 is depleted in heavy elements, having 55% of the solar abundance of iron. WASP-57 is much younger than the Sun at 0.957±0.518 billion years.
Alicante 10, also known as RSGC6, is a young massive open cluster belonging to the Milky Way galaxy. It was discovered in 2012 in the 2MASS survey data. Currently, eight red supergiants have been identified in this cluster. Alicante 10 is located in the constellation Scutum at the distance of about 6000 pc from the Sun. It is likely situated at the intersection of the northern end of the Long Bar of the Milky Way and the inner portion of the Scutum–Centaurus Arm—one of the two major spiral arms.
HD 34868 is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Columba. With an apparent magnitude of 5.97, it's barely visible to the unaided eye. The star is located 410 light years away based on parallax, but is drifting away with a heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s.











