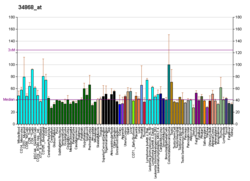
| SMG5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SMG5 , EST1B, LPTS-RP1, LPTSRP1, SMG-5, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor, SMG5 nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610962; MGI: 2447364; HomoloGene: 9095; GeneCards: SMG5; OMA:SMG5 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein SMG5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMG5 gene. [5] [6] [7] This protein contains a PIN domain that appears to have mutated the residues in the active site. [8]