
SMS Meteor was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the North German Federal Navy that was launched in 1865. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Meteor took part in the Battle of Havana in 1870 during the Franco-Prussian War. There, she battled the French aviso Bouvet; both vessels were lightly damaged, though Bouvet was compelled to disengage after a shot from Meteor disabled her engine. After the war, Meteor returned to Germany, where her career was limited; she served briefly as a survey vessel. From 1873 to 1877, she was deployed to the Mediterranean Sea as a station ship in Constantinople during a period of tensions in the Ottoman Empire. After returning to Germany in 1877, she was decommissioned, converted into a coal hulk and expended as a target ship some time later.
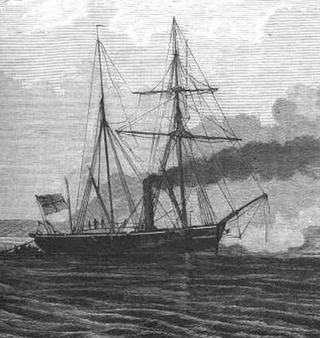
SMS Comet was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Comet served during the Second Schleswig War of 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, part of the conflicts that unified Germany. The ship was present at, but was only lightly engaged in the Battle of Jasmund during the Second Schleswig War. She served in a variety of roles during peacetime, including fishery protection and survey work. Comet went on one lengthy deployment abroad, with an assignment to the Mediterranean Sea from 1876 to 1879. She saw little active service after returning to Germany and was decommissioned and hulked in 1881. The vessel remained in the navy's inventory until at least 1891, being broken up sometime thereafter.

SMS Blitz was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1862. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Blitz served during all three wars of German unification in the 1860s and early 1870s. The ship was present during the Battle of Heligoland in May 1864 during the Second Schleswig War, but was too slow to engage the Danish squadron. During the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, she operated against the Kingdom of Hanover in the North Sea, but did not see extensive action. In August 1870, Blitz and three other light vessels attacked the French blockade force in the Baltic Sea during the Franco-Prussian War, but they withdrew without either side scoring any hits. During her peacetime career, Blitz was sent to the Mediterranean Sea twice, in 1863 and 1867–1868. She was employed as a fisheries protection ship, a guard ship, and a survey vessel in the early 1870s, before being decommissioned in 1875 and broken up for scrap in 1878. Parts of her machinery were reused in the gunboat Wolf.

SMS Basilisk was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1862. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Basilisk served during all three wars of German unification in the 1860s and early 1870s. The ship was present during the Battle of Heligoland in May 1864 during the Second Schleswig War, but was too slow to engage the Danish squadron. During the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 and the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, Basilisk was stationed in the North Sea to help defend the coast, but she did not see action during either conflict. Between 1873 and 1875, she was employed experimentally as the first torpedo-armed warship of the German fleet. Basilisk was decommissioned in 1875, renamed "Mine Barge No. 1", and converted into a naval mine storage hulk. The details of her fate are unrecorded, but she was still in service in that capacity at least as late as 1900. Sometime thereafter, she was broken up.

SMS Cyclop was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Cyclop served during the three wars of German unification; during the first, the Second Schleswig War on 1864, she guarded the Prussian coastline but saw no action. She supported the army's campaign against the Kingdom of Hanover during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, and she defended the Elbe for the duration of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, but again took part in no battles. Badly deteriorated by 1872, she was stricken from the naval register in March that year and reconstructed into an iron-hulled gunboat. Recommissioned in 1875, she thereafter served abroad in the German colonial empire before being stricken again in 1888. She was thereafter used as a storage hulk before ultimately being broken up for scrap after 1914.

SMS Delphin was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Delphin served during the Second Schleswig War of 1864 and the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, part of the conflicts that unified Germany. The ship was present at, but was only lightly engaged in the Battle of Jasmund during the Second Schleswig War. The ship spent much of the rest of her career in the Mediterranean Sea, going on three lengthy deployments there in 1865–1866, 1867–1870, and 1871–1873. During the last tour, she took part in operations off the coast of Spain with an Anglo-German squadron during the Third Carlist War, where she helped to suppress forces rebelling against the Spanish government. For the rest of the 1870s, she served as a survey vessel in the North and Baltic Seas before being decommissioned in August 1881, stricken from the naval register the following month, and subsequently broken up for scrap.

SMS Drache was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. Budgetary problems delayed her completion until 1869, and she first entered service during the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, though she saw no significant action against the French Navy. Drache spent most of her career, between 1872 and 1887, conducting survey work in the North Sea, which later proved to be instrumental to the operations of German U-boats and minelayers during World War I. Drache was ultimately decommissioned in 1887, reduced to a coal hulk, and then expended as a target for the torpedo boat D5 in 1889. Her wreck was later raised and broken up.

The Camäleon class was a group of gunboats built for the Prussian Navy. Eight ships comprised the class: Camäleon, Comet, Cyclop, Delphin, Blitz, Basilisk, Meteor, and Drache. The vessels were armed with a battery of one 15 cm (5.9 in) gun and two 12 cm (4.7 in) guns. In 1865, the ships then in service had their 15 cm gun replaced with a 21 cm (8.3 in) gun; Meteor and Drache, not yet completed, entered service with that gun. The vessels saw action during the wars of German unification, with Comet taking part in the Battle of Jasmund and Blitz and Basilisk present during the Battle of Heligoland, both during the Second Schleswig War in 1864. Several of the ships served in the North Sea during the Austro-Prussian War, where some of them supported operations against the Kingdom of Hanover. During the Franco-Prussian War, Meteor battled the French aviso Bouvet in the Battle of Havana in 1870; the other members of the class were deployed on coastal defense assignments.

The Jäger class of steam gunboats was a class of fifteen ships that were built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The class, which were the first steam gunboats built for the Prussian fleet, comprised the following vessels: Jäger, Crocodill, Fuchs, Hay, Scorpion, Sperber, Hyäne, Habicht, Pfeil, Natter, Schwalbe, Salamander, Wespe, Tiger, and Wolf. They were armed with three guns and were intended to guard the Prussian coast in the shallow waters of the Baltic Sea. They proved to handle poorly in service, and as a result, spent much of their existences laid up ashore. Several of the boats were activated during the Second Schleswig War in 1864, and some took part in a minor battle against Danish warships. Crocodill was scrapped in 1867 due to her poor condition, but the rest of the class remained in the fleet's inventory into the 1870s, when they began to be discarded. Most of the ships served on as storage barges, usually for naval mines, though Jäger and Wolf were both sunk as target ships.

SMS Jäger was the lead ship of the Jäger class of steam gunboats built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw limited time in service. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War in 1864 and saw brief action against Danish naval forces in July. Jäger next recommissioned at the start of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, and was stationed in the mouth of the Elbe river, but she saw no combat with French forces. In poor condition by that time, Jäger was struck from the naval register in 1872. She was initially used as a target ship and later a coal storage hulk. The ship was eventually broken up in the early 1880s.

SMS Fuchs was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw limited time in service. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War in 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, but she did not engage enemy vessels during either conflict. Fuchs served as a gunnery training ship in the late 1870s and early 1880s, and was then used as a storage hulk for a few years before being broken up.

SMS Hay was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864, and she saw brief action during the Battle of Jasmund on 17 March. Hay also participated in the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, but she did not engage any French forces during the conflict. The ship saw little further use and was struck from the naval register in 1880; she was then converted into a coal storage barge, but her ultimate fate is unknown.

SMS Scorpion was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864, and she saw brief action during the Battle of Jasmund on 17 March. Scorpion was commissioned during the Austro-Prussian War in 1866 and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, but she did not engage any enemy forces during either conflict. The navy disposed of the ship in 1877 and she was later used as a coal storage barge. Her ultimate fate is unknown.

SMS Sperber was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, being used to defend the Prussian coast. She saw no action against enemy forces in either conflict, however. Sperber was used intermittently as a tender in the 1870s, and was struck from the naval register in 1878. She was then used as a barge in Kiel.

SMS Hyäne was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864, and she saw brief action during the Battle of Jasmund on 17 March. She next recommissioned during the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, but she did not engage any French warships. In poor condition by that time, she was struck from the naval register in 1873 and sunk as a target ship.

SMS Habicht was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864 and briefly engaged Danish ships in July. She was also commissioned for the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, being used to defend the Prussian coast. She saw no action against French forces in the conflict, however. Habicht largely remained out of service through the 1870s, until she was struck from the naval register in 1877. She was used as a storage hulk for a time in Wilhelmshaven, but details of her eventual disposal are unknown.

SMS Schwalbe was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, being used to defend the Prussian coast. She saw no action against enemy forces in either conflict, however. The ship was found to be in poor condition by the end of the war, and she was discarded in 1872. She was then used as a barge for some time, but her ultimate fate is unknown.

SMS Salamander was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, being used to defend the Prussian coast. During the latter conflict, she was present for a brief action with French ships in the Baltic Sea. She remained in service through 1875, when she was placed in reserve, where she remained until 1878, when she was struck from the naval register. She was thereafter used as a barge.

SMS Tiger was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the three wars of German unification: the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864. the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. She saw no action during the first and last conflict, but she took part in operations against the Kingdom of Hanover during the Austro-Prussian War. Tiger served in a variety of roles in the mid-1870s and was eventually discarded in 1877. The ship was thereafter used as a storage barge in Wilhelmshaven. Her ultimate fate is unknown.

SMS Wolf was a steam gunboat of the Jäger class built for the Prussian Navy in the late 1850s and early 1860s. The ship was ordered as part of a program to strengthen Prussia's coastal defense forces, then oriented against neighboring Denmark. She was armed with a battery of three guns. The ship saw very little activity during her career. She was activated during the three wars of German unification: the Second Schleswig War against Denmark in 1864. the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. She participated in a minor skirmish against Danish forces in the first conflict, and then took part in operations against the Kingdom of Hanover during the Austro-Prussian War. She saw no action during the war with France. Wolf remained in service until mid-1873; she was struck from the naval register in 1875, used as a storage hulk for nearly a decade, before being sunk as a target ship for torpedo tests in 1884. The wreck was then raised and scrapped.



