Gene knockdown is an experimental technique by which the expression of one or more of an organism's genes is reduced. The reduction can occur either through genetic modification or by treatment with a reagent such as a short DNA or RNA oligonucleotide that has a sequence complementary to either gene or an mRNA transcript.
The RNA-induced silencing complex, or RISC, is a multiprotein complex, specifically a ribonucleoprotein, which functions in gene silencing via a variety of pathways at the transcriptional and translational levels. Using single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) fragments, such as microRNA (miRNA), or double-stranded small interfering RNA (siRNA), the complex functions as a key tool in gene regulation. The single strand of RNA acts as a template for RISC to recognize complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript. Once found, one of the proteins in RISC, Argonaute, activates and cleaves the mRNA. This process is called RNA interference (RNAi) and it is found in many eukaryotes; it is a key process in defense against viral infections, as it is triggered by the presence of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA).
Micrococcal nuclease is an endo-exonuclease that preferentially digests single-stranded nucleic acids. The rate of cleavage is 30 times greater at the 5' side of A or T than at G or C and results in the production of mononucleotides and oligonucleotides with terminal 3'-phosphates. The enzyme is also active against double-stranded DNA and RNA and all sequences will be ultimately cleaved.

Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.
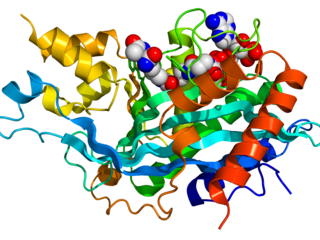
The p300-CBP coactivator family in humans is composed of two closely related transcriptional co-activating proteins :
- p300
- CBP
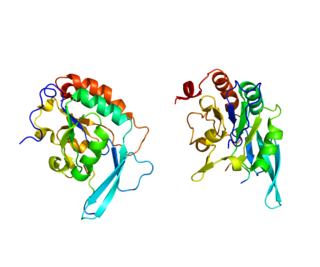
DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1, also known as RPB1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLR2A gene.

Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.

Myb-related protein B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYBL2 gene.
Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX5 also known as DEAD box protein 5 or RNA helicase p68 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX5 gene.

Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 also known as steroid receptor RNA activator protein (SRAP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRA1 gene. The mRNA transcribed from the SRA1 gene is a component of the ribonucleoprotein complex containing NCOA1. This functional RNA also encodes a protein.

Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the G3BP1 gene.

POU domain class 2-associating factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2AF1 gene. The protein is also termed Oct coactivator from B cells, Oct binding factor 1, and, as commonly found in the literature, BOB1. BOB1 is a transcriptional coactivator which is expressed principally by B-cell lymphocytes and controls immunoglobulin and other genes critical for these cells expression of CD20, CRISP-3, and CD36. The expression of BOB1 has proven useful for identifying certain lymphomas as being B-cell lymphomas, as exemplified in studies which use BAB1 expression to help identify lymphomas as being diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified.

Alpha-globin transcription factor CP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFCP2 gene.

Transcription factor Spi-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPIB gene.

CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2, also known as CRTC2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CRTC2 gene.

Metadherin, also known as protein LYRIC or astrocyte elevated gene-1 protein (AEG-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTDH gene.

In molecular biology, a Tudor domain is a conserved protein structural domain originally identified in the Tudor protein encoded in Drosophila. The Tudor gene was found in a Drosophila screen for maternal factors that regulate embryonic development or fertility. Mutations here are lethal for offspring, inspiring the name Tudor, as a reference to the Tudor King Henry VIII and the several miscarriages experienced by his wives.

In molecular biology, mir-221 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology, the BESS domain is a protein domain which has been named after the three proteins that originally defined the domain: BEAF, Suvar(3)7 and Stonewall ). The BESS domain is 40 amino acid residues long and is predicted to be composed of three alpha helices, as such it might be related to the myb/SANT HTH domain. The BESS domain directs a variety of protein-protein interactions, including interactions with itself, with Dorsal, and with a TBP-associated factor. It is found in a single copy in Drosophila proteins and is often associated with the MADF domain.

In biochemistry, the KIX domain (kinase-inducible domain (KID) interacting domain) or CREB binding domain is a protein domain of the eukaryotic transcriptional coactivators CBP and P300. It serves as a docking site for the formation of heterodimers between the coactivator and specific transcription factors. Structurally, the KIX domain is a globular domain consisting of three α-helices and two short 310-helices.