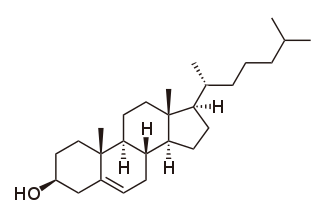
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol, a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid.

Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types.

HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, with the latter being the process by which fatty acids are esterified to glycerol before being packaged into very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Fatty acids are produced in the cytoplasm of cells by repeatedly adding two-carbon units to acetyl-CoA. Triacylglycerol synthesis, on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue. Nevertheless, it also occurs to some extent in other tissues such as the gut and kidney. A review on lipogenesis in the brain was published in 2008 by Lopez and Vidal-Puig. After being packaged into VLDL in the liver, the resulting lipoprotein is then secreted directly into the blood for delivery to peripheral tissues.

Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes SREBF1 and SREBF2. SREBPs belong to the basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper class of transcription factors. Unactivated SREBPs are attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum membranes. In cells with low levels of sterols, SREBPs are cleaved to a water-soluble N-terminal domain that is translocated to the nucleus. These activated SREBPs then bind to specific sterol regulatory element DNA sequences, thus upregulating the synthesis of enzymes involved in sterol biosynthesis. Sterols in turn inhibit the cleavage of SREBPs and therefore synthesis of additional sterols is reduced through a negative feed back loop.

The liver X receptor (LXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors and is closely related to nuclear receptors such as the PPARs, FXR and RXR. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are important regulators of cholesterol, fatty acid, and glucose homeostasis. LXRs were earlier classified as orphan nuclear receptors, however, upon discovery of endogenous oxysterols as ligands they were subsequently deorphanized.
Squalene synthase (SQS) or farnesyl-diphosphate:farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyl transferase is an enzyme localized to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. SQS participates in the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing a two-step reaction in which two identical molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) are converted into squalene, with the consumption of NADPH. Catalysis by SQS is the first committed step in sterol synthesis, since the squalene produced is converted exclusively into various sterols, such as cholesterol, via a complex, multi-step pathway. SQS belongs to squalene/phytoene synthase family of proteins.
Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) also known as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SREBF1 gene.

Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) also known as sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 (SREBF2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SREBF2 gene.

Membrane-bound transcription factor site-1 protease, or site-1 protease (S1P) for short, also known as subtilisin/kexin-isozyme 1 (SKI-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MBTPS1 gene. S1P cleaves the endoplasmic reticulum loop of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors.
Membrane-bound transcription factor site-2 protease, also known as S2P endopeptidase or site-2 protease (S2P), is an enzyme encoded by the MBTPS2 gene which liberates the N-terminal fragment of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors from membranes. S2P cleaves the transmembrane domain of SREPB, making it a member of the class of intramembrane proteases.

Insulin induced gene 1, also known as INSIG1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the INSIG1 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA7 gene.

CAMP responsive element binding protein-like 1, also known as CREBL1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CREBL1 gene.

Oxysterol-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OSBP gene.

Insulin induced gene 2, also known as INSIG2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the INSIG2 gene.

StAR-related lipid transfer protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STARD5 gene. The protein is a 213 amino acids long, consisting almost entirely of a StAR-related transfer (START) domain. It is also part of the StarD4 subfamily of START domain proteins, sharing 34% sequence identity with STARD4.

miR-33 is a family of microRNA precursors, which are processed by the Dicer enzyme to give mature microRNAs. miR-33 is found in several animal species, including humans. In some species there is a single member of this family which gives the mature product mir-33. In humans there are two members of this family called mir-33a and mir-33b, which are located in intronic regions within two protein-coding genes for Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins respectively.

StAR-related lipid transfer protein 4 (STARD4) is a soluble protein involved in cholesterol transport. It can transfer up to 7 sterol molecules per minute between artificial membranes.
A sterol-sensing domain (SSD) is a protein domain which consists of 180 amino acids forming five transmembrane segments capable of binding sterol groups. This type of domain is present in proteins involved in cholesterol metabolism and signalling.




















