
Yang Huanming, also known as Henry Yang, is a Chinese biologist, businessman and one of China's leading genetics researchers. He is Chairman and co-founder of the Beijing Genomics Institute, formerly of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He was elected as member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2007, a foreign academician of Indian National Science Academy in 2009, a member of the German National Academy of Sciences in 2012, and foreign associate of the US National Academy of Science in 2014.

Ameloblastin is an enamel matrix protein that in humans is encoded by the AMBN gene.

Amelogenin, X isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AMELX gene. AMELX is located on the X chromosome and encodes a set of isoforms of amelogenin by alternative splicing. Amelogenin is an extracellular matrix protein involved in the process of amelogenesis, the formation of enamel on teeth.
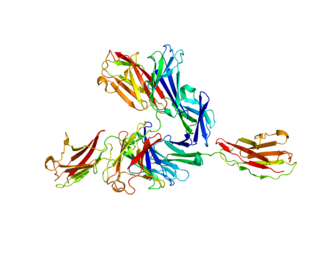
Basigin (BSG) also known as extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) or cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BSG gene. This protein is a determinant for the Ok blood group system. There are three known antigens in the Ok system; the most common being Oka, OK2 and OK3. Basigin has been shown to be an essential receptor on red blood cells for the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. The common isoform of basigin (basigin-2) has two immunoglobulin domains, and the extended form basigin-1 has three.

Thiamine transporter 1, also known as thiamine carrier 1 (TC1) or solute carrier family 19 member 2 (SLC19A2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC19A2 gene. SLC19A2 is a thiamine transporter. Mutations in this gene cause thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome (TRMA), which is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by diabetes mellitus, megaloblastic anemia and sensorineural deafness.

Sorcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRI gene.

Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KLK4 gene.

Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (HMMR), also known as RHAMM (Receptor for Hyaluronan Mediated Motility) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HMMR gene. RHAMM recently has been also designated CD168 (cluster of differentiation 168).
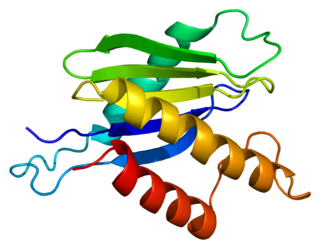
Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 2 (TRAPPC2) also known as MBP-1-interacting protein 2A (MIP-2A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAPPC2 gene. A processed pseudogene of this gene is located on chromosome 19, and other pseuodogenes of it are found on chromosome 8 and the Y chromosome. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.

Galactoside 2-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FUT1 gene.

Chemokine-like factor (CKLF) is a member of the CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family of proteins that in humans is encoded by the CKLF gene. This gene is located on band 22.1 in the long arm of chromosome 16.

GTP-binding protein Rit1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIT1 gene.

Metalloreductase STEAP1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STEAP1 gene.

Metalloreductase STEAP3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STEAP3 gene.

Metalloreductase STEAP2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STEAP2 gene.

Sodium channel protein type 7 subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCN7A gene on the chromosome specifically located at 2q21-23 chromosome site. This is one of 10 Sodium channel types, and is expressed in the heart, the uterus and in glial cells. Its sequence identity is 48, and it is the only sodium channel known to be completely un-blockable by tetrodotoxin (TTX).

In molecular biology, mir-221 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
YedZ of E. coli has been examined topologically and has 6 transmembrane segments (TMSs) with both the N- and C-termini localized to the cytoplasm. von Rozycki et al. 2004 identified homologues of YedZ in bacteria and animals. YedZ homologues exhibit conserved histidyl residues in their transmembrane domains that may function in heme binding. Some of the homologues encoded in the genomes of various bacteria have YedZ domains fused to transport, electron transfer and biogenesis proteins. One of the animal homologues is the 6 TMS epithelial plasma membrane antigen of the prostate (STAMP1) that is over-expressed in prostate cancer. Some animal homologues have YedZ domains fused C-terminal to homologues of NADP oxidoreductases.

Phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PID1 gene.
CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing 5 (CMTM5), previously termed chemokine-like factor superfamily 5, designates any one of the six protein isoforms encoded by six different alternative splices of its gene, CMTM5; CMTM5-v1 is the most studied of these isoforms. The CMTM5 gene is located in band 11.2 on the long arm of chromosome 14.


















